面试-机试-编程题--剑指offer
如果要面试java,最好要看看http://www.cnblogs.com/lanhj/p/4672735.html 概括了所有可能问到的java问题
1 360 内推笔试
以下是代码部分:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
int count = Integer.parseInt(getInput());
List list = new ArrayList();//主要引入的包一定要是util.List.如果是awt.list容易有错误
for(int i =0;i < count;i++){ //注意这个地方实现的是,可以读取到几行数据,然后根据输入的int来去判断,当没有输入count行,程序会在这个地方等待输入。
list.add(getInput());
}
//System.out.println(count);
for(int i=0;i < count;i++){
//System.out.println("list"+ list.get(i));
char flag = getFirstNonChar(list.get(i));
if(flag == '0'){
System.out.println("no");
}
else{
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
}
/*一般都使用entry来遍历整个map:
Map map = new HashMap();
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue());
} */
public static char getFirstNonChar(String str){
Map map = new HashMap(str.length());//我刚开始这个str.length没有加进去,然后如果输入ha的话则输出是a
int flag = 0;
for(char c:str.toCharArray()){
map.put(c, map.containsKey(c) ? map.get(c) + 1 : 1);//这个地方写的非常棒。
}
for(Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()){
if(entry.getValue() == 1){
//System.out.println(entry.getKey());
return entry.getKey();
}
}
//throw new RuntimeException("Can\'t find any non repeated Character");
return '0';
}
public static String getInput(){
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s1 = "";
try {
s1 = in.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return s1;
}
} 2 KMP算法
关于该算法的分析,请看http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4633153.html
比如:str = abcabd,next初始化为:[0,0,0,0,0,0];
已知第0个字符a没有任何相同的前后缀,则next[0] = 0。
加入第1个字符,则前面已知的最长公共前后缀长度为next[0],此时如果str[next[0]]与str[1]相等,就可知道next[1]=next[0]+1,如不相等则可直接判定next[1]=0;这里str[next[0]]!=str[1],故next[1]=0。
...,next[2]=0。
...,next[3]=next[2]+1=1。
...,next[4]=next[3]+1=2。
...,next[5]=0。
最后,next=[0,0,0,1,2,0];
代码附上,其实我也没有看懂,知道大概的思路就可以了:
package com.shu.frnak;
public class KMP {
void getNext(String pattern, int next[]) { //把匹配值算出来放到 next[]数组中
int j = 0;
int k = -1;
int len = pattern.length();
next[0] = -1;
while (j < len - 1) {
if (k == -1 || pattern.charAt(k) == pattern.charAt(j)) {
j++;
k++;
next[j] = k;
} else {
// 比较到第K个字符,说明p[0——k-1]字符串和p[j-k——j-1]字符串相等,而next[k]表示
// p[0——k-1]的前缀和后缀的最长共有长度,所接下来可以直接比较p[next[k]]和p[j]
k = next[k];
}
}
}
int kmp(String s, String pattern) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int slen = s.length();
int plen = pattern.length();
int[] next = new int[plen];
getNext(pattern, next);
while (i < slen && j < plen) {
if (s.charAt(i) == pattern.charAt(j)) {
i++;
j++;
} else {
if (next[j] == -1) {
i++;
j = 0;
} else {
j = next[j];
}
}
if (j == plen) {
return i - j;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
KMP kmp = new KMP();
String str = "bbc abcdab abcdabcdabde";
String pattern = "abcdabd";
System.out.println(kmp.kmp(str, pattern));
}
}
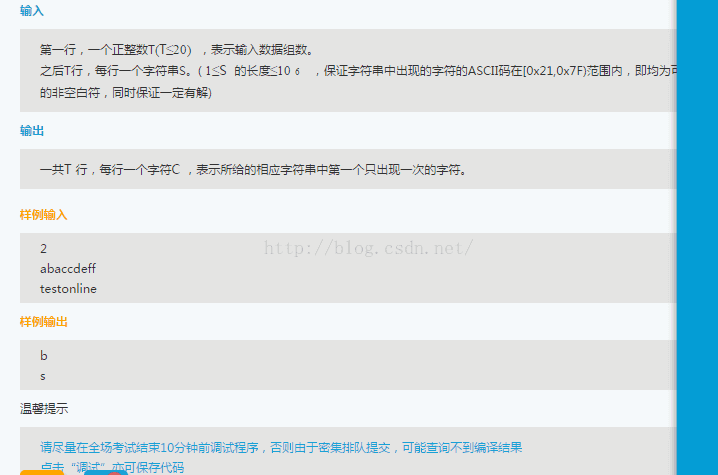
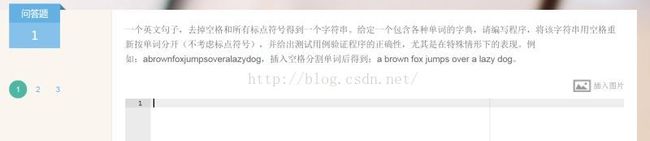
3 阿里测试开发笔试题目
这类题网上有算法差不多的。主要采用递归回溯的方法:
package com.shu.frnak;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestList {
String partString(String input, Set dict){
if(dict.contains(input))
return input;
int length = input.length();
for(int i =1;i dict){
String result = partString(srcinput, dict);
if(result.equals(rightinput)){
return "true";
}
else{
return "false";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
TestList test = new TestList();
Set dict1 = new HashSet();
dict1.add("a");
dict1.add("brown");
dict1.add("fox");
dict1.add("jumps");
dict1.add("over");
dict1.add("lazy");
dict1.add("dog");
//String result = test.partString("abrownfoxjumpsoveralazydog", dict1);
String flags1 = test.testString("abrownfoxjumpsoveralazydog", "a brown fox jumps over a lazy dog", dict1);
System.out.println(flags1);
String flags2 = test.testString("a", "a", dict1);
System.out.println(flags2);
}
} 4 华为机试
注意输入输出的格式,在java中智能用next()或者nextInt()去获取输入的数字,不能用nextLine(),如果用nextLine就会报错误。
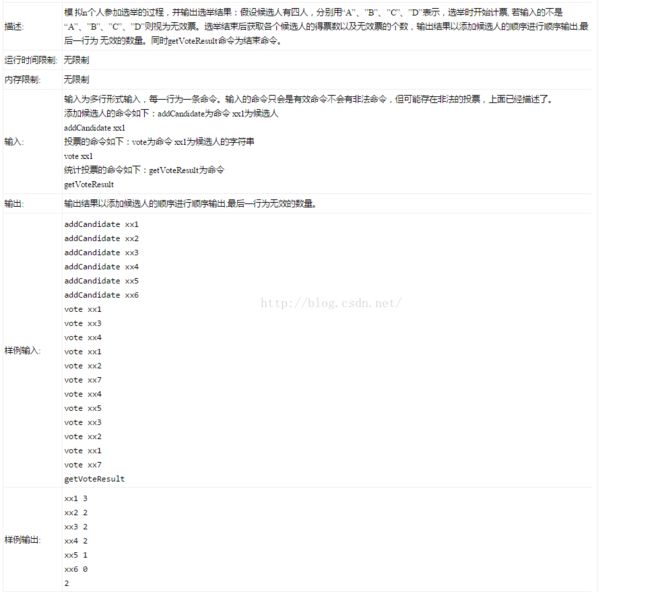
package com.shu.frank;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
List list = new ArrayList();
Pattern votejudgPattern = Pattern.compile("vote");
while(cin.hasNext()){
String oneline = cin.nextLine();
Matcher matcher = votejudgPattern.matcher(oneline);
if(matcher.find()){
list.add(oneline);
}
if((oneline.equals("getVoteResult"))){
int a=0;
int b=0;
int c=0;
int d=0;
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i map = new TreeMap();
map.put("A", a);
map.put("B", b);
map.put("C", c);
map.put("D", d);
List> listsort = new ArrayList>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(listsort, new Comparator>() {
public int compare(Entryo1,Entryo2){
return o2.getValue().compareTo(o1.getValue());
}
});
for(Map.Entry mapping:listsort){
System.out.println(mapping.getKey()+" "+mapping.getValue());
}
System.out.println(m);
//System.out.println("list"+list.toString());
break;
}
}
}
}
总结TreeMap分别对Vaule和Key进行排序的方法:
TreeMap:用于排序
1 TreeMap默认是根据Key进行升序排练的。
//如果要改变排序方式,则需要使用比较器:Comparator,它可以对集合对象或者数组进行排序的比较接口
Map map = new TreeMap(
new Comparator() {
public int compare(String obj1,String obj2){
return obj2.compareTo(obj1);
}
}
);
map.put("b", "ccccc");
map.put("d", "aaaaa");
map.put("c", "bbbbb");
map.put("a", "ddddd");
//遍历整个map
for(Map.Entry mapsort:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(mapsort.getKey()+","+mapsort.getValue());
}
2 //TreeMap的value来进行排序。对value排序我们就需要借助于Collections的sort(List list,
//Comparator c)方法,该方法根据指定比较器产生的顺序对指定列表进行排序。但是有一个前提条件,
//那就是所有的元素都必须能够根据所提供的比较器来进行比较
Map map = new TreeMap();
map.put("a", "ddddd");
map.put("c", "bbbbb");
map.put("d", "aaaaa");
map.put("b", "ccccc");
List> list = new ArrayList>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry o1,
Entry o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for(Map.Entry mapping:list){
System.out.println(mapping.getKey()+":"+mapping.getValue());
}
5 华为机试,注意输入输出的格式
package com.shu.cisco;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public Map getmapCharcount(String s){
Map tree = new TreeMap();
String sx = s.toLowerCase();
//下面这个for循环是统计一个字符串中字符的出现次数,并且把字符和次数,存放到Map中,并且按照次数进行排序。
for(int i=0;i='a' && ch <= 'z'){
if(!tree.containsKey(ch)){
tree.put(ch, new Integer(1));
}
else{
Integer in = (Integer)tree.get(ch) + 1;//注意这个地方,一定要注意
tree.put(ch, in);
}
}
}
ArrayList> list = new ArrayList>(tree.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry o1,
Entry o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o2.getValue().compareTo(o1.getValue());
}
});
int q=26;
int sum=0;
for(Map.Entry mapsort:list){
sum =sum+ mapsort.getValue() * (q--);
//System.out.println(mapsort.getValue()*(q--));
}
System.out.println(sum);
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
Main main = new Main();
int count = cin.nextInt();
String aa = "";
for(int i=0;i 6 对数组进行排序问题
主要使用的是Arrays的sort()方法,注意:Arrays的常用方法还有Arrays.asList(List),返回一个固定长度大小的list,还有binarySearch(char[] a,char key)
a - 要搜索的数组
key - 要搜索的值 ,如果没有找到则返回0
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
Main main = new Main();
char[] array = cin.nextLine().toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(array);
System.out.println(array);
}
}7 华为机试 判断ip以及子网掩码的合法性
这个题目的合法性判断主要是:子网掩码第一部分应为255,第二三部分为0或者255,第四部分为0;IP地址的是个部分均在0到255之间。
package com.shu.cisco;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public int checkNetSegment(String mask, String ip1, String ip2)
{
//子网掩码第一部分应为255,第二三部分为0或者255,第四部分为0;IP地址的是个部分均在0到255之间。
int flags=3;
String[] maskArray = mask.split("\\.");
String[] ip1Array = ip1.split("\\.");
String[] ip2Array = ip2.split("\\.");
int[] maskint = new int[mask.length()];
int[] ip1int = new int[ip1.length()];
int[] ip2int = new int[ip2.length()];
int[] ip1result = new int[4];
int[] ip2result = new int[4];
if(!((maskArray[0].equals("255")) && (maskArray[3].equals("0")) && ((maskArray[1].equals("255"))||(maskArray[1].equals("0"))) && ((maskArray[2].equals("255"))||(maskArray[2].equals("0"))))){
System.out.println("mask不合法");
return flags=1;
}
for(int i=0;i255){
//System.out.println("ip1不合法");
return flags = 1;
}
ip1result[i] = ip1int[i] & maskint[i];
}
for(int i=0;i255){
//System.out.println("ip2不合法");
return flags = 1;
}
ip2result[i] = ip2int[i] & maskint[i];
}
if((ip1result[0]==ip2result[0])&&(ip1result[1]==ip2result[1])&&(ip1result[2]==ip2result[2])&&(ip1result[3]==ip2result[3])){
return 0;
}
else{
return 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
Main main = new Main();
int flags = main.checkNetSegment(cin.next(),cin.next(),cin.next());
System.out.println(flags);
}
}
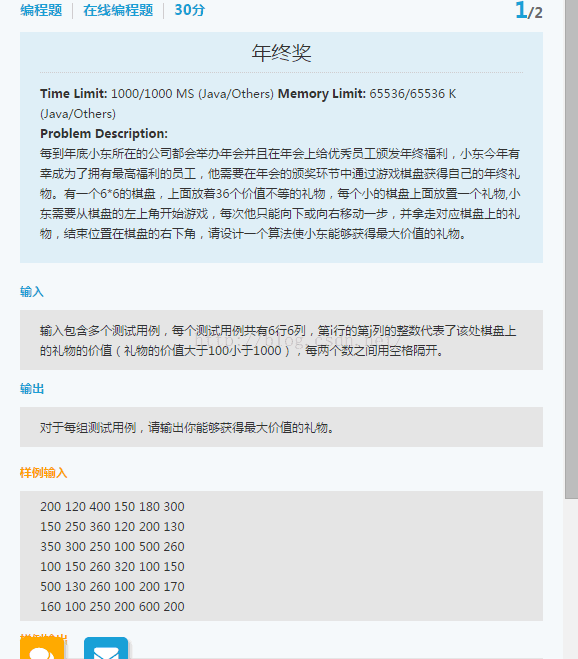
8 京东机试2016
采用动态规划,另外注意对于输入的数据到二维数组中,对于一个二维数组,int[][] input=new int[][], input.length是行的长度,input[0].length是列的长度,注意
参考资料:http://www.cnblogs.com/luxiaoxun/archive/2012/11/15/2771605.html
http://codercareer.blogspot.com/2014/10/no-56-maximal-value-of-gifts.html
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static int getMaxValue(int[][] input) {
int rows = input.length;
int cols = input[0].length;
int[][] maxinput = new int[rows][cols];
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int left = 0;
int up = 0;
if(i > 0) {
up = maxinput[i - 1][j];
}
if(j > 0) {
left = maxinput[i][j - 1];
}
maxinput[i][j] = Math.max(left, up) + input[i][j];
}
}
return maxinput[rows - 1][cols - 1];
}
/* public static int getMaxValue(int[][] values) {
int rows = values.length;
int cols = values[0].length;
int[] maxValues = new int[cols];
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int left = 0;
int up = 0;
if(i > 0) {
up = maxValues[j];
}
if(j > 0) {
left = maxValues[j - 1];
}
maxValues[j] = Math.max(left, up) + values[i][j];
}
}
return maxValues[cols - 1];
}*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int input[][] = new int[6][6];
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
for(int j=0;j<6;j++){
input[i][j]= cin.nextInt();
}
}
int result = getMaxValue(input);
System.out.println(result);
}
}9 京东机试2016
//设原有苹果a1只,
//第一只猴取后剩下a2 = (4 / 5)(a1 - 1)只,a2 + 4 = (4 / 5)(a1 + 4)
//第二只猴取后剩下a3 = (4 / 5)(a2 - 1)只,a3 + 4 = (4 / 5)(a2 + 4)
//第三只猴取后剩下a4 = (4 / 5)(a3 - 1)只,a4 + 4 = (4 / 5)(a3 + 4)
//第四只猴取后剩下a5 = (4 / 5)(a4 - 1)只,a5 + 4 = (4 / 5)(a4 + 4)
//第五只猴取后剩下a6 = (4 / 5)(a5 - 1)只,a6 + 4 = (4 / 5)(a5 + 4)
//第五只猴取走的是(a5 - 1) / 5
//a6 + 4 = (a1 + 4)*(4 / 5) ^ 5
//a6 + 4, a1 + 4都是正整数,所以a1 + 4是5 ^ 5的公倍数,最小值5 ^ 5,
#include
#include
int Fun(int N)
{
int i;
int result=1;
if (N < 1 || N>9)
return NULL;
else {
for (i = 1; i <= N; i++)
result *= N;
result = result -N + 1;
}
return result;
}
void main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
printf("%d\n", Fun(N));
}
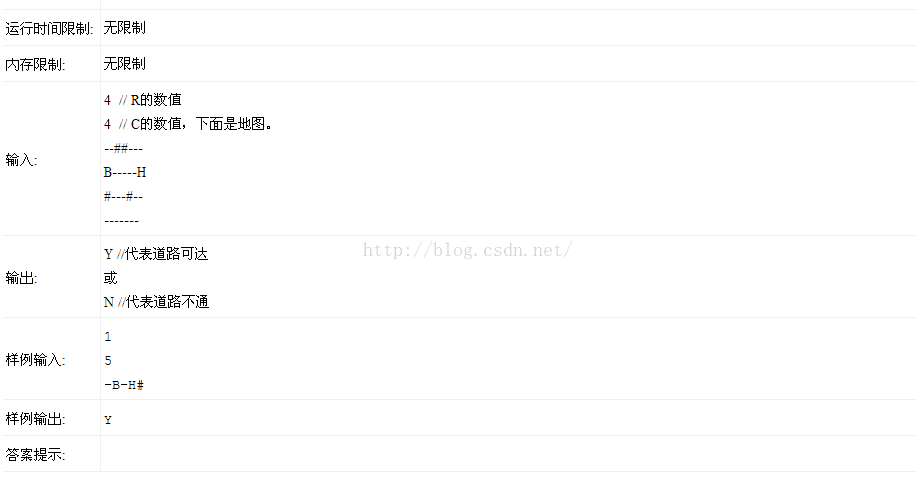
10 华为机试 上海 2016
本题目是放在了华为机试的第二题,感觉难度还是有些大的,这个题目类似于走迷宫问题,可以参考百度文库的ppt,将的很好,形象,关键问题在于:
(1)要重新构建一个二维数组,并且在原来基础上列数和行数都增加2,对增加的部分设为临界区,目的不让出界。
(2)要构建一个栈,每前进一部,入栈,每后退一步出栈。
(3)对于在某个点上可以按照,逆时针顺序,向从向下方向开始。
下面是代码部分,有注释:
package com.cisco.huawei;
import java.util.*;
class Step {
int x, y, d;
public Step(int x, int y, int d) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.d = d;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + x + ", " + y + "]";
}
}
public class Main {
public boolean canReachHome(char[][] board) {
//定义四个方向分别是上,右,下,左
int[][] move = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
Stack s = new Stack<>();
return path(board, move, s);
}
private boolean path(char[][] board, int[][] move, Stack s) {
int m = board.length + 2;
int n = board[0].length + 2;
char[][] maze = new char[m][n];
//新建了一个maze对board的四周加了一层保护膜,防止出界
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maze[0][i] = '*';
maze[m - 1][i] = '*';
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
maze[i][0] = '*';
maze[i][n - 1] = '*';
}
//把maze的非四周部分内容,用board的内容替换
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
maze[i][j] = board[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
int tempx = 0;
int tempy = 0;
int finalx = 0;
int finaly = 0;
//找出,B(出发点) H(结束点),并记住坐标
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (maze[i][j] == 'B') {
tempx = i;
tempy = j;
}
if (maze[i][j] == 'H') {
finalx = i;
finaly = j;
maze[i][j] = '-';
}
}
}
Step temp = new Step(tempx, tempy, -1);
s.push(temp);
//每前进一步,入栈,每回退一部出栈
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
s.pop();
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
temp = s.peek();
}
int x = temp.x;
int y = temp.y;
int d = temp.d + 1;
//int[][] move = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
while (d < 4) {
//往上下左右四个方向,依次去试,如果有等于'-'的情况,则入栈
int i = x + move[d][0];
int j = y + move[d][1];
if (maze[i][j] == '-') {
temp = new Step(i, j, -1);
s.push(temp);
x = i;
y = j;
maze[x][y] = '#';
if (x == finalx && y == finaly) {
return true;
} else {
d = 0;
}
} else {
d++;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int row, col;
Main m = new Main();
while (cin.hasNext()) {
row = Integer.valueOf(cin.nextLine());
col = Integer.valueOf(cin.nextLine());
char[][] board = new char[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
String str = cin.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
board[i][j] = str.charAt(j);
}
}
boolean ans = m.canReachHome(board);
if (ans) {
System.out.println("Y");
} else {
System.out.println("N");
}
}
}
}
/*1
5
-B-H#*/ 11 和尚挑水问题华为机试 2016
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/sunnyyoona/article/details/46778981
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_18989901/article/details/48413087
我是把第二位大神的改成了用java的代码:
package com.cisco.huawei;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static int day = 8;
private static int count=0;
private static int spare[][] = new int[8][8];
private static int monk[] = new int[8];
private static int done[] = new int[8];
public void printMonk(int t){
if(t >= 8){
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
System.out.print(monk[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
count++;
}
else{
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
monk[t] = i;
if(done[i] == 0 && spare[i][t] == 1){
done[i]=1;
printMonk(t+1);
done[i] =0;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Main main = new Main();
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
for(int j=1;j<8;j++){
spare[i][j] = cin.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
monk[i] = 0;
done[i] = 0;
}
main.printMonk(1);
System.out.println("count"+count);
}
}
/*
0 1 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 1 1
*/下面这段是先传输方案总数,然后输出每一个方案,是先用temp把方案存起来:
package com.cisco.huawei;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
// private static int day = 8;
private static int count=0;
private static int spare[][] = new int[8][8];//放入输入的数据
private static int temp[][] = new int[1000][8];
private static int day[] = new int[8];//7天,其中第一天不算,每周几哪个和尚挑水
private static int done[] = new int[8];//7天 记录哪个和尚挑过水了
public void printday(int t){ //t表示周几
if(t >= 8){
count++;
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
temp[count][i]=day[i];
//System.out.print(day[i] + " ");
}
//System.out.println("");
}
else{
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
day[t] = i;
if(done[i] == 0 && spare[i][t] == 1){
done[i]=1;
printday(t+1);
done[i] =0;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Main main = new Main();
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=1;i<8;i++){
for(int j=1;j<8;j++){
spare[i][j] = cin.nextInt();
}
}
main.printday(1);
System.out.println("count"+count);
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++){
for(int j=1;j<8;j++){
System.out.print(temp[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} 下面是c++代码实现:主要就是用:
vector
vector
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void DrawingWater(vector > &spare,int index,vector &week,vector &visited,vector > &t,int &num)
{
int i;
if(index==7)
{
++num;
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
t[num][i]=week[i]+1;
return;
}
for(i=0;i<7;++i)
{
week[index]=i;//week[0]=0; index是第几个和尚,
if (!visited[i]&&spare[i][index]==1) {//这个和尚没有挑过水,并且可以挑水。就是一个
visited[i]=1;//说明这个和尚挑过水
DrawingWater(spare,index+1,week,visited,t,num);
visited[i]=false;//ok
}
}
}
int main(){
vector > spare(7,vector(7,0));//第一个7行,第二个
vector > t(1000,vector(7,0));//先储存起来
int num=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 7;++i){
for(int j = 0;j < 7;++j){
cin>>spare[i][j];
}
}
int count = 0;
vector week(7,0);//7天,都是0,是为了记录到底是周几
vector visited(7,false);//那个和尚是否挑过水
DrawingWater(spare,0,week,visited,t,num);
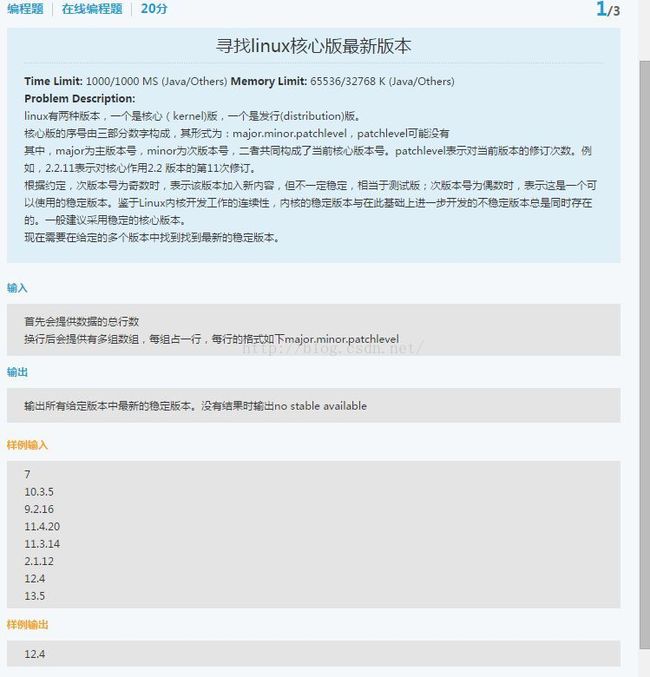
cout< 12 去哪儿网笔试2016
下面这份代码测试为86%
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public int linuxCheck(Map input){
List> list = new ArrayList>(input.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry o1,
Entry o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o2.getValue().compareTo(o1.getValue());
}
});
int ll=0;
for(Map.Entry mapping:list){
String[] keys = mapping.getKey().split("\\.");
int flags = Integer.parseInt(keys[1])%2;
ll++;
if(flags ==0){
System.out.println(mapping.getKey());
ll=1;
return 1;
}
if(ll==0){
System.out.println("no stable available");
}
//System.out.println(mapping.getKey()+":"+mapping.getValue());
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Main main = new Main();
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
Map map = new TreeMap();
int count = Integer.parseInt(cin.nextLine());
String[] input = new String[count];
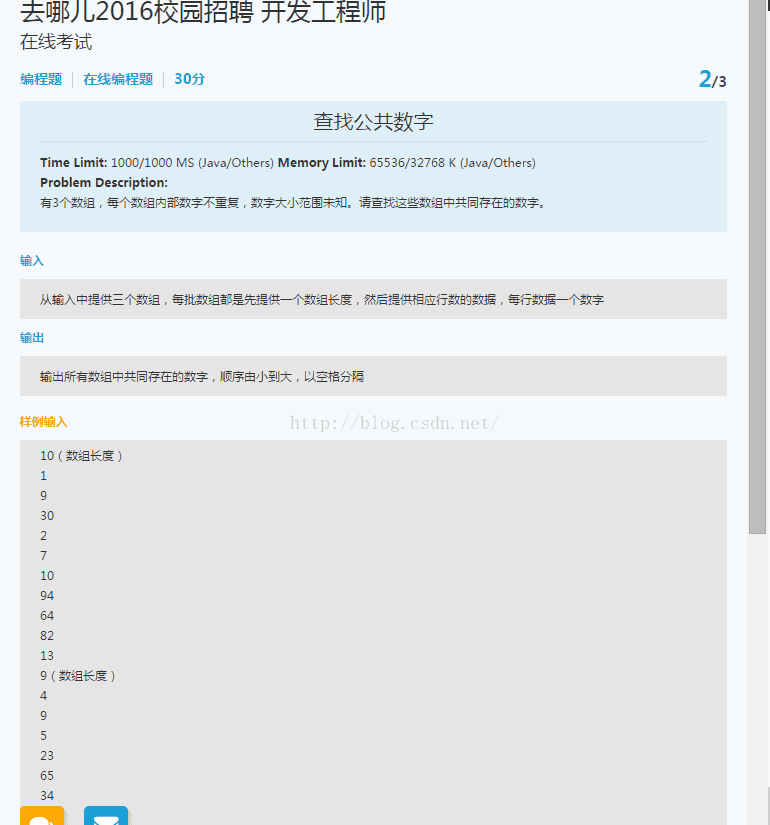
for(int i=0;i 13 去哪儿网笔试2016
下面这份代码测试通过100%,刚开始的时候,没有对三个数组进行排序,直接int[] array = new int[65536]是不正确的,后来对三个数组进行排序后,选出最大的值然后,int [] array = new int[max]正确
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public int searchPublic(List alist,List blist,List clist){
Collections.sort(alist,new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o2 - o1;
}
});
Collections.sort(blist,new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o2 - o1;
}
});
Collections.sort(clist,new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o2 - o1;
}
});
int max = alist.get(0)> blist.get(0)? alist.get(0):blist.get(0);
int maxx = max > clist.get(0)? max:clist.get(0);
int[] array = new int[maxx+1];
for(int i=0;i alist = new ArrayList(a);
for(int i=0;i blist = new ArrayList(b);
for(int i=0;i clist = new ArrayList(c);
for(int i=0;i 14 去哪儿笔试2016
代码,当时没有写出来,后面有时间更行ing
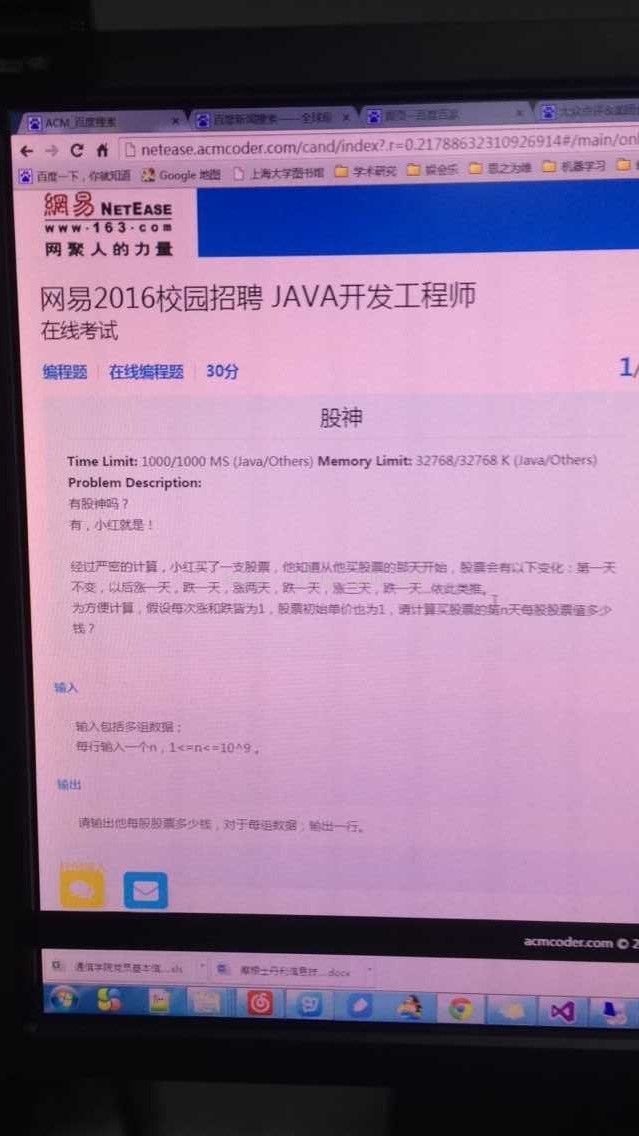
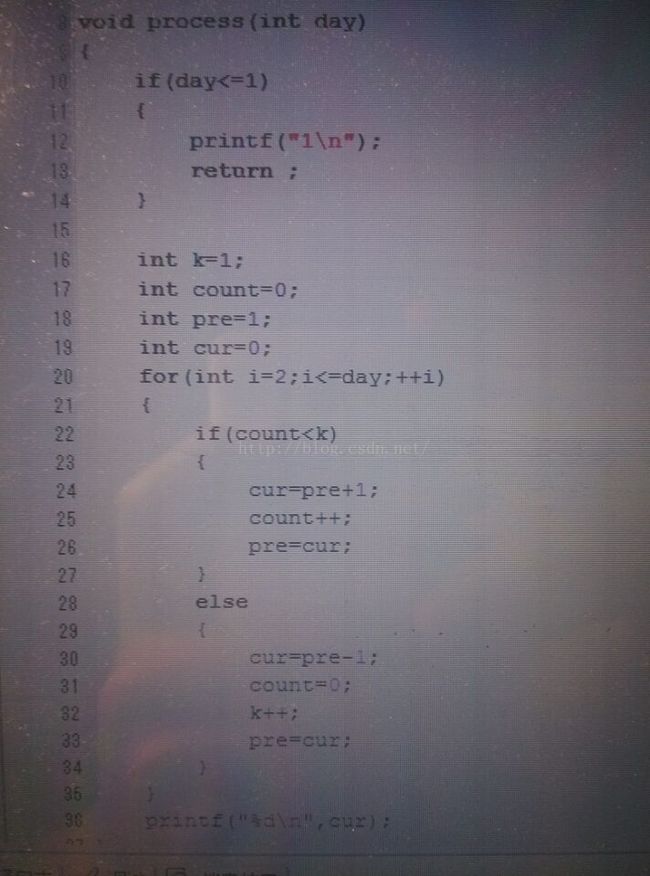
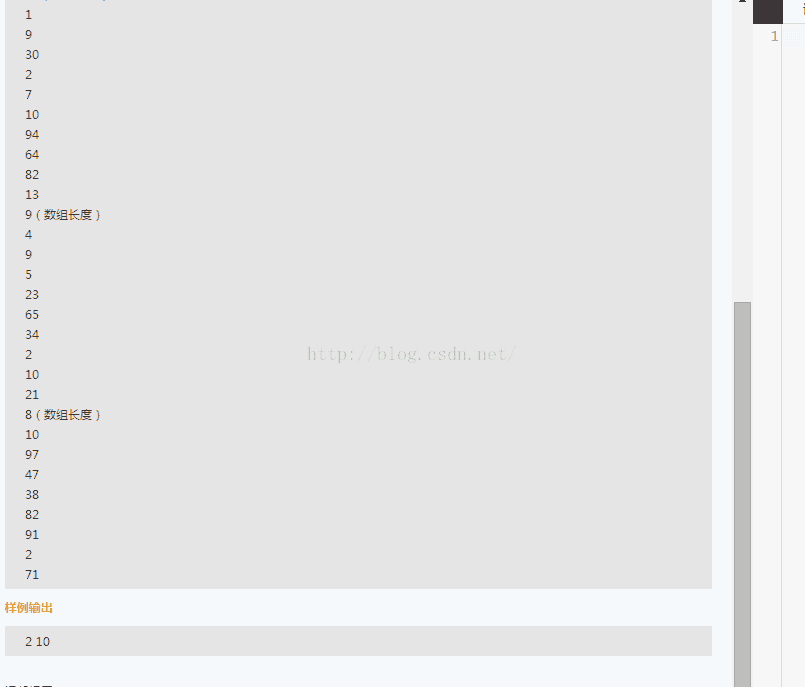
15 网易笔试2016
网易笔试,这次不知道为什么公司的网站就是登不上。然后找同学做的,不管结果咋样了,就算是经历一次吧。
这次网易的笔试的输入输出有点坑,不像其他笔试一样告诉你输入时多上行,而是没有告诉你输入是多上行数据,这样每输入一次完整数据就会有输出,并且一直检测输入,用while(cin.hasNext)
难度不大,主要是求了一个最大公约数:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while (cin.hasNext()){
int n = cin.nextInt();
int a = cin.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i< n;i++)
{
arr[i] = cin.nextInt();
}
int currenta = a;
for(int i = 0;i< n;i++)
{
if(currenta > arr[i])
{
currenta += arr[i];
}
else
currenta += gcd(arr[i],currenta);
}
System.out.println(currenta);
}
}
//求最大公约数
public static int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if(a < b){
return gcd(b,a);
}
if(b == 0){
return a;
}
else{
return gcd(a - b,b);
}
}
}