剑指offer-面试题6.重建二叉树
题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设
输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历
序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建出如图
所示的二叉树并输出它的头结点。二叉树的定义如下:

1 struct BinaryTreeNode 2 { 3 int m_nValue; 4 BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft; 5 BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight; 6 }
1 1 2 / \ 3 2 3 4 / / \ 5 4 5 6 6 \ / 7 7 8
首先要明白一些基本概念:前序遍历,中序遍历,后续遍历
以上图中的二叉树为例:
前序遍历:我的理解是 “根-左-右” 先访问根结点 再访问左子树 最好访问右子树
比如:先访问根结点1,再访问左子节点,左子节点为一颗子树,那么又用根-左-右
的规则,先访问根节点2,再访问左在节点4,再访问右子节点。这样知道所有
节点遍历结束:那么遍历的节点列表是:1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8
中序遍历遵循规则:“左-根-右” 遍历的节点列表是:4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6
后序遍历遵循规则:“左-右-根” 遍历的节点列表是:7,4,2,5,8,6,3,1
那么从另外一个方面来说:任何一个二叉树三种遍历方式的结果是唯一。
反之也就是说这三种遍历结果唯一的确定一颗二叉树。
其实当我们分析会发现实际上在唯一确定一个二叉树的时候并非
完全给出三种方式的遍历结果,实际上我们只需要前序遍历与
中序遍历 又或者中序遍历与后序遍历。注意,如果仅仅是先序
遍历和后序遍历是不能唯一确定一个二叉树的。这点是需要特别注意的
下面我们来分析一下:
如果我们只知道一个二叉树的中序遍历:4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6
与后序遍历:7,4,2,5,8,6,3,1
现在我们开分析一下能不能通过这两中遍历结果推出先序
遍历结果:1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8
我们知道后序遍历可知,遍历列表最后一个元素为二叉树的根结点
可知该最后一个元素为1,那么跟结点为1.
在中序遍历结果中找到根节点所在的位置,那么该位置前面的即为
二叉树的左子树:4,7,2 该位置后面的为二叉树的右子树:5,3,8,6
那么我们可以通过找到的左右子树确定后序遍历的左右子树遍历结果:
7,4,2和5,8,6,3
现在我们又分别针对每个子树重复上述步骤:显然前序遍历结果为:1,2,4,7,3,5,8,6
很显然前序与中序结果退出后序遍历结果的步骤是一样一样的。
那么问题来了,为什么不能通道前序和后序遍历结果推出中序遍历结果呢?
因为我们不能通过前序和中序遍历确定遍历结果中关于根节点的左右子树。
也就是说前序和后序遍历结果重建的二叉树不一定是唯一的。
好了有了前面的分析我们不难通过递归的方式解决这道题,
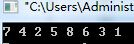
剑指Offer书上是通过前序和中序遍历推出后序遍历()
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct BinaryTreeNode 5 { 6 int m_nValue; 7 BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft; 8 BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight; 9 }; 10 11 12 BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder,int* endPreorder,int*startInorder,int* endInorder) 13 { 14 int rootValue = startPreorder[0]; 15 struct BinaryTreeNode* root = (struct BinaryTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTreeNode)); 16 root->m_nValue=rootValue; 17 root->m_pLeft=NULL; 18 root->m_pRight=NULL; 19 20 if(startPreorder == endPreorder) 21 { 22 if(startInorder == endInorder&& *startPreorder==*startInorder) 23 return root; 24 else 25 throw exception("Invalid Input."); 26 } 27 28 int* rootInorder=startInorder; 29 while(rootInorder<=endInorder&&*rootInorder!=rootValue) 30 ++rootInorder; 31 32 if(rootInorder==endInorder&&*rootInorder!=rootValue) 33 throw exception("Invalid Input."); 34 35 int leftLength = rootInorder-startInorder; 36 int* LeftPreorderEnd=startPreorder+leftLength; 37 if(leftLength>0) 38 { 39 root->m_pLeft=ConstructCore(startPreorder+1,LeftPreorderEnd,startInorder,rootInorder-1); 40 } 41 42 if(leftLength<endPreorder-startPreorder) 43 { 44 root->m_pRight=ConstructCore(LeftPreorderEnd+1,endPreorder,rootInorder+1,endInorder); 45 } 46 47 48 return root; 49 } 50 51 52 BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* preorder,int* inorder,int length) 53 { 54 if(preorder==NULL||inorder==NULL||length<=0) 55 return NULL; 56 return ConstructCore(preorder,preorder+length-1,inorder,inorder+length-1); 57 } 58 59 60 void AfterOrderPrint(struct BinaryTreeNode* root) 61 { 62 if(root) 63 { 64 AfterOrderPrint(root->m_pLeft); 65 AfterOrderPrint(root->m_pRight); 66 cout<<root->m_nValue<<" "; 67 } 68 } 69 70 71 int main() 72 { 73 BinaryTreeNode *Root; 74 int preList[8]={1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}; 75 int inList[8]={4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6}; 76 Root=Construct(preList,inList,8); 77 AfterOrderPrint(Root); 78 cout<<endl; 79 return 0; 80 }
截图:
对的吧
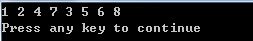
接下来我们模仿剑指offer书中的上述代码,通过前后序遍历和中序遍历
推出前序遍历进而重建这颗二叉树。
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct BinaryTreeNode 5 { 6 int m_nValue; 7 BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft; 8 BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight; 9 }; 10 11 12 BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startAfterorder,int* endAfterorder,int*startInorder,int* endInorder) 13 { 14 int rootValue = endAfterorder[0]; 15 struct BinaryTreeNode* root = (struct BinaryTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTreeNode)); 16 root->m_nValue=rootValue; 17 root->m_pLeft=NULL; 18 root->m_pRight=NULL; 19 20 int* rootInorder=startInorder; 21 while(rootInorder<=endInorder&&*rootInorder!=rootValue) 22 ++rootInorder; 23 24 int leftLength = rootInorder-startInorder; 25 int* LeftAfterorderEnd=startAfterorder+leftLength; 26 if(leftLength>0) 27 { 28 root->m_pLeft=ConstructCore(startAfterorder,LeftAfterorderEnd-1,startInorder,rootInorder-1); 29 } 30 31 if(leftLength<endAfterorder-startAfterorder) 32 { 33 root->m_pRight=ConstructCore(LeftAfterorderEnd,endAfterorder-1,rootInorder+1,endInorder); 34 } 35 36 37 return root; 38 } 39 40 41 BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* Afterorder,int* inorder,int length) 42 { 43 if(Afterorder==NULL||inorder==NULL||length<=0) 44 return NULL; 45 return ConstructCore(Afterorder,Afterorder+length-1,inorder,inorder+length-1); 46 } 47 48 49 void PreOrderPrint(struct BinaryTreeNode* root) 50 { 51 if(root) 52 { 53 cout<<root->m_nValue<<" "; 54 PreOrderPrint(root->m_pLeft); 55 PreOrderPrint(root->m_pRight); 56 } 57 } 58 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 BinaryTreeNode *Root; 63 int AfterList[8]={7,4,2,5,8,6,3,1}; 64 int inList[8]={4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6}; 65 Root=Construct(AfterList,inList,8); 66 PreOrderPrint(Root); 67 cout<<endl; 68 return 0; 69 }
咦 正确了哦
两点说明:
1.使用前序中序以及中序后序重建一个二叉树,这颗二叉树中的节点元素值必须完全不相等。
为什么呢,假设除开根节点外还有另外一个节点值为1 那么在前序或者后序遍历中怎么能
确定这个节点左子树和右子树的分界点呢,既然不能确定,那么显然不能递归重建一个唯一的
二叉树
2.注意关于前序中序重建二叉树时应该注意前序遍历与中序遍历的一致性,否则无法重建这可二叉树。
