Android-Fragment课堂学习(初步学习版笔记)
(初步学习记录)
一 .Fragment是什么
- Fragment是一种可以嵌入在Activity当中的UI片段,它能让程序更加合理和充分地利用大屏幕的空间,因而在平板上应用得非常广泛。
- 和Activity很像,同样都能包含布局,同样都有自己的生命周期。
- 手机平板要兼顾,探究Fragment
二. Fragment的基本用法
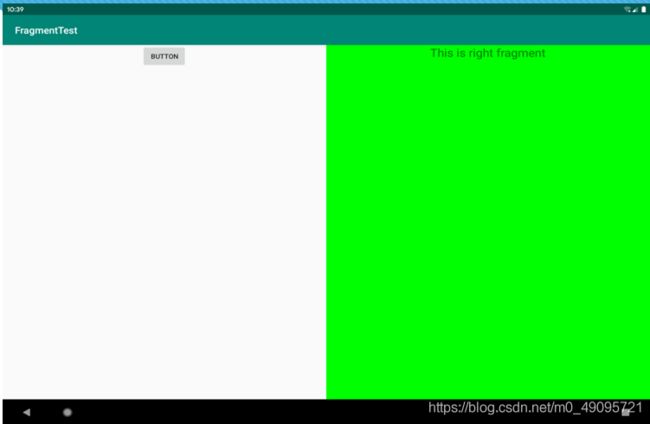
通过一个实例来具体了解吧:
- 定义Fragment的布局
新建一个左侧Fragment的布局left_fragment.xml,再新建一个右侧Fragment的布局right_fragment.xml,代码如下所示:
left_fragment.xml 要实现
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="Button"
/>
LinearLayout>
right_fragment.xml要实现
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#00ff00">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:text="This is right fragment"
/>
LinearLayout>
- 创建Fragment
然后编写LeftFragment和RightFragment中的代码,如下所示:
class LeftFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.left_fragment, container, false)
}
}
class RightFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.right_fragment, container, false)
}
}
- 在布局中引入Fragment
接下来修改activity_main.xml,在布局中引入Fragment。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/rightFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
LinearLayout>
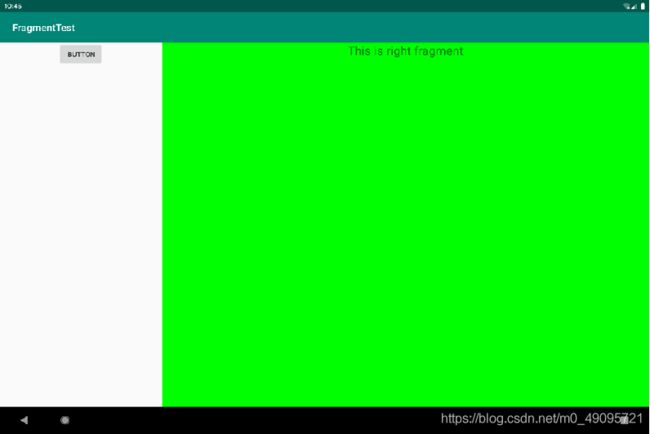
- 动态添加Fragment
先需要准备一个布局作为动态添加Fragment的窗口。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/rightLayout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" >
FrameLayout>
LinearLayout>
- 然后在代码中向FrameLayout里添加内容,实现动态添加Fragment的功能。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
button.setOnClickListener {
replaceFragment(AnotherRightFragment())
}
}
private fun replaceFragment(fragment: Fragment) {
val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager
val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction()
transaction.replace(R.id.rightLayout, fragment)
transaction.commit()
}
}
AnotherRightFragment文件:
class AnotherRightFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.another_right_fragment, container, false)
}
}
another_right_fragment布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#ffff00"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="12sp"
android:text="This is another right fragment"
/>
LinearLayout>
动态添加Fragment的步骤
- 创建待添加Fragment的实例。
- 获取FragmentManager,在Activity中可以直接调getSupportFragmentManager()方法获取。
- 开启一个事务,通过调用beginTransaction()方法开启。
- 向容器内添加或替换Fragment,一般使用replace()方法实现,需要传入容器的id和待添加的Fragment实例。
- 提交事务,调用commit()方法来完成。
在Fragment中实现返回栈
FragmentTransaction中提供了一个addToBackStack()方法,可以用于将一个事务添加到返回栈中,从而实现类似于Activity返回栈的效果。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
…
private fun replaceFragment(fragment: Fragment) {
val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager
val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction()
transaction.replace(R.id.rightLayout, fragment)
transaction.addToBackStack(null)
transaction.commit()
}
}
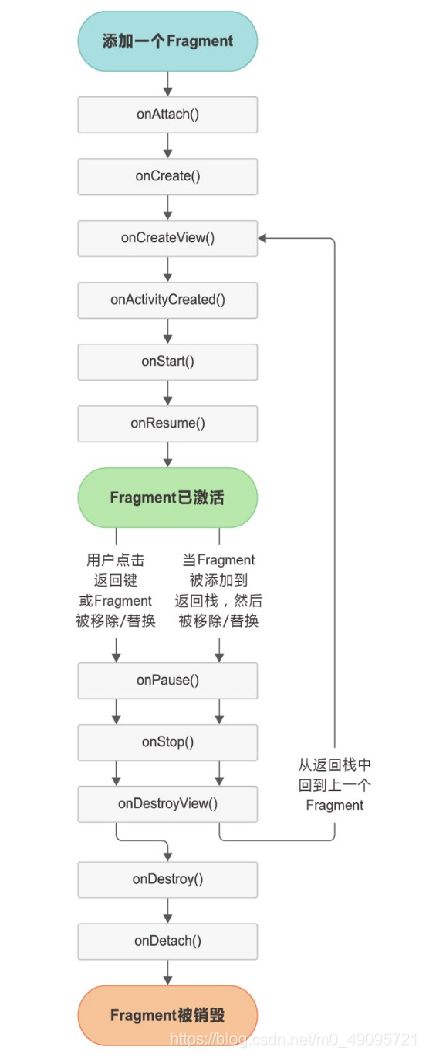
三.Fragment的生命周期
-
onAttach() 当Fragment和Activity建立关联时调用。
-
onCreateView() 为Fragment创建视图(加载布局)时调用。
-
onActivityCreated() 确保与Fragment相关联的Activity已经创建完毕时调用。
-
onDestroyView() 当与Fragment关联的视图被移除时调用。
-
onDetach() 当Fragment和Activity解除关联时调用。
-
large限定符
很多平板应用采用的都是双页模式,那么怎样才能在运行时判断程序应该是使用双页模式还是单页模式呢?这就需要借助限定符(qualifier)来实现了。
使用large限定符,那些屏幕被认为是large的设备就会自动加载layout-large文件夹下的布局,小屏幕的设备则还是会加载layout文件夹下的布局。
- 最小宽度限定符
使用large限定符可以成功解决单页双页的判断问题,不过很快又有一个新的问题出现了:large到底是指多大呢?有的时候我们希望可以更加灵活地为不同设备加载布局,不管它们是不是被系统认定为large,这时就可以使用最小宽度限定符(smallest-width qualifier)了。
在res目录下新建layout-sw600dp文件夹,这样当程序运行在屏幕宽度大于等于600dp的设备上时,会加载layout-sw600dp/activity_main布局,当程序运行在屏幕宽度小于600dp的设备上时,则仍然加载默认的layout/activity_main布局