数据挖掘算法和实践(二十三):XGBoost集成算法案列(鸢尾花数据集)
本节继续探讨集成学习算法,上一节介绍的是LGB的使用和调参,这里使用datasets自带的鸢尾花数据集介绍XGB,关于集成学习算法的介绍可以参考:数据挖掘算法和实践(十八):集成学习算法(Boosting、Bagging),XGB和LGB都是竞赛和真实场景用得很多的算法,这里详细分析XGB调参和特征选择;
一、引包与加载数据
import time
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import plot_importance,plot_tree
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
%matplotlib inline
# 加载样本数据集
iris = load_iris()
X,y = iris.data,iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1234565) # 数据集分割二、建模和参数
# 训练算法参数设置
params = {
# 通用参数
'booster': 'gbtree', # 使用的弱学习器,有两种选择gbtree(默认)和gblinear,gbtree是基于
# 树模型的提升计算,gblinear是基于线性模型的提升计算
'nthread': 4, # XGBoost运行时的线程数,缺省时是当前系统获得的最大线程数
'silent':0, # 0:表示打印运行时信息,1:表示以缄默方式运行,默认为0
'num_feature':4, # boosting过程中使用的特征维数
'seed': 1000, # 随机数种子
# 任务参数
'objective': 'multi:softmax', # 多分类的softmax,objective用来定义学习任务及相应的损失函数
'num_class': 3, # 类别总数
# 提升参数
'gamma': 0.1, # 叶子节点进行划分时需要损失函数减少的最小值
'max_depth': 6, # 树的最大深度,缺省值为6,可设置其他值
'lambda': 2, # 正则化权重
'subsample': 0.7, # 训练模型的样本占总样本的比例,用于防止过拟合
'colsample_bytree': 0.7, # 建立树时对特征进行采样的比例
'min_child_weight': 3, # 叶子节点继续划分的最小的样本权重和
'eta': 0.1, # 加法模型中使用的收缩步长
}
plst = params.items()
# 数据集格式转换
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test)
# 迭代次数,对于分类问题,每个类别的迭代次数,所以总的基学习器的个数 = 迭代次数*类别个数
num_rounds = 50
model = xgb.train(plst, dtrain, num_rounds) # xgboost模型训练
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(dtest)
# 计算准确率
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
print("accuarcy: %.2f%%" % (accuracy*100.0))
# 显示重要特征
plot_importance(model)
plt.show()三、模型评估
# 可视化树的生成情况,num_trees是树的索引
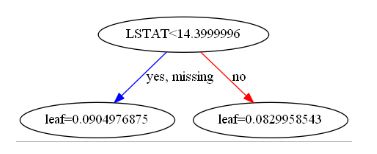
plot_tree(model, num_trees=5)
# 将基学习器输出到txt文件中
model.dump_model("model1.txt")XGB的回归问题
# 加载数据集
boston = load_boston()
# 获取特征值和目标指
X,y = boston.data,boston.target
# 获取特征名称
feature_name = boston.feature_names
# 划分数据集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# 参数设置
params = {
'booster': 'gbtree',
'objective': 'reg:gamma', # 回归的损失函数,gmma回归
'gamma': 0.1,
'max_depth': 5,
'lambda': 3,
'subsample': 0.7,
'colsample_bytree': 0.7,
'min_child_weight': 3,
'silent': 1,
'eta': 0.1,
'seed': 1000,
'nthread': 4,
}
plst = params.items()
# 数据集格式转换
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train,feature_names = feature_name)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test,feature_names = feature_name)
# 模型训练
num_rounds = 30
model = xgb.train(plst, dtrain, num_rounds)
# 模型预测
y_pred = model.predict(dtest)
# 显示重要特征
plot_importance(model,importance_type ="weight")
plt.show()
# 可视化树的生成情况,num_trees是树的索引
plot_tree(model, num_trees=17)
# 将基学习器输出到txt文件中
model.dump_model("model2.txt")