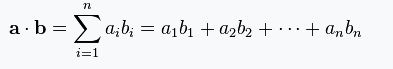【LeetCode】周赛纪录(二)第 190 场周赛20200524 检查单词前缀 定长子串中元音的最大数目 二叉树中的伪回文路径 两个子序列的最大点积
第190场周赛
-
- [5416. 检查单词是否为句中其他单词的前缀](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/check-if-a-word-occurs-as-a-prefix-of-any-word-in-a-sentence/)
-
- 题目描述:
- [5417. 定长子串中元音的最大数目](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-number-of-vowels-in-a-substring-of-given-length/)
-
- 题目描述:
- Solution
- [5418. 二叉树中的伪回文路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree/)
-
- 题目描述:
- Solution
- [5419. 两个子序列的最大点积](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/max-dot-product-of-two-subsequences/)
-
- 题目描述
- Solution
5416. 检查单词是否为句中其他单词的前缀
难度:简单
题目描述:
给你一个字符串 sentence 作为句子并指定检索词为 searchWord ,其中句子由若干用 单个空格 分隔的单词组成。
请你检查检索词 searchWord 是否为句子 sentence 中任意单词的前缀。
如果 searchWord 是某一个单词的前缀,则返回句子 sentence 中该单词所对应的下标(下标从 1 开始)。
如果 searchWord 是多个单词的前缀,则返回匹配的第一个单词的下标(最小下标)。
如果 searchWord 不是任何单词的前缀,则返回 -1 。
字符串 S 的 「前缀」是 S 的任何前导连续子字符串。
示例:
输入:sentence = "i love eating burger", searchWord = "burg"
输出:4
解释:"burg" 是 "burger" 的前缀,而 "burger" 是句子中第 4 个单词。
输入:sentence = "this problem is an easy problem", searchWord = "pro"
输出:2
解释:"pro" 是 "problem" 的前缀,而 "problem" 是句子中第 2 个也是第 6 个单词,但是应该返回最小下标 2 。
输入:sentence = "i am tired", searchWord = "you"
输出:-1
解释:"you" 不是句子中任何单词的前缀。
输入:sentence = "i use triple pillow", searchWord = "pill"
输出:4
输入:sentence = "hello from the other side", searchWord = "they"
输出:-1
提示:
1 <= sentence.length <= 100
1 <= searchWord.length <= 10
sentence 由小写英文字母和空格组成。
searchWord 由小写英文字母组成。
前缀就是紧密附着于词根的语素,中间不能插入其它成分,并且它的位置是固定的——-位于词根之前。(引用自 前缀_百度百科 )
自己一开始写的代码
class Solution {
public int isPrefixOfWord(String sentence, String searchWord) {
String[] str = sentence.split(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < str.length; i++){
String s = str[i];
//比较s和searchWord
boolean flag = true;
if(searchWord.length() > s.length()){
continue;
}
for(int k = 0, j = 0; k < searchWord.length(); k++, j++){
if(searchWord.charAt(k) != s.charAt(j)){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
//符合
if(flag == true){
return i+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
可以用startsWith
public int isPrefixOfWord(String sentence, String searchWord) {
String[] str = sentence.split(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < str.length; i++){
if(str[i].startsWith(searchWord)){
return i + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
5417. 定长子串中元音的最大数目
难度:中等
题目描述:
给你字符串 s 和整数 k 。
请返回字符串 s 中长度为 k 的单个子字符串中可能包含的最大元音字母数。
英文中的 元音字母 为(a, e, i, o, u)。
示例:
输入:s = "abciiidef", k = 3
输出:3
解释:子字符串 "iii" 包含 3 个元音字母。
输入:s = "aeiou", k = 2
输出:2
解释:任意长度为 2 的子字符串都包含 2 个元音字母。
输入:s = "leetcode", k = 3
输出:2
解释:"lee"、"eet" 和 "ode" 都包含 2 个元音字母。
输入:s = "rhythms", k = 4
输出:0
解释:字符串 s 中不含任何元音字母。
输入:s = "tryhard", k = 4
输出:1
Solution
滑动窗口。以k长度的窗口每次计算窗口内的元音字母数,然后更新最大数目max
class Solution {
public int maxVowels(String s, int k) {
int n = s.length();
if(s == null || n == 0) return 0;
int i = 0;
int j;
int count = 0;
//右边界先移到k为止 [0,k-1]
for(j = 0; j < k; j++){
if(isLegal(s.charAt(j))){
count++;
}
}
j--;
int max = count;
//i,j一起右移
while(j < s.length()-1){
if(isLegal(s.charAt(i))){
count--;
}
i++;
j++;
if(isLegal(s.charAt(j))){
count++;
}
max = Math.max(max, count);
}
return max;
}
public boolean isLegal(char c){
if(c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u'){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
5418. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
难度:中等
题目描述:
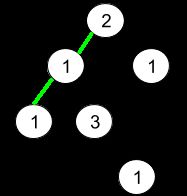
给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。
请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。
示例:
输入:root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
输出:2
解释:上图为给定的二叉树。总共有 3 条从根到叶子的路径:红色路径 [2,3,3] ,绿色路径 [2,1,1] 和路径 [2,3,1] 。
在这些路径中,只有红色和绿色的路径是伪回文路径,因为红色路径 [2,3,3] 存在回文排列 [3,2,3] ,绿色路径 [2,1,1] 存在回文排列 [1,2,1] 。
输入:root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
输出:1
解释:上图为给定二叉树。总共有 3 条从根到叶子的路径:绿色路径 [2,1,1] ,路径 [2,1,3,1] 和路径 [2,1] 。
这些路径中只有绿色路径是伪回文路径,因为 [2,1,1] 存在回文排列 [1,2,1] 。
输入:root = [9]
输出:1
Solution
-
思路一:
最开始的想法:先递归出所有的路径,再判断路径是不是伪回文的
-
找二叉树的路径,用递归,参考257. 二叉树的所有路径
-
判断伪回文:路径长度为偶数时,所有值的个数都要为偶数;路径长度为奇数时,只能有一个值个数为奇数,其他都是偶数
这样写最后一个用例超时了……所以不需要把所有的路径写出来再去遍历,要边递归边判断
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths (TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<String> paths = new LinkedList();
construct_paths(root,"",paths);
System.out.println(paths);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < paths.size(); i++){
String s = paths.get(i);
//统计每个字符个数
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int j = 0; j < s.length(); j++){
char c = s.charAt(j);
map.put(c, map.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
//分奇偶
boolean flag = true;
if(s.length() % 2 == 0){
for(Integer value : map.values()){
if(value % 2 == 0){
continue;
}else{
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag == true){
res++;
}
}else{
int odd = 0;
for(Integer value : map.values()){
if(value % 2 == 0){
continue;
}else{
odd++;
}
if(odd > 1){
//奇数个数大于1了,不合法
flag = false;
// break;
}
}
if(flag == true){
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public void construct_paths(TreeNode root, String path, LinkedList<String> paths){
if(root != null){
path += Integer.toString(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
paths.add(path);
}else{
construct_paths(root.left, path, paths);
construct_paths(root.right, path, paths);
}
}
}
}
-
思路二:
改进:
- 用异或来判断字符出现的次数
- 不用等所有路径全部写完了再判断回文,边写边判断
res当成变量穿进去的话一直输出为0?是传值传引用的问题吗?
必须把res写成全局变量来修改才能通过
//不通过
class Solution {
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths (TreeNode root) {
int res = 0;
int[] path = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(path, 0);
recur(root, path, res);
return res;
}
public void recur(TreeNode root, int[] path, int res){
if(root == null){
return;
}
path[root.val] ^= 1;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
int sum = 0;
for(int count : path){
sum += count;
}
if(sum <= 1){
res++;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
recur(root.left, path, res);
recur(root.right, path, res);
path[root.val] ^= 1;
}
}
//通过
class Solution {
int res;
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths (TreeNode root) {
res = 0;
int[] path = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(path, 0);
recur(root, path);
return res;
}
public void recur(TreeNode root, int[] path){
if(root == null){
return;
}
path[root.val] ^= 1;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
int sum = 0;
for(int count : path){
sum += count;
}
if(sum <= 1){
res++;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
recur(root.left, path);
recur(root.right, path);
path[root.val] ^= 1;
}
}
- 思路三:
用二进制bits来存每个数字出现的次数
Integer.bitCount()方法用于统计二进制中1的个数
class Solution {
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) {
return recur(root, 0);
}
public int recur(TreeNode root, int bits) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
bits ^= 1 << root.val;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return Integer.bitCount(bits) <= 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
int ans = recur(root.left, bits) + recur(root.right, bits);
return ans;
}
}
5419. 两个子序列的最大点积
难度:困难
题目描述
给你两个数组 nums1 和 nums2 。
请你返回 nums1 和 nums2 中两个长度相同的 非空 子序列的最大点积。
数组的非空子序列是通过删除原数组中某些元素(可能一个也不删除)后剩余数字组成的序列,但不能改变数字间相对顺序。比方说,[2,3,5] 是 [1,2,3,4,5] 的一个子序列而 [1,5,3] 不是。
输入:nums1 = [2,1,-2,5], nums2 = [3,0,-6]
输出:18
解释:从 nums1 中得到子序列 [2,-2] ,从 nums2 中得到子序列 [3,-6] 。
它们的点积为 (2*3 + (-2)*(-6)) = 18 。
输入:nums1 = [3,-2], nums2 = [2,-6,7]
输出:21
解释:从 nums1 中得到子序列 [3] ,从 nums2 中得到子序列 [7] 。
它们的点积为 (3*7) = 21 。
输入:nums1 = [-1,-1], nums2 = [1,1]
输出:-1
解释:从 nums1 中得到子序列 [-1] ,从 nums2 中得到子序列 [1] 。
它们的点积为 -1 。
点积:
定义 a = [a1, a2,…, an] 和 b = [b1, b2,…, bn] 的点积为:
这里的 Σ 指示总和符号。
Solution
动态规划。
-
状态:假设
dp[i][j]是num1取第i个数,num2取第j个数时能够取得的最大点积值,即:取到nums1[i],nums2[j]时的最大值,但nums1[i],nums2[j]不一定要使用 -
初始化:
dp[0][0]一定等于nums1[0] x nums2[0] -
状态转移方程:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j-1] + nums1[i] x nums2[j], nums1[i] x nums2[j], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])解释:
- 当
nums1[i] x nums2[j]<0的时候,不加nums1[i] x nums2[j],此时就是max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) - 加
nums1[i] x nums2[j]的时候,分保留dp[i-1][j-1]和抛弃dp[i-1][j-1],即max(dp[i-1][j-1] + nums1[i] x nums2[j], nums1[i] x nums2[j])
- 当
class Solution {
public int maxDotProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int len1 = nums1.length;
int len2 = nums2.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len1][len2];
//初始化
dp[0][0] = nums1[0] * nums2[0];//非空
//dp[i][0]
for(int i = 1; i < len1; i++){
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i-1][0], nums1[i] * nums2[0]);
}
//dp[0][j]
for(int j = 1; j < len2; j++){
dp[0][j] = Math.max(dp[0][j-1], nums1[0] * nums2[j]);
}
//dp[i][j]
for(int i = 1; i < len1; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < len2; j++){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(Math.max(nums1[i]*nums2[j], dp[i-1][j-1]+nums1[i]*nums2[j]), Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]));
}
}
return dp[len1-1][len2-1];
}
}