ACM Weekly 3(待修改)
ACM Weekly 3(待修改)
- 涉及的知识点
-
- 栈
- 队列
- STL
- 难题解析
- 拓展知识点
涉及的知识点
第三周练习主要涉及栈、队列、STL
本周训练主要是题目,知识点的讲解较少。
拓展:最大权闭合图
栈
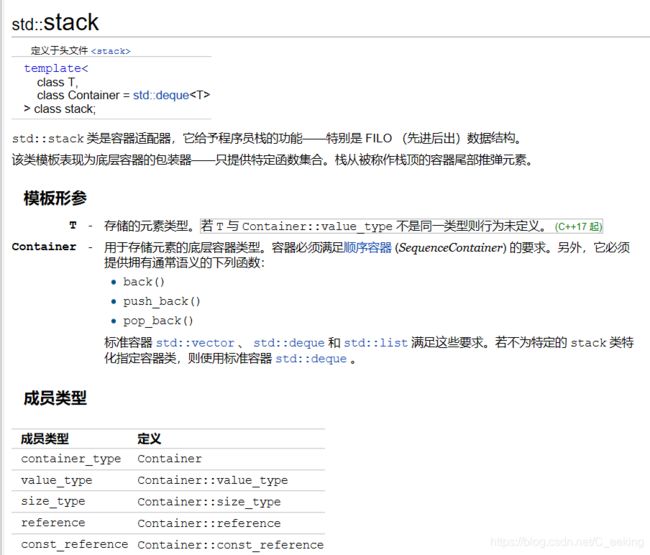
栈作为一种数据结构被广泛使用,基本性质为先进后出。
例题1(HDU 1022)
思路:通过比较两个序列所对应的元素来判断
证明:首先我们可以知道,第二个序列为出栈序列,那么问题就是如何利用栈进行操作实现每一次的栈顶都符合右边出栈序列的对应元素,对于两个序列的元素,设置两个迭代器L,R。当L≠R,代表当R弹出时,L不为栈顶,此时需要查找下一个L,记录操作入栈,直到找到第一个与R相同的L,代表此时的L为应该出栈的栈顶元素,记录操作出栈,查找下一个R,如此反复
代码
#include 思路:在线处理,根据每次录入的符号直接处理相关数据
代码
#include 使用STL的写法
#include 题目

题目大意:给定数值为1~n的纸牌以及各自的翻转状态,每次操作将最左或最右边的一堆纸牌通过翻转放置在次左或次右上,最后查询给定纸牌的状态。
思路:开辟n个栈,每个栈存放纸牌,再开辟n个栈存储翻转状态,每次合并两个栈的元素
代码
#include 题目
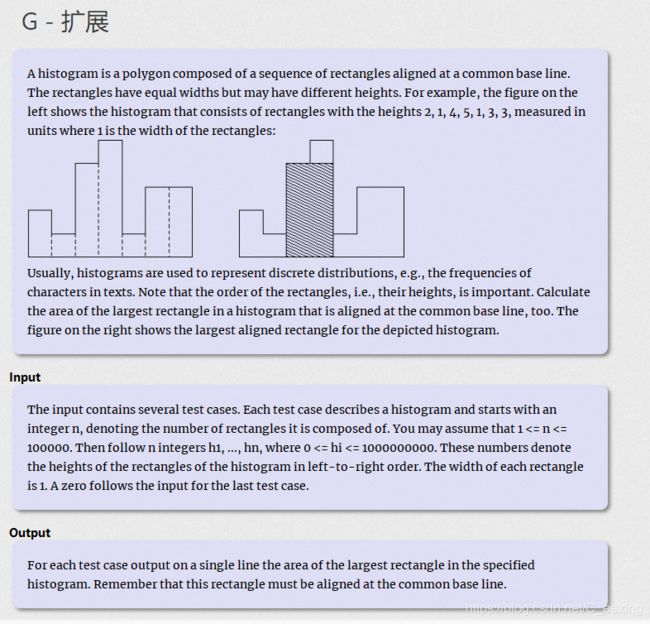
题目大意:给一系列相连的矩形块,求出其构成的最大的相连无空隙的矩形的面积
思路:对每个矩形块找出可拓展的最左端和最右端并记录,对每个矩形块来说可以使用先前的已经求出的结果,最后计算以每个矩形块为中心所构成矩形的最大值
代码
#include 本题还有另外的方法:单调栈
思路:维持一个单调栈,遇到小于栈顶的待测元素,进行弹出,每次弹出统计已经弹出的数量作为弹出元素最多可构造的面积的长,并且遇到第一个小于等于待测元素的栈内元素,待测元素入栈,此时待测元素的可构造面积为先前弹出的数量(都大于它)加上1(它自己)的和乘以它的高度
代码
#include 队列
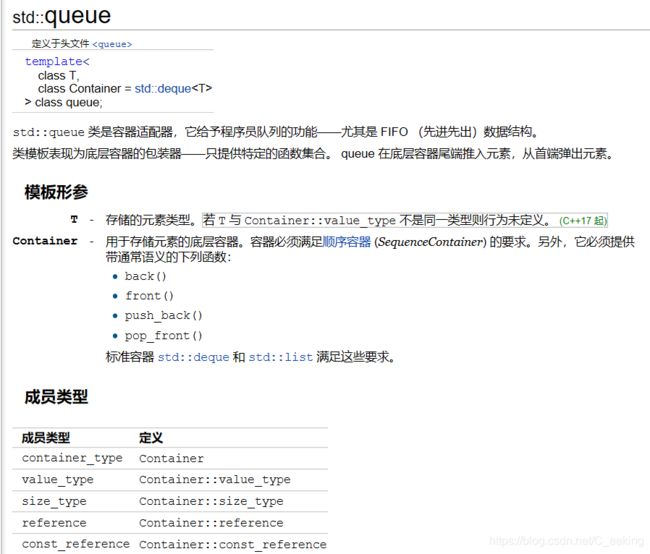
队列基本特征,先进先出。
思路:
代码
题目

题目大意:团体队列,首先给出哪些元素为一组,对应每一个元素,如果在队列中它已经有同组元素在其中,则它直接插入在其同组队友之后,否则就加在最后,对每次操作输出对应结果
思路:解题过程中参考了CSDN上的其他代码。以队为单元入整个队列,之后的元素入队列块。

代码
#include 如果使用了STL便可以大幅简化代码
#include STL
STL是C++的一大特性,它实现了数据结构与算法的分离,并且其性质不为面向对象。
本篇收录一些常用的适配器与容器的相关用法。
相关的较为详细用法参考
《C++STL基础及应用(第2版)》——清华大学出版社
实现原理参考
《STL源码解析》 (计划等到阅读完《C++ Primer》之后细读)
-
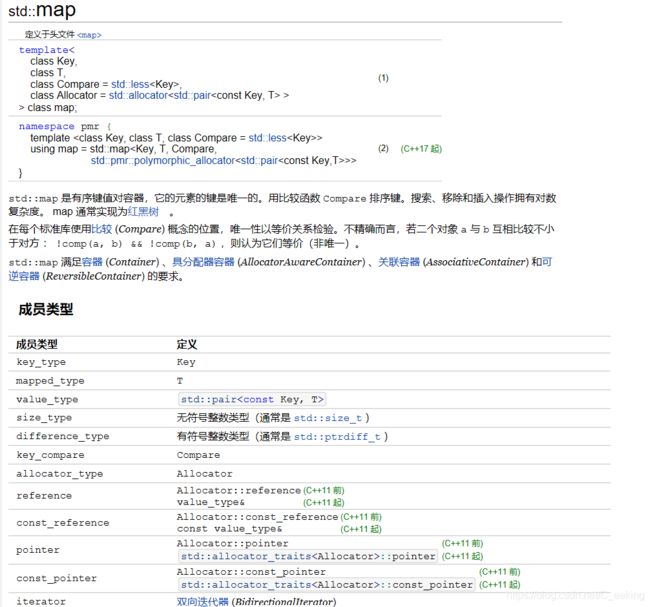
map/unordered_map
unordered_map的底层采用哈希表的实现,查询的时间复杂度为O(1)。unordered_map内部是无序的,属于关联式容器,采用std::pair保存key-value形式的数据。用法与map一致。
unoredered_map使用不需要比较元素的key值的大小。
如果需要对map中的数据排序,就首选map,其会把数据按照key的自然排序排序,如果不需要排序,一般都会选择unordered_map,它的查找效率会更高。
unordered_map在上一篇已经提及。
-
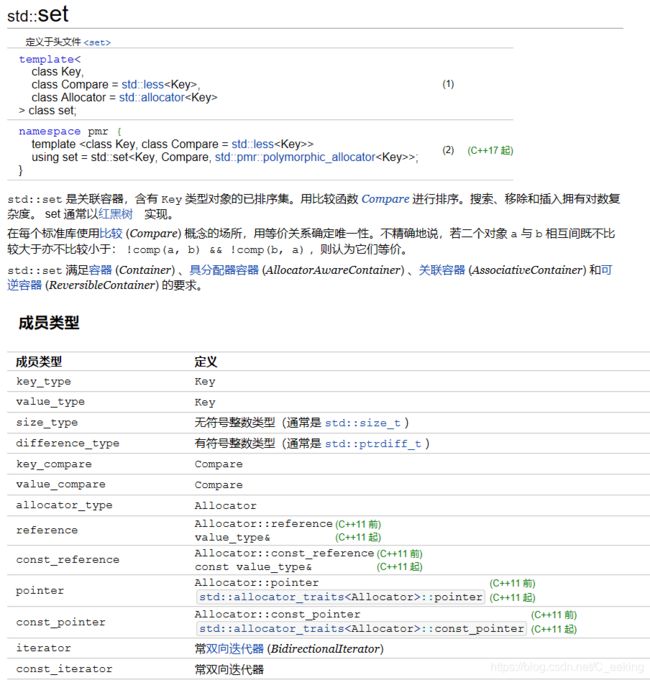
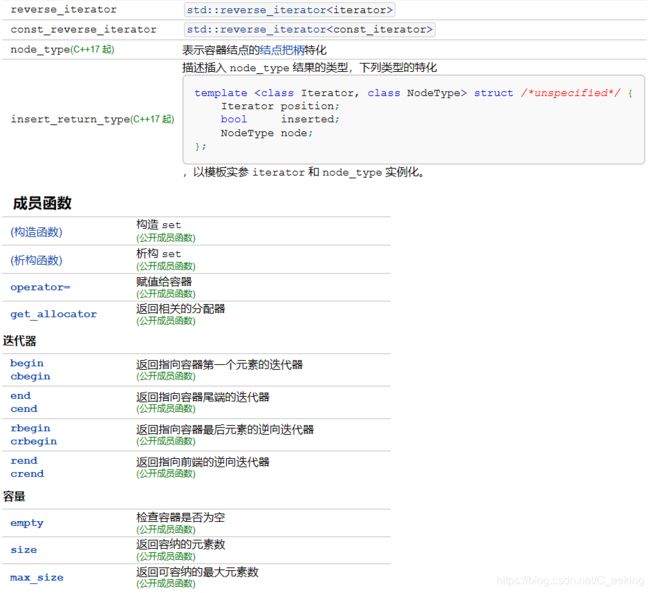
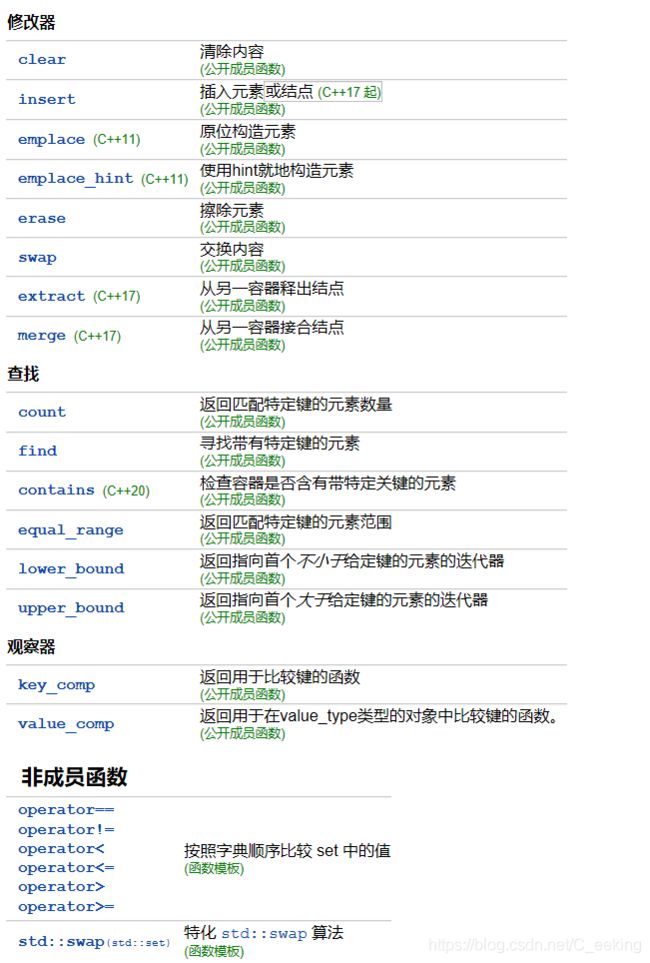
set/multiset
std::set 是关联容器,含有 Key 类型对象的已排序集。用比较函数compare进行排序。搜索、移除和插入拥有O(logN)复杂度。
set容器内的元素会被自动排序,set与map不同,set中的元素即是键值又是实值,set不允许两个元素有相同的键值。不能通过set的迭代器去修改set元素。
由于set元素是排好序的,且默认为升序,因此当set集合中的元素为结构体或自定义类时,该结构体或自定义类必须实现运算符‘<’的重载。
multiset特性及用法和set完全相同,唯一的差别在于它允许键值重复。
set和multiset的底层实现是一种高效的平衡二叉树,即红黑树。
难题解析
例题(HDU 1276)

题目大意:每一次对序列中2的倍数和3的倍数进行剔除,之后向同序号小的方向收缩,循环,直到剩下元素个数不超过3个
思路:直接模拟该过程,用链表应该能加快速度,但是数组每次遍历也可以AC,数据规模比较小
代码
#include 拓展知识点