手写数字识别-KNN与CNN
手写数字识别-KNN与CNN
文章目录
- KNN算法
-
- 1.KNN算法步骤
- 2.KNN的实现-手写数字识别
- CNN神经网络
-
- 1.网络结构
- 2.CNN的实现-手写数字识别
KNN算法
1.KNN算法步骤
step1:计算已知类别数据集中的所有样本与当前样本之间的距离
step2:按距离递增次序对所有样本排序
step3:选取与当前当前样本距离最小的前K个样本
step4:统计这K个样本所在的类别出现的频率
step5:把这K个点出现频率最高的类别作为当前点的预测分类
2.KNN的实现-手写数字识别
MNIST数据集由60000个训练样本和10000个测试样本组成,每个样本都是一张28 * 28像素的灰度手写数字图片。

KNN算法实现代码如下。
def my_knn_classify(img, train_imgs, train_labels, k):
img = np.tile(img.reshape(1, 784), (60000, 1))
distance = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(img - train_imgs), axis=1))
sortedindex = np.argsort(distance)
sortedlabel = train_labels[sortedindex]
return Counter(sortedlabel[0:k]).most_common(1)[0][0]
下面是一副手写数字,我们要对这副图像进行手写数字识别。

首先要对图片进行预处理,包括滤波,二值化,反色等,然后进行字符定位,使用边界提取方法,提取字符边框。然后进行字符分割,将字符分成一个个28*28的小图片。最后在使用我们的KNN算法进行识别。处理代码如下:
def pre_processing(raw_image):
# 高斯去噪
image = cv2.GaussianBlur(raw_image, (3, 3), 0)
# 灰度处理并二值化
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
image[image < 130] = 0
image[image >= 130] = 255
# 颜色倒转
image = 255 - image
return image
def Character_segmentation(image):
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(image, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# img_vector = 255 - img_vector
expanding = 20
coordinates = dict()
images = []
for index, item in enumerate(contours):
rect = cv2.boundingRect(item)
x = rect[0]
y = rect[1]
weight = rect[2]
height = rect[3]
image_tmp = image[y-expanding:y + height+expanding, x-expanding:x + weight+expanding]
# filename = 'segmentation/num-' + str(index + 1) + '.png'
# cv2.imwrite(filename, image_tmp)
image_tmp = cv2.resize(image_tmp, (28, 28))
images.append(image_tmp)
coordinates[index] = [x, y, weight, height]
return images,coordinates
为加快计算以及准确度,我们需要将MINIST数据集也进行二值化,将我们的手写图片经过上述处理以后,可以直接使用KNN算法进行预测,将结果展示到原图上。代码如下:
raw_image = cv2.imread('test_pic.png')
image = pre_processing(raw_image)
images, coordinates = Character_segmentation(image)
draw_image = raw_image.copy()
for index,image in enumerate(images):
# cv_show(image)
image[image < 130] = 0
image[image >= 130] = 1
img_vector = np.reshape(image, (784, 1))
y = my_knn_classify(img_vector, train_imgs, train_labels, k=5)
# print(y)
cv2.rectangle(draw_image, (coordinates[index][0], coordinates[index][1]), (coordinates[index][0]+coordinates[index][2], coordinates[index][1]+ coordinates[index][3]), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(draw_image,str(y),((2*coordinates[index][0]+coordinates[index][2])//2,coordinates[index][1]+ coordinates[index][3]+30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,2.0, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv_show(draw_image)
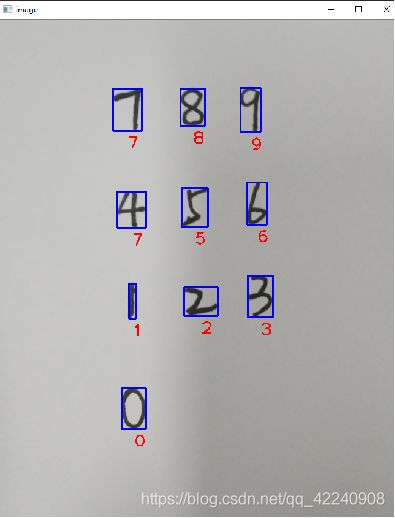
最后的识别结果如下图,这里手写数字4被错误地识别成了7。KNN算法对于手写数字识别的准确率还是很高的,但是深度学习的方法准确率更高一些。
CNN神经网络
1.网络结构
conv - relu - pool - affine - relu - affine - softmax
2.CNN的实现-手写数字识别
用视频文件做一个动态识别,效果如下图。

CNN识别的代码如下,这里做了个非常简易的GUI,网络需要自己训练哦~。
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import messagebox
from tkinter.filedialog import *
import numpy as np
from simple_convnet import SimpleConvNet
import cv2
def cv_video(img, name='video'):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(100)
def cv_picture(img, name='image'):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def pre_processing(raw_image):
# 高斯去噪
image = cv2.GaussianBlur(raw_image, (3, 3), 0)
# 灰度处理并二值化
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
image[image < 130] = 0
image[image >= 130] = 255
# 颜色倒转
image = 255 - image
return image
def Character_segmentation(image):
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(image, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# img_vector = 255 - img_vector
expanding = 20
coordinates = dict()
images = []
index = 0
for item in contours:
rect = cv2.boundingRect(item)
x = rect[0]
y = rect[1]
weight = rect[2]
height = rect[3]
image_tmp = image[y-expanding:y + height+expanding, x-expanding:x + weight+expanding]
if image_tmp.shape[0] !=0 and image_tmp.shape[1]!=0:
image_tmp = cv2.resize(image_tmp, (28, 28))
image_tmp = np.expand_dims(np.expand_dims(image_tmp, 0), 0)
images.append(image_tmp)
coordinates[index] = [x, y, weight, height]
index += 1
return images,coordinates
class Application(Frame):
def __init__(self, master=None):
super().__init__(master) # super() 代表的是父类的定义,而不是父类对象
self.master = master
self.pack()
self.createWidget()
def createWidget(self):
Button(self,text="打开视频文件",command=self.open_video).pack()
Button(self, text="打开图片文件", command=self.open_picture).pack()
Button(self, text="打开摄像头", command=self.open_camera).pack()
def open_video(self):
filename = askopenfilename(title="打开视频或者图片文件",initialdir="C:",filetypes=[("视频文件",".mp4")])
if filename:
videoCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
while True:
ret, raw_image = videoCapture.read()
if ret:
image = pre_processing(raw_image)
images, coordinates = Character_segmentation(image)
draw_image = raw_image.copy()
if images:
for index, image in enumerate(images):
y = network.predict(image)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
cv2.rectangle(draw_image, (coordinates[index][0], coordinates[index][1]), (
coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2], coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3]),
(255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(draw_image, str(y[0]), ((2 * coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2]) // 2,
coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3] + 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2.0, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# print(y)
cv_video(draw_image)
else:
break
videoCapture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def open_picture(self):
filename = askopenfilename(title="打开视频或者图片文件", initialdir="C:", filetypes=[("图片文件", ".jpg", ".png")])
if filename:
raw_image = cv2.imread(filename)
raw_image = cv2.resize(raw_image, (640, 480))
image = pre_processing(raw_image)
images, coordinates = Character_segmentation(image)
draw_image = raw_image.copy()
for index, image in enumerate(images):
y = network.predict(image)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
cv2.rectangle(draw_image, (coordinates[index][0], coordinates[index][1]), (
coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2], coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3]), (255, 0, 0),
2)
cv2.putText(draw_image, str(y[0]), ((2 * coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2]) // 2,
coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3] + 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2.0, (0, 0, 255), 2)
#print(y)
cv_picture(draw_image)
def open_camera(self):
videoCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, raw_image = videoCapture.read()
if ret:
image = pre_processing(raw_image)
images, coordinates = Character_segmentation(image)
draw_image = raw_image.copy()
if images:
for index, image in enumerate(images):
y = network.predict(image)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
cv2.rectangle(draw_image, (coordinates[index][0], coordinates[index][1]), (
coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2],
coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3]),
(255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(draw_image, str(y[0]),
((2 * coordinates[index][0] + coordinates[index][2]) // 2,
coordinates[index][1] + coordinates[index][3] + 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2.0, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# print(y)
cv_video(draw_image)
else:
break
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
videoCapture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
network = SimpleConvNet(input_dim=(1, 28, 28),
conv_param={
'filter_num': 30, 'filter_size': 5, 'pad': 0, 'stride': 1},
hidden_size=100, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01)
network.load_params()
root = Tk()
root.title("手写数字识别系统")
root.geometry("1000x800+500+100")
app = Application(master=root)
root.mainloop()