前言
启动一个Android组件时,当App进程还不存在,应先创建一个App进程。追踪Ams源码,在栈监管者startSpecificActivityLocked方法中有判断进程是否存在。
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
.....
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
...//进程存在
realStartActivityLocked()
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
Ams#getProcessRecordLocked方法查找进程ProcessRecord记录。若未找到,创建进程 。
当用户第一次点击App图标,系统启动App的AndroidManifest中配置action为android.intent.action.MAIN的Activity组件。
ActivityStackSupervisor#startActivityMayWait方法。
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,..) {
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException
("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
boolean componentSpecified = intent.getComponent() != null;
// Don't modify the client's object!
intent = new Intent(intent);
// Collect information about the target of the Intent.
// 搜集目标Intent的信息
ActivityInfo aInfo =resolveActivity(intent, resolvedType, startFlags,
profilerInfo, userId);
...
}
栈监管者resolveActivity方法解析Intent信息。注意,这是启动App第一个Activity组件,App进程还未创建。
ActivityInfo resolveActivity(Intent intent, String resolvedType, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, int userId) {
ActivityInfo aInfo;
try {
//AppGlobals获取包管理器IPackageManager。
ResolveInfo rInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
intent, resolvedType,
PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY
| ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
aInfo = null;
}
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
...
}
return aInfo;
}
从ActivityThread#getPackageManager*获取包管理器,
public static IPackageManager getPackageManager() {
if (sPackageManager != null) {
return sPackageManager;
}
//从ServiceManager获取包服务,仅初始化一次。
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("package");
//代理
sPackageManager = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return sPackageManager;
}
进程名processName,ActivityInfo内部有一个ApplicationInfo对象。
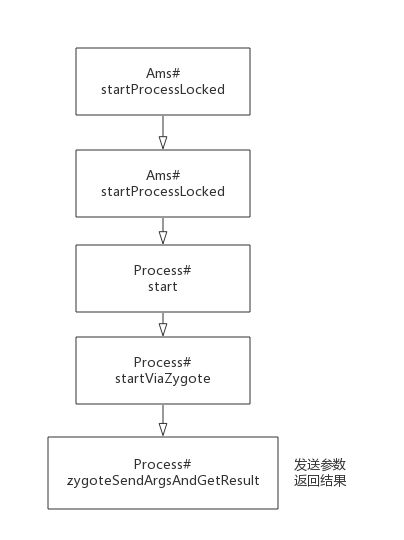
进程创建
进程创建流程图。下面是Ams#startProcessLocked方法。
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo
info,boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String
hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,boolean
allowWhileBooting,boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean
keepIfLarge,String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[]
entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {//非孤立
//根据进程名查询进程记录ProcessRecord
app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid, keepIfLarge);
if ((intentFlags & Intent.FLAG_FROM_BACKGROUND) != 0) {
...
} else {
//当用户显式启动进程时,清除其崩溃计数
mProcessCrashTimes.remove(info.processName, info.uid);
...
}
} else {
// 如果是孤立进程,无法重用存在的进程
app = null;
}
//如果app不空,说明存在进程记录,调用者不认为该进程已经死掉或者没有线程对象,
//pid存在
if (app != null && app.pid > 0) {
if (!knownToBeDead || app.thread == null) {
//app已经开始运行,则加入新包,返回ProcessRecord
app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.versionCode, mProcessStats);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done, added package to proc");
return app;
}
//app记录绑定了以前的进程。清理,需要启动进程
killProcessGroup(app.info.uid, app.pid);
handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
}
if (app == null) {
//创建ProcessRecord
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid);
if (app == null) {
return null;
}
app.crashHandler = crashHandler;
} else {
// ProcessRecord存在,则加入新包
app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.versionCode, mProcessStats);
}
//创建进程,Ams#startProcessLocked方法。
startProcessLocked(app, hostingType, hostingNameStr, abiOverride,
entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
return (app.pid != 0) ? app : null;
}
创建ProcessRecord,它当的pid是0,startProcessLocked启动进程。
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint,
String[] entryPointArgs) {
...
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
...
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi,
instructionSet,app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
...
}
设置entryPoint为android.app.ActivityThread,ActivityThread类的main方法的是新进程App启动入口。
Process的start方法,向zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求,启动成功的结果是ProcessStartResult中包含新进程pid。
Process#startViaZygote方法,创建一个字符串参数列表,调用Process#zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法,将参数列表发送给zygote进程。zygote进程收到后,启动一个子进程,将子进程pid返回。
startViaZygote方法参数图。
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(...String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
Process#openZygoteSocketIfNeeded方法,利用ZygoteState#connect返回ZygoteState。
private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
writer.newLine();
int sz = args.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(
"embedded newlines not allowed");
}
writer.write(arg);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.flush();
ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();
//读取返回的pid
result.pid = inputStream.readInt();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
Process保存主ZygoteState和次ZygoteState两个静态对象,代表两个与zygote进程的socket连接。当主ZygoteState连接可用,则直接使用,否则利用次ZygoteState,若都不可用,抛出异常。
通过socket与zygote进程通信,连接与数据流读写链路封装在ZygoteState。主ZygoteState定义的连接地址名称是zygote,次ZygoteState定义的连接地址名称是zygote_secondary。
BufferedWriter和DataInputStream数据流,发送和读取。
与zygote进程Socket通信
与zygote进程的Socket通信结构图。创建ZygoteState的connect方法。
public static ZygoteState connect(String socketAddress) throws IOException {
DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = null;
BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = null;
final LocalSocket zygoteSocket = new LocalSocket();
try {
//到zygote进程的socket连接
zygoteSocket.connect(new LocalSocketAddress(socketAddress,
LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED));
//建立读写数据通道
zygoteInputStream = new DataInputStream(zygoteSocket.getInputStream());
zygoteWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
zygoteSocket.getOutputStream()), 256);
} catch (IOException ex) {
//socket关闭,抛出异常
}
....
return new ZygoteState(zygoteSocket, zygoteInputStream, zygoteWriter,
Arrays.asList(abiListString.split(",")));
}
1.创建LocalSocket,委托LocalSocketImpl实现类,利用LocalSocketImpl的文件描述符FileDescriptor建立连接。
2.建立读写数据通道,创建ZygoteState对象,封装通道与连接。
LocalSocket#connect方法。
public void connect(LocalSocketAddress endpoint) throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
implCreateIfNeeded();//初始化连接描述符
impl.connect(endpoint, 0);
isConnected = true;
isBound = true;
}
}
建立连接。implCreateIfNeeded方法,通过LocalSocketImpl#create方法初始化连接描述符Fd。
利用Os.socket(OsConstants.AF_UNIX, osType, 0)。
委托LocalSocketImpl#connect方法。
protected void connect(LocalSocketAddress address, int timeout)
throws IOException{
if (fd == null) {//Fd已在implCreateIfNeeded初始化。
throw new IOException("socket not created");
}
connectLocal(fd, address.getName(), address.getNamespace().getId());
}
JNI#方法进行连接,address就是上面提到过的主ZygoteState定义的zygote。
LocalSocket#getInputStream方法,getOutputStream方法委托LocalSocketImpl的方法创建读写数据流,SocketInputStream与SocketOutputStream,数据流封装在LocalSocketImpl。
数据流返回后,再次封装,BufferedWriter与DataInputStream。
本质:BufferedWriter#write,利用SocketOutputStream向Fd发送数据,DataInputStream#read,利用SocketInputStream从Fd读取数据。
最后,进程创建成功,pid保存在ProcessStartResult。
App入口方法
ActivityThread的main方法是新进程入口。
public static void main(String[] args) {
.....
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
//ActivityThread内部H对象,负责处理主线程消息,如AMS,WMS利用Binder发来的消息。
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
...
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
初始化主线程消息队列,启用主线程Looper,等待消息,创建ActivityThread对象,触发ActivityThread#attach方法。
private void attach(boolean system) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
//mAppThread是ApplicationThread类型
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
...
} else {
...
}
}
非系统应用时,Ams#attachApplication方法,Ams利用ApplicationThread访问App进程,这是刚创建的进程,此时主线程消息队列已经创建,可向队列插入消息,但Loop循环还未起来。
Ams#attachApplicationLocked方法中,先ApplicationThread#bindApplication回调App进程,向主线程消息队列发送BIND_APPLICATION消息,待Looper起来后,就会执行啦。
后续,还会触发ActivityStackSupervisor#attachApplicationLocked方法,进入realStartActivityLocked方法,它就是刚开篇介绍过的,进程存在时代码执行的选择,在realStartActivityLocked继续往下走,启动Activity组件。
总结
创建App进程的核心知识点是建立一个与zygote进程通信的Socket连接,通过向其发送参数,请求zygote创建App进程。
任重而道远