图片标注工具Labelme-简明使用教程
前言
记录Labelme的使用方法,方便快速上手使用。
labelme简介
LabelMe 可用于实例分割,语义分割,目标检测,分类任务的数据集标注工作。
在线标注版本
python版本
labelme官方文档
分类标注:Classification
目标检测标注:Object Detection
语义分割标注:Semantic Segmentation
实例分割标注:Instance Segmentation
视频标注:Video Annotation
其他形式标注:LabelMe Primitives
安装
所有操作在已经安装Anaconda环境下运行
1.安装pyqt5
pip install pyqt5 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
2.安装labelme
pip install labelme -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
3.安装完成后命令行启动labelme
labelme
使用
此处打开一个图片文件夹做示范:
1.点击左侧Open Dir选择需要标注的数据文件夹。
2.在顶部 edit 菜单栏中可选不同的标记方案,依次为:多边形(默认),矩形,圆、直线,点。
3.制作图像分割的数据,选择多边形,点击左侧的 create polygons ,回到图片,按下鼠标左键会生成一个点,完成标注后会形成一个标注区域,同时弹出labelme的框,键入标签名字,点击 OK或者回车完成标注。
1.如果需要更改标注的数据,可以选择左侧的编辑框,或者把鼠标移动到标签上,点击鼠标右键,可以选择编辑标签或者标注的名字。在编辑模式下,把鼠标移动到边界上,右键,可以增加点。
2.标注完成后点击Save保存。会在图片路径下生成同名的json文件。在目录下打开终端键入:
labelme_json_to_dataset <文件名>.json
会把生成的json转化成对应的数据文件:
*.png
info.yaml
label.png
label_names.txt
label_viz.png
常用命令
1.启动labelme的方式
# 直接打开labelme
labelme
# 打开某个文件夹,加载该文件夹下及其子文件夹下的所有图片
labelme path/to/imgfile/
# 直接打开指定的图片
labelme cat.1.jpg
# 标注保存为json文件同时自动关闭gui窗口
labelme cat.1.jpg -O cat.1.jpg.json
# 指定label list
labelme cat.1.jpg \
--labels cat,eye
# 或者传入文件形式的label list
--labels labels.txt
2.将json文件转换为image和label
# 在当前目录下生成一个文件夹cat_1_json
labelme_json_to_dataset cat.1.json
# 指定生成文件夹的名字为cat1
labelme_json_to_dataset cat.1.json -o cat1
3.可视化json文件
# 终端输入
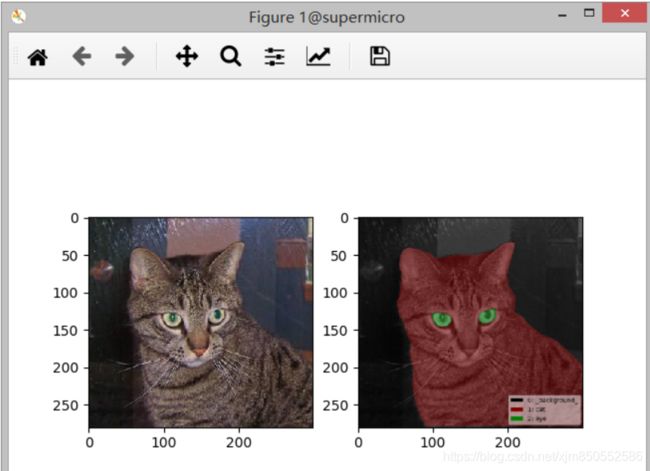
labelme_draw_json cat.1.json
4.生成VOC格式的标签数据
1.在目录下新建一个labels.txt文件,内容是分割的标签,默认内容设置如下:

2.新建一个labelme2voc.py文件。
内容可以从labelme工程目录下的labelme2voc.py文件拷贝过来,或者使用如下代码。
#!/usr/bin/env python
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import glob
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("input_dir", help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("output_dir", help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(
osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassVisualization")
)
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
class_names = []
class_name_to_id = {
}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
elif class_id == 0:
assert class_name == "_background_"
class_names.append(class_name)
class_names = tuple(class_names)
print("class_names:", class_names)
out_class_names_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "class_names.txt")
with open(out_class_names_file, "w") as f:
f.writelines("\n".join(class_names))
print("Saved class_names:", out_class_names_file)
for filename in glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json")):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
out_lbl_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass", base + ".npy"
)
out_png_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG", base + ".png"
)
if not args.noviz:
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir,
"SegmentationClassVisualization",
base + ".jpg",
)
with open(out_img_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(label_file.imageData)
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
lbl, _ = labelme.utils.shapes_to_label(
img_shape=img.shape,
shapes=label_file.shapes,
label_name_to_value=class_name_to_id,
)
labelme.utils.lblsave(out_png_file, lbl)
np.save(out_lbl_file, lbl)
if not args.noviz:
viz = imgviz.label2rgb(
label=lbl,
img=imgviz.rgb2gray(img),
font_size=15,
label_names=class_names,
loc="rb",
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.转换为voc数据格式
# 终端输入
python labelme2voc.py [图像路径] [voc文件夹名称] --labels [label list]
# 比如
python labelme2voc.py ./id_labelme/images ./id_labelme/target --labels labels.txt
在目录下会根据设定自动生成目标文件夹。文件夹下内容如下所示:

参考
labelme使用
深度学习图像标注工具-labelme