1、Redis集群说明
1.1 分片、哨兵有哪些缺点
1、分片缺点:分片的主要的功能是实现内存的扩容,但是没有高可用的效果
2、哨兵缺点:数据没有扩容,哨兵本身没有高可用机制
需求:既可以实现内存数据的扩容,同时实现高可用机制(不用第三方)
1.2 Redis集群搭建
修改redis.conf文件
1、注释本地绑定IP地址
把文件内容里的7000全部改为7002
命令::%s/7000/7002/g
1、首先关闭所有的Redis服务器
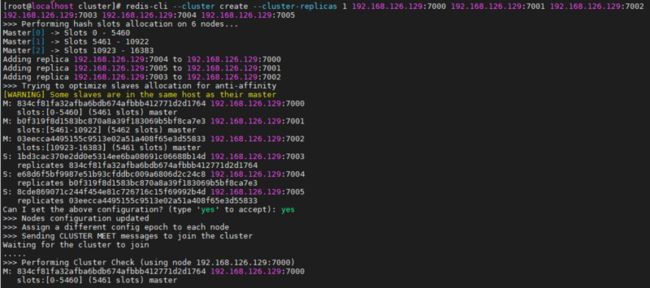
5、搭建redis集群
执行命令:
redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 192.168.126.129:7000 192.168.126.129:7001 192.168.126.129:7002 192.168.126.129:7003 192.168.126.129:7004 192.168.126.129:70051.3 集群入门案例
@Test
public void testCluster(){
Set sets = new HashSet<>();
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7000));
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7001));
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7002));
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7003));
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7004));
sets.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.126.129", 7005));
JedisCluster jedisCluster = new JedisCluster(sets);
jedisCluster.set("jedis", "集群赋值");
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("jedis"));
} 1.4 面试题
1、redis集群中一共可以存储16384个key???
不对的
答:16384只是槽位的数量,只负责规划这个数据归谁管理的问题,至于数据如何存储,是由redis内存决定的
2、redis集群中最多可以有多少台主机
16384台主机
3、redis中如果遇到多线程操作,是否有线程安全性问题?
没有
因为:redis服务器是单进程线程操作,每次操作都是由一个线程执行,所以不会有线程安全性问题
4、redis如何实现内存数据的优化?
LRU、LFU、随机算法、TTL
1.5 SpringBoot整合redis集群
1.5.1 编辑properties文件
说明:将redis集群的节点写入pro配置文件中
#redis集群配置
redis.nodes=192.168.126.129:7000,192.168.126.129:7001,192.168.126.129:7002
,192.168.126.129:7003,192.168.126.129:7004,192.168.126.129:70051.5.2 编辑配置类
package com.jt.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import redis.clients.jedis.HostAndPort;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@Configuration//标识我是配置类
@PropertySource("classpath:/properties/redis.properties")
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.nodes}")
private String nodes; //node,node,node
//实现redis集群操作
@Bean
public JedisCluster jedisCluster(){
Set nodeSet=new HashSet<>();
String[] nodeArray=nodes.split(",");
for (String node:nodeArray) { //host:port
String host=node.split(":")[0];
int port=Integer.parseInt(node.split(":")[1]);
nodeSet.add(new HostAndPort(host,port));
}
return new JedisCluster(nodeSet);
}
/*
SpringBoot整合Redis分片,实质:ShardedJdeis对象,交给容器管理
*/// @Bean
// public ShardedJedis shardedJedis(){
// List shards=new ArrayList<>();
// String[] nodeArray=nodes.split(","); //截取
// for (String node:nodeArray) { //node=ip:port
// String host=node.split(":")[0]; //截取
// int port=Integer.parseInt(node.split(":")[1]); //转化为int类型
// //准备分片节点信息
// JedisShardInfo info=new JedisShardInfo(host,port);
// shards.add(info);
// }
// return new ShardedJedis(shards);
// }
// @Value("${redis.host}")
// private String host;
// @Value("${redis.port}")
// private Integer port;
//
// @Bean
// public Jedis jedis(){
// return new Jedis(host,port);
// }
} 1.5.3 编辑AOP配置
在AOP中注入Redis缓存对象
package com.jt.aop;
import com.jt.anno.CacheFind;
import com.jt.util.ObjectMapperUtil;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect //标识我是一个切面
@Component //交给spring容器管理
public class CacheAOP {
@Autowired
private JedisCluster jedis; //完成集群的注入
//private ShardedJedis jedis; //完成分片对象的注入
//private Jedis jedis;
/* 注意事项:当有多个参数时,joinPoint参数必须位列第一位
需求:
1、准备key=注解的前缀 + 用户的参数
2、从redis中获取数据
有:从缓存中获取数据之后,直接返回值
没有:查询数据库之后再次保存到缓存中即可
方法: 动态获取注解的类型,看上去是注解的名称,但是实质是注解的类型,只要切入点表达式满足条件
则会传递注解对象类型
*/
@Around("@annotation(cacheFind)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, CacheFind cacheFind) throws Throwable {
Object result=null; //定义返回值对象
String preKey=cacheFind.preKey(); //获取key
String key=preKey+"::"+ Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); //拼接key
//1、校验redis中是否有数据
if(jedis.exists(key)){
//如果数据存在,需要从redis中获取json数据,之后直接返回
String json=jedis.get(key); //获取该数据
//1、获取方法对象 2、获取方法的返回值类型
MethodSignature methodSignature= (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();//MethodSignature该方法里有获取该方法的返回值类型
//2、获取返回值类型
Class returnType=methodSignature.getReturnType(); //获取返回值类型
result=ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(json,returnType); //将JSON转化为对象
System.out.println("AOP查询缓存");
}else {
//代表没有数据,需要查询数据库
result=joinPoint.proceed();
//将数据转化为JSON
String json= ObjectMapperUtil.toJSON(result); //转化为JSON
if (cacheFind.seconds()>0){
jedis.setex(key,cacheFind.seconds(),json); //如果有设定时间,则执行
}else{
jedis.set(key, json); //没有设定时间执行
}
System.out.println("AOP查询数据库");
}
return result; //返回该数据
}
/* @Around("@annotation(com.jt.anno.CacheFind)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { //1.获取目标对象的Class类型
Class targetClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass(); //2.获取目标方法名称
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); //3.获取参数类型
Object[] argsObj = joinPoint.getArgs(); Class[] argsClass = null; //4.对象转化为class类型
if(argsObj.length>0){ argsClass = new Class[argsObj.length]; for(int i=0;i2、京淘前台项目搭建
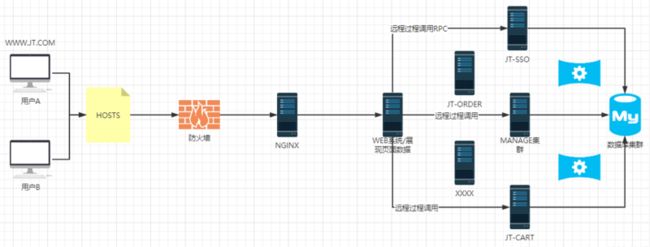
2.1 京淘架构图设计
2.2 JT-WEB项目创建
2.2.1 创建JT-WEB服务器
2.2.2 添加继承、依赖、插件
4.0.0
jt-web
war
jt2007
com.jt
1.0-SNAPSHOT
com.jt
jt-common
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.2.3 导入静态资源文件
说明:将课前资料中的文件src目录导入到jt-web中![]()
2.2.4 关于主启动类说明
说明:jt-web服务器启动时会加载数据源的自动化配置,但是web服务器没有配置数据源,所以报错
2.2.5 配置工作目录
2.3 域名反向代理
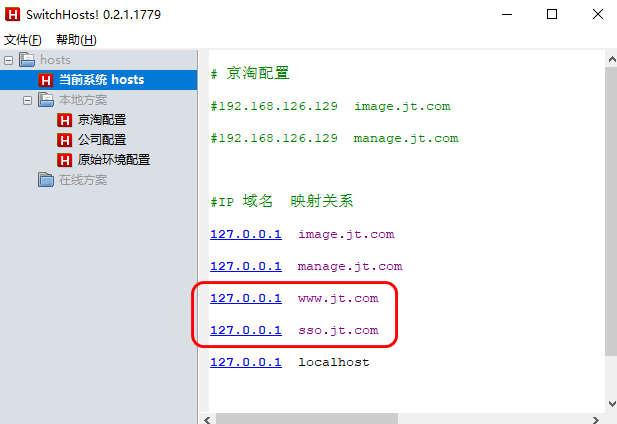
需求:要求用户通过http://www.jt.com访问localhost:8092服务器
2.3.1 修改hosts文件
2.3.2 修改Nginx配置文件
#配置前台服务器
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.jt.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8092;
}
}2.3.3 页面效果展现
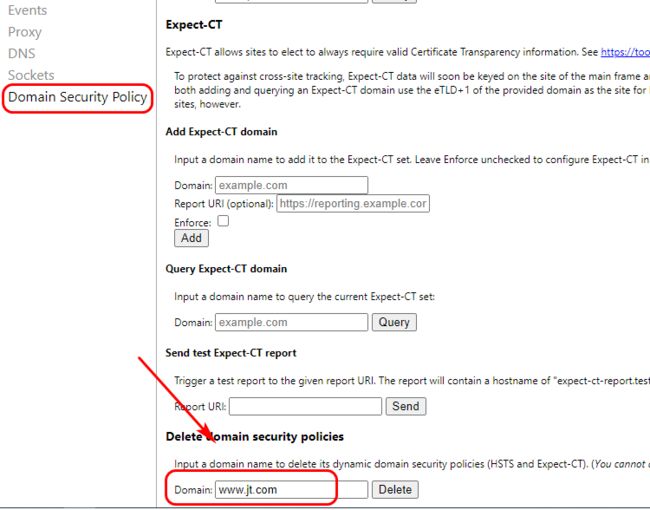
2.4 谷歌浏览器禁用HTTPS
键入地址:
chrome://net-internals/#hsts:2.5 开启后缀类型匹配
说明: 由于京东商城的商品展现时通过
url:https://item.jd.com/100213774...
package com.jt.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.PathMatchConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MvcConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer{
//开启匹配后缀型配置
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(true);
}
}URL地址小结:
1、http://www.jt.com/index 该请求会被Controller进行拦截
2、http://www.jt.com/index.html 该请求默认条件下表示获取静态资源文件,不会被拦截
一般条件下:Controller只拦截前缀类型的请求. 如果需要拦截后缀类型的请求需要单独配置
3、登录注册页面跳转
3.1 实现通用的页面跳转
url1:http://www.jt.com/user/login.... 跳转页面login.jsp
url2:http://www.jt.com/user/regist... 跳转页面register.jsp
需求: 能否利用一个Controller方法.实现通用页面的跳转?
package com.jt.config.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
/*
实现用户登录、注册页面的跳转
url1: http://www.jt.com/user/login.html 跳转页面login.jsp
url2: http://www.jt.com/user/register.html 跳转页面register.jsp
*/
@RequestMapping("/{moduleName}")
public String module(@PathVariable String moduleName){
return moduleName;
}
}3.2 伪静态
伪静态是相对真实静态来讲的,通常我们为了增强搜索引擎的友好性,都将文章内容生成静态页面,但是有的朋友为了实时的显示一些信息。或者还想运用动态脚本解决一些问题。不能用静态的方式来展示网站内容。但是这就损失了对搜索引擎的友好性。怎么样在两者之间找个中间方法呢,这就产生了伪静态技术。伪静态技术是指展示出来的是以html一类的静态页面形式,但其实是用ASP一类的动态脚本来处理的。
总结:以.html结尾的一种动态页面的形式
作业
1、预习什么是跨域?
1、JSONP
2、CORS方式