CEOI2001-Bitmap-黑书1.3.7 **
题目:
Components of a Bitmap
PROBLEM
Black and white pictures are usually stored as bitmaps. A bitmap is a rectangular grid of pixels.
A polyline between pixels P and Q is a sequence of black pixels P=P1, P2, …, Pk=Q, where Pi and Pi+1 (i=1, …, k-1) are (vertically or horizontally) adjacent pixels. A polyline P1, P2, ..., Pk is closed if P1=Pk, and Pi <> Pj (i=1, …, k-1, j=2, …, k) for i<j unless i=1 and j=k (that is the polyline does not contain the same pixel twice).
A set of black pixels S is connected if for each pair of pixels (P,Q) in S there is at least one polyline L between P and Q with all pixels of L belonging to S.
A component of a bitmap is a maximal connected set of black pixels. A component may enclose holes. A hole consists of white pixels that are inside a closed polyline. A compact component encloses no holes.
Note that in Figure 1 the white pixel in the middle, marked with x, is not inside the highlighted closed polyline.
Figure 1
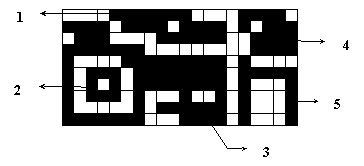
Figure 2
Figure 2 shows a bitmap with five components, of which two are compact ones.
You are to write a program that computes the total number of components and the number of compact components of a given coded bitmap.
Encoding. The bitmaps under investigation are coded (compressed) with the following method. Each row is coded with a sequence of integers W1, B1, ..., Wk, Bk, where Wi is the number of consecutive white pixels, and Bi is the number of consecutive black pixels, respectively.
For example, the code of the first line of the bitmap in Figure 2 is the sequence 4 7 4 4 1 0. Components 4 and 5 are compact, while components 1, 2 and 3 are not compact.
INPUT
The first line of the file bitmap.in contains two positive integers, N and M. N (2<=N<=10000) is the number of rows and M (2<=M<=1000) is the number of columns of the bitmap. The next N lines contain the coded bitmap according to the paragraph on encoding. Each line terminates with -1.
OUTPUT
The file bitmap.out must contain two lines, with a single integer in each line. The first line contains the number of all components and the second line contains the number of compact components of the input bitmap.
EXAMPLE INPUT AND OUTPUT
| bitmap.in |
bitmap.out |
| 10 20 |
5 |
| 4 7 4 4 1 0 -1 |
2 |
| 0 4 1 4 1 4 1 1 1 3 -1 |
|
| 1 3 4 6 2 4 -1 |
|
| 0 7 9 4 -1 |
|
| 0 1 4 9 1 1 4 0 -1 |
|
| 0 1 1 3 1 8 1 5 -1 |
|
| 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 8 1 1 3 1 -1 |
|
| 0 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 3 1 -1 |
|
| 0 1 5 1 1 6 1 1 3 1 -1 |
|
| 0 7 3 4 1 1 3 1 -1 |
GRADING
If the first line of your output file contains the correct number of all components, then you obtain 50% of the scores. If the second line of your output file contains the correct number of compact components, then you obtain an additional 50% of the scores.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
/*
* Bitmap
* 算法 : floodfill(种子填充)
*
* 设白色为w, 黑色为b, g为不同于w、b的一种颜色
* 1、先在输入的矩形的边界找空白的点,分别以这些点为种子,做8连通的floodfill,填为g色,则填充的方块都是黑块之间的间隙
* 2、遍历整个矩形, 遇到一个黑格,就说明遇到了一个黑块, blackNnum++。 并以此黑格为种子做4连通的floodfill,把黑块填为
* g色。。
* 3、在floodfill黑块的同时,如果遇到一个白块, 则这个白块一定是这个黑块的洞, 于是closeBlackNum不变。
* 4、但由样例可以发现,黑块里面可能套着另一个黑块, 而且里面的黑块周围有一圈白块, 所以如果只用3的方法,则可能少数closeBlackNum,
* 比如样例里的2如果中间的白块改为黑块,则closeBlackNum应变为3, 但只用第3步的方法,则仍是2.
* 所以,在第3步的时候遇到一个白块,就以这个白块为种子,做8连通的floodfill,把白块填为g。(我做成了4连通的,居然也过了。。)
* 。这样就避免了上面的问题,因为套在外面的黑块一定先被找到,当找到里面的黑快的时候,围在它外面的白块已经被改为g色了。
*/
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 10000 + 5;
const int maxM = 1000 + 5;
const int w = 1, b = 2, g = 3;
const int dx[8] = {-1, +1, 0, 0, -1, -1, +1, +1};
const int dy[8] = {0, 0, -1, +1, -1, +1, -1, +1};
int n, m, map[maxN][maxM], queue[maxN * maxM], floodfillQueue[maxN * maxM],
blackNum = 0, closeBlackNum = 0;
//按type连通填充
void floodfill(int x, int y, int color, int type){
int head = 0, tail = 0, curx, cury, nextx, nexty;
floodfillQueue[tail++] = x * m + y;
map[x][y] = color;
while(head != tail){
curx = floodfillQueue[head] / m;
cury = floodfillQueue[head] % m;
for(int i=0; i<type; i++){
nextx = curx + dx[i];
nexty = cury + dy[i];
if(map[nextx][nexty] == w){
map[nextx][nexty] = color;
floodfillQueue[tail++] = nextx * m + nexty;
}
}
head++;
}
}
//以x,y为种子
int checkClose(int x, int y){
int isClose = 1;
int head = 0, tail = 0, curx, cury, nextx, nexty;
queue[tail++] = x * m + y;
while(head != tail){
curx = queue[head] / m;
cury = queue[head] % m;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
nextx = curx + dx[i];
nexty = cury + dy[i];
if(map[nextx][nexty] == b){
map[nextx][nexty] = g;
queue[tail++] = nextx * m + nexty;
}
else if(map[nextx][nexty] == w){
isClose = 0;
floodfill(nextx, nexty, g, 8);
}
}
head++;
}
return isClose;
}
int main(){
//建图
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
int tmp, curColor = w, lastPos = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
curColor = w; lastPos = 0;
while(scanf("%d", &tmp)){
if(tmp == -1) break;
for(int j=lastPos; j<lastPos+tmp; j++)
map[i][j] = curColor;
curColor = (curColor == w ? b : w);
lastPos = lastPos + tmp;
}
}
//找边界上的白点,用8连通填充成g色
for(int j=0; j<m; j++){
if(map[0][j] == w)
floodfill(0, j, g, 8);
if(map[n-1][j] == w)
floodfill(n-1, j, g, 8);
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(map[i][0] == w)
floodfill(i, 0, g, 8);
if(map[i][m-1] == w)
floodfill(i, m-1, g, 8);
}
//计算 blackNum \ closeBlackNum
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<m; j++){
if(map[i][j] == b){
blackNum++;
closeBlackNum += checkClose(i, j);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n%d\n", blackNum, closeBlackNum);
return 0;
}
测试数据在: http://www.licejus.lt/~antanas2010/uzdaviniai/CEOI/ceoi2001/tests/bitmap/
