工作队列中的sleep导致控制台无法输入问题
通常我们会在workqueue中调用msleep(50);之类的函数进行延时。而且是可行的。
使用方法如下:
=========================
定义工作队列的一个工作线结构体:
struct work_struct ch450_wq;
初始化工作的服务函数:
void wq_try_read_ch450_server(struct work_struct *work)
{
… …
msleep(xx);
… …
}
INIT_WORK(&ch450_wq,wq_try_read_ch450_server);
在中断服务函数中将工作线程,挂载到全局工作队列,启动工作线程:
static irqreturn_t ch450_kbd_irq(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
schedule_work(&ch450_wq);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
========================
在通常情况下,上面的使用不会有问题,因为msleep(xx)很快会执行完。但是如果这个sleep较长就会出问题。例如:串口控制台无响应,flash文件
系统中的文件无法操作,等。这些问题出现的原因是sleep将全局工作队列阻塞了。全局工作队列是一个内核线程。因此与这个工作队列相关的其它
工作服务函数无法执行。解决办法是创建一个局部的工作队列,也就是另启一个工作队列线程,将工作服务函数挂到局部工作队列之中。举例如下:
========================
定义一个局部工作队列:
struct workqueue_struct *keventd_wqch450;
创建局部工作队列(创建局部工作队列的方法有很多):
keventd_wqch450 = create_workqueue("namexx");
定义工作队列的一个工作线结构体:
struct work_struct ch450_wq;
初始化工作的服务函数:
void wq_try_read_ch450_server(struct work_struct *work)
{
… …
msleep(xx);
… …
}
INIT_WORK(&ch450_wq,wq_try_read_ch450_server);
在中断服务函数中将工作线程,挂载到局部工作队列,启动工作线程:
static irqreturn_t ch450_kbd_irq(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
queue_work(keventd_wqch450,&ch450_wq);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
========================
局部工作队列启动,相关函数如下:
int queue_work( struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work );
int queue_work_on( int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work );
int queue_delayed_work( struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
int queue_delayed_work_on( int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
全局工作队列相关启动函数如下:
int schedule_work( struct work_struct *work );
int schedule_work_on( int cpu, struct work_struct *work );
int scheduled_delayed_work( struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
int scheduled_delayed_work_on(
int cpu, struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
参考如下:
http://hi.baidu.com/ajoe/blog/item/8d85f2d3b59a71d1a8ec9a46.html
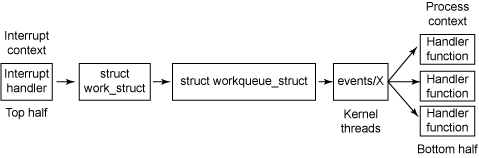
延时处理一般用在中断的bottom-half中。
tasklet 函数不能休眠,采用一步到位的延时方式。
workqueue是可以休眠的,采用通用的延时方式。
图 tasklet_struct 结构体的内部情况 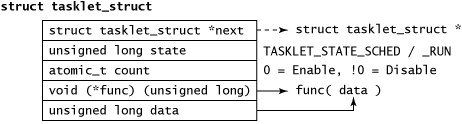
通过软中断机制来调度微线程,当机器处于严重软件中断负荷之下时, 可通过 ksoftirqd
清单 1. 声明并调度微线程
/* Declare a Tasklet (the Bottom-Half) */
void tasklet_function( unsigned long data );
DECLARE_TASKLET( tasklet_example, tasklet_function, tasklet_data );
...
/* Schedule the Bottom-Half */
tasklet_schedule( &tasklet_example );
一个给定的微线程只运行在一个 CPU 中(就是用于调用该微线程的那个 CPU), 同一微线程永远不会同时运行在多个 CPU 中。 但是不同的微线程可以同时运行在不同的 CPU 中。
清单 2. 微线程的创建以及 enable/disable 函数
DECLARE_TASKLET( name, func, data );
DECLARE_TASKLET_DISABLED( name, func, data);
void tasklet_init( struct tasklet_struct *, void (*func)(unsigned long),
unsigned long data );
void tasklet_disable_nosync( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_disable( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_enable( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_hi_enable( struct tasklet_struct * );
清单 4. 微线程 kill 函数
void tasklet_schedule( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_hi_schedule( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_kill( struct tasklet_struct * );
void tasklet_kill_immediate( struct tasklet_struct *, unsigned int cpu );
INIT_WORK( work, func );
INIT_DELAYED_WORK( work, func );
INIT_DELAYED_WORK_DEFERRABLE( work, func );
int queue_work( struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work );
int queue_work_on( int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work );
int queue_delayed_work( struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
int queue_delayed_work_on( int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
int schedule_work( struct work_struct *work );
int schedule_work_on( int cpu, struct work_struct *work );
int scheduled_delayed_work( struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
int scheduled_delayed_work_on(
int cpu, struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay );
还有一些帮助函数用于清理或取消工作队列中的任务。想清理特定的任务项目并阻塞任务, 直到任务完成为止, 可以调用 flush_work 来实现。 指定工作队列中的所有任务能够通过调用 flush_workqueue 来完成。 这两种情形下,调用者阻塞直到操作完成为止。 为了清理内核全局工作队列,可调用 flush_scheduled_work。
int flush_work( struct work_struct *work );
int flush_workqueue( struct workqueue_struct *wq );
void flush_scheduled_work( void );
还没有在处理程序当中执行的任务可以被取消。 调用 cancel_work_sync 将会终止队列中的任务或者阻塞任务直到回调结束(如果处理程序已经在处理该任务)。 如果任务被延迟,可以调用 cancel_delayed_work_sync。
int cancel_work_sync( struct work_struct *work );
int cancel_delayed_work_sync( struct delayed_work *dwork );
最后,可以通过调用 work_pending 或者 delayed_work_pending 来确定任务项目是否在进行中。
work_pending( work );
delayed_work_pending( work );