零、插播2020CSDN博客之星投票新闻
近日(1月11日-1月24日),2020CSDN博客之星评选正在火热进行中,作为码龄1年的小白有幸入选Top 200,首先很感谢CSDN官方把我选上,本来以为只是来凑热闹,看大佬们PK 。
综合过去9天大佬们战况,前10名大佬基本坐得很稳,后期出现黑马发力,势不可挡,都在冲刺Top 20,有了微妙的变化,不得不令人佩服点赞!真正的实力可以看出,文章数量不重要,更重要的是质量!一切用数据说话,如图:
截至 2021-01-20 11:50:02
看了大佬的惊人数据,与我差距甚大,不禁感慨,接下来看看我自己!
首先,很感谢每一位帮忙投票的粉丝和兄弟姐妹们,感谢您的关注和支持,经过大家上一周的共同努力,我已进入2020博客之星投票排行榜Top 100。
投票还有一周时间,进入更激烈更有悬念的阶段,希望读者们下来一周能投出您手中宝贵的票权,让我更进一步!
投票地址:https://bss.csdn.net/m/topic/blog_star2020/detail?username=charzous
或者扫码投票:
重点:每一个投票都会被记录,投了之后找Charzous帮忙也容易了(疯狂暗示投票拉票)!
比如,帮忙下载资源,或者博客一键三连,再次对每位帮我投票的粉丝表示感谢! 新的一年,让我们一起变得更强!
即日起到24号,每天都可以投票哦,票数越多,贡献排行榜就越靠前,我就记住你的名字啦!
24号是否能和大佬们在顶峰相见,就靠大家了哈!
一、承上启下
前一篇学习了Java并发程序设计原理之后,为了对这个部分有了更深层的理解,并运用于实际场景中,所以我找了比较实际的案例进行实践——文件搜索,简单来说,这也是电脑文件系统中的一个常见功能,用户可以通过用户名搜索文件系统中符合条件的文件。
文件搜索的程序需要用到Java并发API中的Thread类和Runnable接口,其中一些重要的内容先简单了解一下。
二、Java中的多线程
线程类Thread,有两种方式创建执行线程。
1、扩展Thread类并重载run()方法
Thread类包含了丰富的方法,在实现线程时候必须重载run方法,扩展Thread类和调用start方法创建新的线程。其他常用方法:
getId():获取Thread对象的标识符,线程整个生命周期中唯一不变的一个正整数。getName()/setName():String类型,获取或设置Thread对象名。
getPriority()/setPriority():获取或设置线程的优先级。值范围:Thread.MIN_PRIORITY~Thread.MAX_PRIORITY(1~10),创建时默认Thread.NORM_PRIORITY(5)。getState():线程对象的状态。包括:NEW(新创建)、RUNNABLE(运行中)、BLOCKED(等待锁定)、WAITING(等待)、TIME_WAITING(有时间限制等待)、THREAD(完成)。
线程在一段时间中只能处于一种状态,而且是在JVM中的状态,不能映射到操作系统的线程状态。interrupt():请求结束执行Thread对象。
interrupted():检查中断状态,清除中断标志的值。
isInterrupted():检查中断状态,不清除中断标志的值。
sleep():线程执行睡眠时间,单位毫秒。
join():暂停调用线程的执行,直到调用该方法的线程执行结束为止。
currentThread():静态方法,返回实际执行当前任务的Thread对象。
2、实现Runnable接口
可以通过线程来执行Runnable对象,更灵活更改并发程序,还可以通过不同线程使用同一个Runnable对象。
相对来说,使用Runnable接口创建线程的方法更加推荐,它只定义了run方法,是每个线程的主方法。当执行start方法启动新线程时,就会调用run方法。
三、串行文件搜索
这里分为两种版本,串行(单线程)和并发(多线程),后续可以进行比较。
1、创建公共类Result保存搜索结果
/**
* Result.java
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/1/20 11:00
*
*/
package SearchFiles;
public class Result {
boolean found;
String path;
public void setFound(boolean found){
this.found=found;
}
public boolean isFound(){
return this.found;
}
public void setPath(String path){
this.path=path;
}
public String getPath(){
return this.path;
}
}
2、查找算法
算法思路简单,通过初始路径,获取文件和目录内容,并与目标文件名进行比较,相同则记录Result,算法完成;不同则递归遍历文件,直到算法完成。
/**
*
* SerialSearch.java
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/1/20 11:15
*
*/
package SearchFiles;
import java.io.File;
public class SerialFileSearch {
public static void searchFiles(File file,String fileName,Result result){
File[] contents;
contents=file.listFiles();
if ((contents==null)||(contents.length==0))
return;
for (File content:contents){
if (content.isDirectory())
searchFiles(content,fileName,result);
else{
if (content.getName().equals(fileName)){
result.setPath(content.getAbsolutePath());
result.setFound(true);
System.out.println("Serial Search Path: "+result.getPath());
return;
}
}
if (result.isFound())
return;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result result=new Result();
File file=new File("D:\\");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
String fileName="maskOrder.txt";
SerialFileSearch.searchFiles(file,fileName,result);
if (!result.isFound())
System.out.println("未找到该文件:"+fileName);
else
System.out.println("找到该文件:"+fileName+"!");
System.out.println("查询时间:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)+"ms");
}
}
四、并行文件搜索(多线程)
1、创建ParallelGroupFileTask类
它实现所有用于查找文件的线程,实现Runnable接口,重载run方法,其中包括了处理目录的processDirectory方法,处理文件的processFile方法。
/**
* ParallelGroupFileTask.java
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/1/20 11:31
*
*/
package SearchFiles;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
class ParallelGroupFileTask implements Runnable {
private final String fileName;
private final ConcurrentLinkedQueue directories;
private final Result parallelResult;
private boolean found;
public ParallelGroupFileTask(String fileName, ConcurrentLinkedQueue directories, Result parallelResult) {
this.fileName = fileName;
this.directories = directories;
this.parallelResult = parallelResult;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (directories.size() > 0) {
File file = directories.poll();
try {
processDirectory(file,fileName,parallelResult);//递归
if (found) {
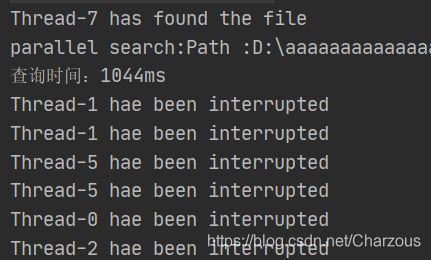
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " has found the file");
System.out.println("parallel search:Path :" + parallelResult.getPath());
return;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hae been interrupted");
}
}
}
public void processDirectory(File file, String fileName, Result parallelResult) throws InterruptedException {
File[] contents;
contents = file.listFiles();
if ((contents == null) || (contents.length == 0))
return;
for (File content : contents) {
if (content.isDirectory()) {
processDirectory(content, fileName, parallelResult);
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (found)
return;
} else {
processFile(content, fileName, parallelResult);//递归
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (found)
return;
}
}
}
public void processFile(File content, String fileName, Result parallelResult) {
if (content.getName().equals(fileName)) {
parallelResult.setPath(content.getAbsolutePath());
this.found = true;
}
}
public boolean getFound() {
return found;
}
}
2、多线程算法
创建ParallelGroupFileSearch类,其中包括了存放基本路径的线程安全的列表ConcurrentLinkedQueue,然后创建新线程,数量有JVM中可用的线程数量,通过Runtime的availableProcessors方法获得。
其中,若某个线程找到目标文件,会使用interrupt方法取消其他线程的执行。具体实现代码如下:
/**
* ParallelGroupFileSearch.java
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/1/20 11:40
*
*/
package SearchFiles;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class ParallelGroupFileSearch {
public static void searchFiles(File file, String fileName, Result parallelResult) {
ConcurrentLinkedQueue directories = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
File[] contents = file.listFiles();
for (File content : contents) {
if (content.isDirectory())
directories.add(content);
}
int numThreads = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
Thread[] threads = new Thread[numThreads];
ParallelGroupFileTask[] tasks = new ParallelGroupFileTask[numThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) {
tasks[i] = new ParallelGroupFileTask(fileName, directories, parallelResult);
threads[i] = new Thread(tasks[i]);
threads[i].start();
}
boolean finish = false;
int numFinished = 0;
while (!finish) {
numFinished = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
if (threads[i].getState() == Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
numFinished++;
if (tasks[i].getFound())
finish = true;
}
}
if (numFinished == threads.length)
finish = true;
}
if (numFinished != threads.length) {
for (Thread thread : threads)
thread.interrupt();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result result=new Result();
File file=new File("D:\\");
String fileName="maskOrder.txt";
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
ParallelGroupFileSearch.searchFiles(file,fileName,result);
System.out.println("查询时间:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)+"ms");
}
}
五、结果
1、串行(单线程)
串行版本多次测试结果用时在1900ms左右!
10次测试数据:
查询时间:1978ms 2036 1860 1926 1861 2100 1889 2030 1905 1990
2、并发(多线程)
并发版本多线程测试用时在1400ms左右!
10次测试数据:
查询时间:1441ms 1368 1258 1546 1444 1430 1490 1432 1338 1435
从简单的测试结果可以看出,并发搜索的算法速度提升明显。
这一篇通过实际的案例进行实践——文件搜索,简单来说,这也是电脑文件系统中的一个常见功能,用户可以通过用户名搜索文件系统中符合条件的文件。Runnable接口和Thread类的基本使用也有了更深的认识。在文件搜索这个案例中,学习了Java并发原理的实际应用,首先设计一种串行的版本,然后再实现并发的版本,这也是一个改进的过程。
到此这篇关于Java并发(Runnable+Thread)实现硬盘文件搜索的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java并发硬盘文件搜索内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!