机器学习之数据预处理——缺失值填充
机器学习之数据预处理——缺失值
上一节给大家回顾了Pandas进行数据预处理会用到哪些方法,学习缺失值简单的填充方法(0、unknown、均值等),这节课学习线性回归法填补缺失值和拉格朗日插值法。
1.线性回归法填补缺失值
#随机生成一个线性回归数据
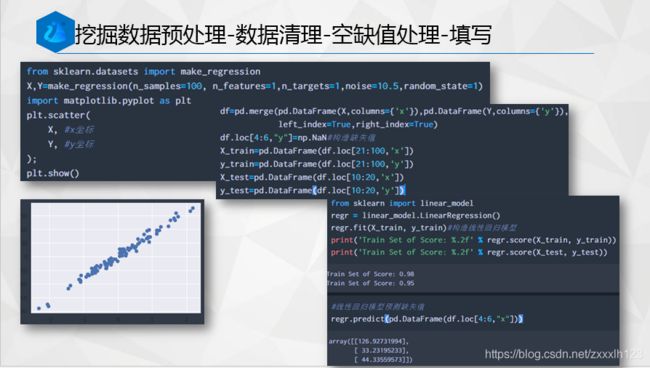
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X,Y=make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1,n_targets=1,noise=10.5,random_state=1)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(
X, #x坐标
Y, #y坐标
);
plt.show()
x=np.arange(100)
y=3*x+4
data={
'x':x,'y':y}
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
df.loc[4:6,"y"]=np.NaN#构造缺失值
X_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'x'])
y_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'y'])
X_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'x'])
y_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'y'])
from sklearn import linear_model
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(X_train, y_train)#构造线性回归模型
print('Train Set of Score: %.2f' % regr.score(X_train, y_train))
print('Train Set of Score: %.2f' % regr.score(X_test, y_test))
#线性回归模型预测缺失值
regr.predict(pd.DataFrame(df.loc[4:6,"x"]))
#构建模型的训练集与测试集
df=pd.merge(pd.DataFrame(X,columns={
'x'}),pd.DataFrame(Y,columns={
'y'}),\
left_index=True,right_index=True)
df.loc[4:6,"y"]=np.NaN#构造缺失值
X_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'x'])
y_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'y'])
X_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'x'])
y_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'y'])
#构建模型的训练集与测试集
df=pd.merge(pd.DataFrame(X,columns={
'x'}),pd.DataFrame(Y,columns={
'y'}),\
left_index=True,right_index=True)
df.loc[4:6,"y"]=np.NaN#构造缺失值
X_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'x'])
y_train=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[21:100,'y'])
X_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'x'])
y_test=pd.DataFrame(df.loc[10:20,'y'])
#线性回归模型预测缺失值
regr.predict(pd.DataFrame(df.loc[4:6,"x"]))
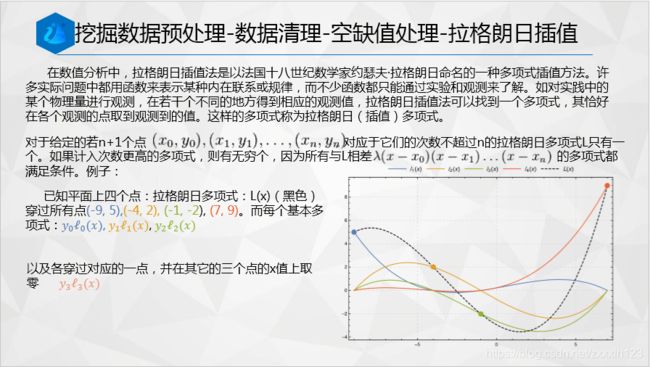
2.拉格朗日插值法
#拉格朗日插值法
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import lagrange
def polyinterp(data,k=5):
df1=data.copy()
print("原始数据(含缺失值):",'\n',data)
for i in range(len(df1)):
if (df1['y'].isnull())[i]:
#取数索引范围,向插值前取k个,向后取k个
index_=list(range(i-k, i)) + list(range(i+1, i+1+k))#Series索引不为负数
list0=[j for j in index_ if j in df1['y'].sort_index()]
y= df1['y'][list0]
#y= df1['y'][list(range(i-k, i)) + list(range(i+1, i+1+k))]
y = y[y.notnull()]#索引为负则为缺失值,去掉缺失值
f = lagrange(y.index, list(y))
df1.iloc[i,1] = f(i)
print("副本插值后:",'\n',df1)
return(df1)
def chart_view(df01,df1):
df1.rename(columns={
'y': 'New y'}, inplace=True)
df01['y'].plot(style='k--')
df1['New y'].plot(alpha=0.5)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
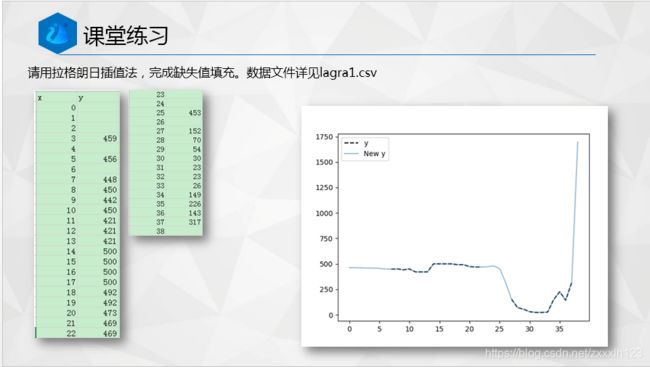
x=np.linspace(0,10,11)
y=x**3+10
data1=np.vstack((x,y))
df0=pd.DataFrame(data1.T,columns=['x','y'])
print(df0)
df01=df0.copy()#建立副本
df01.loc[2:3,"y"]=np.NaN#构造缺失值
df1=df01.copy()
new_data=polyinterp(df1,5)#插值后
chart_view(df01,new_data)#插值前后绘图
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import lagrange
def polyinterp(data,k=5):
df1=data.copy()
print("原始数据(含缺失值):",'\n',data)
for i in range(len(df1)):
if (df1['y'].isnull())[i]:
#取数索引范围,向插值前取k个,向后取k个
index_=list(range(i-k, i)) + list(range(i+1, i+1+k))#Series索引不为负数
list0=[j for j in index_ if j in df1['y'].sort_index()]
y= df1['y'][list0]
y = y[y.notnull()]#索引为负则为缺失值,去掉缺失值
f = lagrange(y.index, list(y))
df1.iloc[i,1] = f(i)
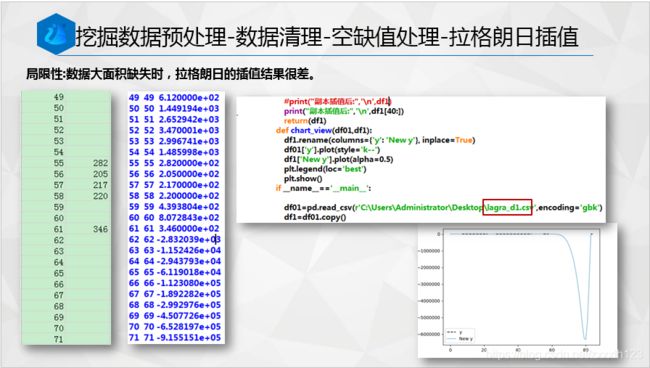
#print("副本插值后:",'\n',df1)
print("副本插值后:",'\n',df1[40:])
return(df1)
def chart_view(df01,df1):
df1.rename(columns={
'y': 'New y'}, inplace=True)
df01['y'].plot(style='k--')
df1['New y'].plot(alpha=0.5)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
df01=pd.read_csv(r'lagra_d1.csv',encoding='gbk')
df1=df01.copy()
new_data=polyinterp(df1,5)#插值后
chart_view(df01,new_data)#插值前后绘图
编写打磨课件不易,走过路过别忘记给咱点个赞,小女子在此(❁´ω`❁)谢过!如需转载,请注明出处,Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ
参考文献:
1.https://blog.csdn.net/shener_m/article/details/81706358
2.https://blog.csdn.net/qq_20011607/article/details/81412985