java练习答案总合
-
变量和运算符
1、已知a,b均是整型变量,写出将a,b两个变量中的值互换的程序。(知识点:变量和运算符综合应用)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=10;
int b=20;
int temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
System.out.println("a:"+a+"b:"+b);
}
第二种方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=10;
int b=20;
a=a+b;
b=a-b;
a=a-b;
System.out.println("a:"+a+"b:"+b);
}
2、给定一个0~1000的整数,求各位数的和,例如345的结果是3+4+5=12注:分解数字既可以先除后模也可以先模后除(知识点:变量和运算符综合应用)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=789;
int i1=i%10;
int i2=i/100;
int i3=i%100/10;
System.out.println(i1+i2+i3);
}
3、给定一个任意的大写字母A-Z,转换成小写字母。(知识点:变量和运算符)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Char(“90”) Z
// Char(“122”) z
char c1='Z';
int c2=c1+32;
// char c2=c1+32;
System.out.println((char)c2);
}
-
流程控制语句
1、假设有整型变量x,判断x是否为偶数,若为偶数,则在控制台上打印“输入的数值是偶数”。
无论x是否为偶数,最后都要在控制台上输出x的值
int x = 4;
if ((x % 2) == 0)
{
System.out.println("输入的数值是偶数");
}
System.out.println("x的值为:"+ x);
2、有一个数字为45327,判断该数字是否能被13整除,是否能被17整除。
int i=45327;
if(i%13==0){
System.out.println("能被13整除");
}else if(i%17==0) {
System.out.println("能被17整除");
}else {
System.out.println("都不能被整除");
}//显示:都不能被整除
3、判断2064年是不是闰年。
闰年判断规则:
能被400整除的是闰年
能被100整除,不能被400整除的不是闰年
能被4整除,不能被100整除的是闰年
其他的不是闰年
int year=2064;
if(year%400==0 || year%100==0 && year%400!=0 || year%4==0 && year%100!=0){
System.out.println("是闰年");
}else {
System.out.println("不是闰年");
}
//另一种写法
int year = 2064;
if(year%400==0){
System.out.println(year+"是闰年");
}else if((year%4==0)&&(year%100!=0)){
System.out.println(year+"是闰年");
}else{
System.out.println(year+"不是闰年");
}
}
4、有两个整型变量x,y,请编写代码在控制台上输出x与y中值较大的那个数。
int x = 5;
int y = 6;
if(x>y){
System.out.println(x);
}else{
System.out.println(y);
}
}
- for循环
1、用for循环改写从1到100的所有奇数相加的和
int sum=0;
for( int x=1;x<=100;x++){
if(x%2!=0){
sum+=x;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
2、循环得到用户从控制台输入的5个整数,该整数为用户购买商品的价格,计算用户一共需要花费的总金额。
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个商品价格:");
int x=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
sum+=x;
}
System.out.println(sum);
3、随机产生一个10以内的正整数,用户循环输入三个整数,如果用户输入的整数包含随机数,输出“猜对了”;反之,输出“没猜到”。
例如:
随机数为4,用户输入数为:2,3,4。输出:猜对了
随机数为4,用户输入数为:1,2,3。输出:没猜到
int ran = new Random().nextInt(10);
boolean flag = false;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个猜测数字(0--9):");
int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
if(x == ran){
flag = true;
}
}
if(flag){
System.out.println("猜对了,随机数是:"+ran);
}else{
System.out.println("没猜到,随机数是:"+ran);
}
}
#### switch语句
1、如果月份month为1—12的一个月份,输出该月份的天数;如果数字不符合,输出“错误的月份”。
1、3、5、7、8、10、12月天数为31
2月天数为28
4、6、9、11月天数为30
```java
int month =2;
switch(month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
System.out.println("为31天");
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
System.out.println("为30天");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("为28天");
break;
default:
System.out.println("错误的月份");
}
// 显示:为28天
String name= new Scanner(System.in).next();
switch(name) {
case"可乐":
System.out.println("可乐:2.5元/瓶");
break;
case"薯片":
System.out.println("薯片:12.5元/包");
break;
case"咖啡":
System.out.println("咖啡:45元/瓶");
break;
default:
System.out.println("没有该产品!");
}
- while和do while循环
1、计算1+2+3+…+100的和(提示利用while语句)
int x=1;
int sum=0;
while(x<=100) {
sum+=x;
x++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
计算1+2+3+…+100的和(用do while 循环完成)
// 使用do while循环做出
int x=0;
int sum=0;
do {
sum+=x;
System.out.println(sum);
x++;
}while(x<=100);
2、计算从1到100的所有奇数相加(提示利用while语句)
int x=1;
int sum=0;
while(x<=100) {
if(x%2!=0) {
sum+=x;
}
x++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
// for循环
for(int x=1;x<=100;x+=2) {
sum=sum+x;
}
System.out.println("和为:"+sum);
- 循环中断
1、用户输入数字,如果是0,退出程序,界面如下:
for(;;){
System.out.println("**********kg跨境电商交易平台**********");
System.out.println("* *");
System.out.println("* 1、制造商资料管理 *");
System.out.println("* 2、销售商品品牌管理 *");
System.out.println("* 3、商品类别管理 *");
System.out.println("* 4、商品详细信息管理 *");
System.out.println("* 0、退出程序 *");
System.out.println("* *");
System.out.println("*********************************");
System.out.print("请输入数字选择操作:");
int input = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
if(input == 0){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,再见!!");
break;
}
}
2、得到用户从控制台输入的五个正整数,该整数为用户购买商品的价格,如果用户输入整数为0或负数,不计入统计,结束输入后计算用户一共需要花费的总金额。
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;;){
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个商品价格:");
int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
if(x<=0){
System.out.println("价格错误,请再次输入");
}else{
sum += x;
i++;
}
if(i>=5){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("总价格为:"+sum);
// 随机产生一个10以内的正整数,用户循环输入三个整数,如果用户输入的整数包含随机数,输出“猜对了”;反之,输出“没猜到”。
// 例如:
// 随机数为4,用户输入数为:2,3,4。输出:猜对了
// 随机数为4,用户输入数为:1,2,3。输出:没猜到
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random cs=new Random();
int i=cs.nextInt(10);
int a,b,c;
System.out.println("请输入三个0-9的数字:");
Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in);
a=x.nextInt();
b=x.nextInt();
c=x.nextInt();
if(a==i || b==i || c==i) {
System.out.println("猜对了");
}else {
System.out.println("猜错了");
}
System.out.println("随机数为:"+i);
}
1、企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。利润低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%;利润高于10万元,低于或等于20万元时,高于10万元的部分,可提成7.5%;高于20万,低于或等于40万时,高于20万元的部分,可提成5%;高于40万,低于或等于60万时,高于40万元的部分,可提成3%;高于60万,低于或等于100万时,高于60万元的部分,可提成1.5%,高于100万元时,超过100万元的部分按1%提成,输入一个整数变量为当月利润,求应发放奖金总数?(知识点:条件语句) [必做题]
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入当月利润:");
double profit=sc.nextDouble();
double bonus1=0.0;
double bonus2=0.0;
double bonus3=0.0;
double bonus4=0.0;
double bonus5=0.0;
double bonus6=0.0;
if(profit<=10) {
bonus1=profit*0.1;
}
if(profit>10 && profit <=20) {
bonus2=(profit-10)*0.75;
profit=10;
}
if(profit>20 && profit <=40) {
bonus3=(profit-20)*0.05;
profit=60;
}
if(profit>40 && profit <=60) {
bonus4=(profit-40)*0.05;
profit=40;
}
if(profit>60 && profit <=100) {
bonus5=(profit-60)*0.015;
profit=60;
}
if(profit>100) {
bonus6=(profit-100)*0.01;
profit=100;
}
double bonus=bonus1+bonus2+bonus3+bonus4+bonus5+bonus6;
System.out.println("应发奖金总数是:"+bonus);
}
2、输入一个成绩a,使用switch结构求出a的等级。A:90-100,B:80-89,C:70-79,D:60-69,E:0~59(知识点:条件语句switch)[必做题]
public static void main(String[] args) {
int results=100;
int level=results/10;
switch(level) {
case 6:
System.out.println("等级为D");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("等级为C");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("等级为B");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
System.out.println("等级为A");
break;
default:
System.out.println("等级为E");
}```
3、输入一个数字,判断是一个奇数还是偶数(知识点:条件语句) [必做题]
```java
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=7;
if(i%2!=0) {
System.out.println("这是奇数");
}else {
System.out.println("这是偶数");
}
}
4、编写程序, 判断一个随机变量x的值,如果是1,输出x=1,如果是5,输出x=5,如果是 10,输出x=10,除了以上几个值,都输出x=none。(知识点:条件语句)
5、判断一个随机整数是否能被5和6同时整除(打印能被5和6整除),或只能被5整除(打印能被5整除),或只能被6整除,(打印能被6整除),不能被5或6整除,(打印不能被5或6整除)(知识点:条件语句)
6、输入一个年份,判断这个年份是否是闰年(知识点:条件、循环语句)
7、输入一个0~100的分数,如果不是0~100之间,打印分数无效,根据分数等级打印A,B,C,D,E(知识点:条件语句if elseif)
8、输入三个整数x,y,z,请把这三个数由小到大输出(知识点:条件语句) }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入三位数");
int a=sc.nextInt();
int b=sc.nextInt();
int c=sc.nextInt();
int temp;
if(a>b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if(b>c) {
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if(a>b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
System.out.println("从小到大输出为:"+a+","+b+","+c);
}
9、有一个不多于5位的正整数,求它是几位数,分别打印出每一位数字。(知识点:条件语句)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a=sc.nextInt();
if(a/10000<10) {
if(a/10000>0) {
System.out.println("五位数");
}else if(a/1000>0) {
System.out.println("四位数");
}else if(a/100>0) {
System.out.println("三位数");
}else if(a/10>0) {
System.out.println("二位数");
}else
System.out.println("个位数");
}else {
System.out.println("输入的数多于5位");
}
}
1、假设某员工今年的年薪是30000元,年薪的年增长率6%。编写一个Java应用程序计算该员工10年后的年薪,并统计未来10年(从今年算起)总收入。(知识点:循环语句for)
2、猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不瘾,又多吃了一个,第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下的一半零一个。到第10天早上想再吃时,见只剩下一个桃子了。求第一天共摘了多少。(知识点:循环语句 while)
3、编写一个程序,计算邮局汇款的汇费。如果汇款金额小于100元,汇费为一元,如果金额在100元与5000元之间,按1%收取汇费,如果金额大于5000元,汇费为50元。汇款金额由命令行输入。(知识点:条件语句)
4、分别使用for循环,while循环,do循环求1到100之间所有能被3整除的整数的和。(知识点:循环语句)
5、输出0-9之间的数,但是不包括5。
6、编写一个程序,求整数n的阶乘,例如5的阶乘是12345
7、编写一个程序,找出小于300的所有质数(素数) 只能被1和本身整除的数 1既不是素数,也不是合数 2是素数
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=2;i<300;i++) {
// 一开始规定每个数都为素数
boolean flag=true;
// 如果i为2输出i 因为2是素数
if(i==2) {
System.out.println(i);
continue;
}
for(int j=2;j<i;j++) {
// 如果能被其他数整除,就不是素数
if(i%j==0) {
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
7、编写一个程序,找出大于200的最小的质数
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=200;i<300;i++) {
// 一开始规定每个数都为素数
boolean flag=true;
for(int j=2;j<i;j++) {
// 如果能被其他数整除,就不是素数
if(i%j==0) {
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println(i);
break;
}
}
}
8、由命令行输入一个 4位整数,求将该数反转以后的数,如原数为1234,反转后的数位4321
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个四位整数:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=sc.nextInt();
if(num>=10000 || num<1000) {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入!");
}
int a=num%10;
int b=num%100/10;
int c=num/100%10;
int d=num/1000;
System.out.println(a+""+b+""+c+""+d+"");
}
####数组
编写一个长度为5的整型数组,每个元素赋值为0-10的随机整数,遍历该数组,输出每个元素
Random r = new Random();
int[] a=new int[5];
for(int b =0;b<a.length;b++) {
a[b] =r.nextInt(10)+1;
}
int temp;
for(int c =0;c<a.length-1;c++) {
for(int d=0;d<a.length-c-1;d++) {
if(a[d]>a[d+1]) {
temp=a[d];
a[d]=a[d+1];
a[d+1]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
for(int e:a) {
System.out.print(e+" ");
}
从键盘输入班级学员成绩,计算全班学员的平均分
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arry1=new int[5]; //成绩数组
int sum=0; //成绩总和
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入5位学生的成绩:");
for(int x=0;x<arry1.length;x++) {
arry1[x]=sc.nextInt();
sum=sum+arry1[x];
}
System.out.println("平均分是:"+sum/arry1.length);
}
从键盘输入班级学员成绩,找出全班学员的最高分
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arry1=new int[5]; //成绩数
int max=0; //最高成绩
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入5位学生的成绩:");
for(int x=0;x<arry1.length;x++) {
arry1[x]=sc.nextInt();
if(max<arry1[x]) {
max=arry1[x];
}
}
System.out.println("最高分是:"+max);
}
从键盘输入班级学员成绩,计算全班学员每科的平均分
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arry1=new int[3][5]; //成绩数组,3科5人
int[] sum=new int[3]; //每科成绩总和
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<arry1.length;i++) {
System.out.println("请输入5位学生的第"+(i+1)+"科成绩:");
for(int j=0;j<arry1[i].length;j++) {
arry1[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
sum[i]=sum[i]+arry1[i][j]; //成绩累加
}
}
for(int i=0;i<sum.length;i++) {
System.out.print("第"+(i+1)+"科的平均分是:");
System.out.println((double)sum[i]/arry1[i].length);
}
}
1、已知两个一维数组:{1,2,3,4,5}和{6,7,8},将这两个一维数组合并成一个一维数组{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}。
2、生成一个4*6的二维整型数组,使用随机数填充,遍历输出该数组的所有值,并且找出最大值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
int[][] arry1=new int[4][6];
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<arry1.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arry1[i].length;j++) {
arry1[i][j]=r.nextInt(100);
}
}
for(int[] k:arry1) {
for(int t:k) {
if(t>max) {
max=t;
}
System.out.println(t+",");
}
}
System.out.println("最大"+max);
面向对象编程基础
定义一个矩形类Rectangle: [必做题]
2.1 定义三个方法:getArea()求面积、getPer()求周长,showAll()分别在控制台输出长、宽、面积、周长。
2.2 有2个属性:长length、宽width
2.3 通过构造方法Rectangle(int width, int length),分别给两个属性赋值
2.4 创建一个Rectangle对象,并输出相关信息
public class Rectangle {
double length;
double width;
public Rectangle(int width,int length) {
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public double getArea() {
return length*width;
}
public double getPer() {
return (length+width)*2;
}
public void showAll() {
System.out.println("长:"+length+"宽:"+"面积:"+getArea()+"周长:"+getPer());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r1=new Rectangle(2,3);
r1.showAll();
}
}
设计一个类Student,该类包括姓名、学号和成绩。设计一个方法,按照成绩从高到低的顺序输出姓名、学号和成绩信息。
public class xiaoxuesheng {
String name;
int stuNo;
double grade;
public xiaoxuesheng(String name, int stuNo, double grade) {
this.name = name;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.grade = grade;
}
public xiaoxuesheng() {
}
public String toString() {
return "xiaoxuesheng [name=" + name + ", stuNo=" + stuNo + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
xiaoxuesheng x1=new xiaoxuesheng("xiaoming",1,20);
xiaoxuesheng x2=new xiaoxuesheng("xiaohong",1,100);
xiaoxuesheng x3=new xiaoxuesheng("xiaofang",1,80);
xiaoxuesheng[] xx= {
x1,x2,x3};
// for(xiaoxuesheng xiaoxu:xx) {
// System.out.println(xiaoxu.toString());
// }
for(int i=1;i<xx.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<xx.length-1;j++) {
if(xx[j].grade<xx[j+1].grade) {
xiaoxuesheng x=xx[j];
xx[j]=xx[j+1];
xx[j+1]=x;
}
}
}
// 将排好序的数组输出
for(xiaoxuesheng xiaoxu:xx) {
System.out.println(xiaoxu.toString());
}
}
}
面向对象高级特性
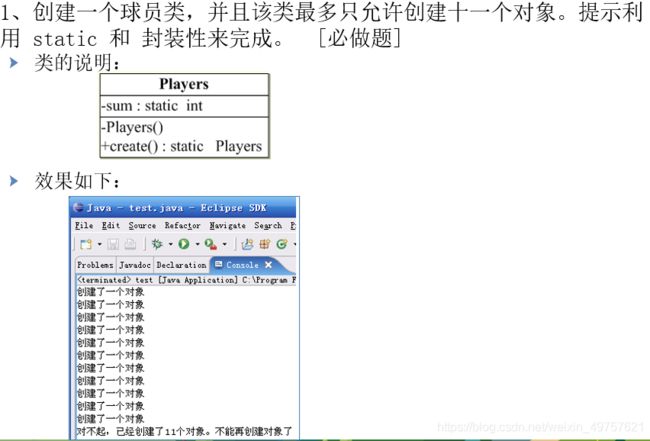
public class Players {
private static int sum;
private Players() {
}
public static Players create() {
if(sum<11) {
sum++;
// return new Players();
System.out.print("创建了一个对象");
}else {
System.out.print ("对不起,已经创建了11个对象。不能再创建对象了");
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<12;i++) {
System.out.print(Players.create());
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public class Players {
private static int sum;
private Players(){
}
public static Players create()
{
sum = 1;
Players players = null;
while(sum <= 11)
{
Players players1 = new Players();
System.out.println("创建了"+sum+"个对象");
sum++;
}
System.out.println("对不起,已经创建了11个对象,不能再创建对象了");
return players;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Players.create();
}
}
定义一个汽车类Vehicle,
属性包括:汽车品牌brand(String类型)、颜色color(String类型)和速度speed(double类型)。
至少提供一个有参的构造方法(要求品牌和颜色可以初始化为任意值,但速度的初始值必须为0)。
为属性提供访问器方法。注意:汽车品牌一旦初始化之后不能修改。
定义一个一般方法run(),用打印语句描述汽车奔跑的功能
在main方法中创建一个品牌为“benz”、颜色为“black”的汽车。
定义一个汽车类Vehicle,
属性包括:汽车品牌brand(String类型)、颜色color(String类型)和速度speed(double类型)。
至少提供一个有参的构造方法(要求品牌和颜色可以初始化为任意值,但速度的初始值必须为0)。
为属性提供访问器方法。注意:汽车品牌一旦初始化之后不能修改。
定义一个一般方法run(),用打印语句描述汽车奔跑的功能
在main方法中创建一个品牌为“benz”、颜色为“black”的汽车。
public class Vehicle {
String brand;
String color;
double speed;
public Vehicle(){
}
public Vehicle(String brand, String color, double speed) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
this.speed = 0;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public double getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
// 如果品牌为null 可以修改
if(this.brand==null) {
this.brand = brand;
}else {
System.out.println("不能修改已经初始化的品牌");
}
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void setSpeed(double speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(color+"的"+brand+"牌汽车使用"+speed+"速度奔跑在马路上");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle benz=new Vehicle("brand", "color", 999);
benz.run();
}
定义一个Vehicle类的子类轿车类Car,要求如下:
轿车有自己的属性载人数loader(int 类型)。
提供该类初始化属性的构造方法。
重新定义run(),用打印语句描述轿车奔跑的功能。
在main方法中创建一个品牌为“Honda”、颜色为“red”,载人数为2人的轿车。
public class Car extends Vehicle{
int loader;
public Car() {
}
public Car(int loader,String brand, String color, double speed) {
super(brand, color, speed);
this.loader=loader;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(color+"的"+brand+"牌汽车使用"+speed+"速度奔跑在马路上载人数为:"+loader);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c=new Car(2,"Honda","red",99);
c.run();
}
}
演示接口和类的关系
有类图为:
编写一个Student类,并创建一个测试方法,测试Student类
要求:
该类继承了Person类,并实现了Consumer接口
该类具有String类型的属性school
并有一个study方法,在该方法中,系统可打印出学生在那所学校学习
Student
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public class Student extends Person implements Consumer {
private String school;
public Student(String school,String name,int age,String sex){
super(name,age,sex);
this.school=school;
}
public void study() {
System.out.println(this.school+","+this.getName()+","+this.getAge()+","+this.getSex());
}
public void useCredit() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s=new Student("某某学校", "小明", 20, "男");
s.study();
}
}
Person
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Person(String name, int age, String sex) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
public void getInfo() {
}
public void sayHello() {
}
}
Consumer
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public interface Consumer {
public void useCredit();
}
面向对象高级特性
4、 Cola公司的雇员分为以下若干类:(知识点:多态)
4.1 ColaEmployee :这是所有员工总的父类,属性:员工的姓名,员工的生日月份。方法:getSalary(int month) 根据参数月份来确定工资,如果该月员工过生日,则公司会额外奖励100 元。
4.2 SalariedEmployee : ColaEmployee 的子类,拿固定工资的员工。属性:月薪
4.3 HourlyEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,按小时拿工资的员工,每月工作超出160 小时的部分按照1.5 倍工资发放。属性:每小时的工资、每月工作的小时数
4.4 SalesEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,销售人员,工资由月销售额和提成率决定。属性:月销售额、提成率
4.5 定义一个类Company,在该类中写一个方法,调用该方法可以打印出某月某个员工的工资数额,写一个测试类TestCompany,在main方法,把若干各种类型的员工放在一个ColaEmployee 数组里,并单元出数组中每个员工当月的工资。
ColaEmployee
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public class ColaEmployee {
String name;
int month;
public ColaEmployee() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public ColaEmployee(String name, int month) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.month = month;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
/**
* this.month:员工的生日
* @param month 当前月份
* @return
*/
public int getSalary(int month) {
if(this.month==month) {
return 100;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
}
Company.java
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public class Company {
public static void getResult(ColaEmployee e) {
// 怎么知道是什么样的员工
if(e instanceof SalariedEmployee) {
System.out.println("计算固定工资员工的工资");
// 向下塑型
SalariedEmployee se=(SalariedEmployee)e;
System.out.println(se.getName()+"的工资是"+(se.getMonthSal()+se.getSalary(7)));
}else if(e instanceof SalesEmployee){
System.out.println("计算销售员工的工资");
SalesEmployee se=(SalesEmployee)e;
// 销售工资
double sal=se.getMonthSales()*se.getRate()+se.getSalary(7);
System.out.println(se.getName()+"的工资是:"+sal);
}else {
System.out.println("计算小时工的工资");
HourlyEmployee se=(HourlyEmployee)e;
// 小时工工资
double sal=0;
if(se.getHour()<=160){
sal=se.getHour()*se.getHourSal();
}else {
sal=(se.getHour()-160)*1.5*se.getHourSal()+16*se.getHourSal();
}
System.out.println(se.getName()+"的工资是:"+sal);
}
}
}
HourlyEmployee.java
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
/**
* 小时工
* @author icekingdom
*
*/
public class HourlyEmployee extends ColaEmployee{
double hourSal; //每小时工资
double hour; //每个月工作小时数
public HourlyEmployee() {
super();
}
public HourlyEmployee(double hourSal,double hour,String name, int month) {
super(name, month);
this.hourSal=hourSal;
this.hour=hour;
}
public double getHourSal() {
return hourSal;
}
public void setHourSal(double hourSal) {
this.hourSal = hourSal;
}
public double getHour() {
return hour;
}
public void setHour(double hour) {
this.hour = hour;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HourlyEmployee [hourSal=" + hourSal + ", hour=" + hour + ", name=" + name + ", month=" + month + "]";
}
}
SalariedEmployee
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
/**
* 固定工资的员工
* @author icekingdom
*
*/
public class SalariedEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
double monthSal;//月薪
public SalariedEmployee() {
}
public SalariedEmployee(double monthSal,String name, int month) {
super(name, month);
this.monthSal=monthSal;
}
public double getMonthSal() {
return monthSal;
}
public void setMonthSal(double monthSal) {
this.monthSal = monthSal;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SalariedEmployee [monthSal=" + monthSal + ", name=" + name + ", month=" + month + "]";
}
}
SalesEmployee.java
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
/**
* 销售员工
* @author icekingdom
*
*/
public class SalesEmployee extends ColaEmployee{
// 月销售额
double monthSales;
// 提成率
double rate;
public SalesEmployee() {
super();
}
public SalesEmployee(double monthSales,double rate,String name, int month) {
super(name, month);
this.monthSales=monthSales;
this.rate=rate;
}
public double getMonthSales() {
return monthSales;
}
public void setMonthSales(double monthSales) {
this.monthSales = monthSales;
}
public double getRate() {
return rate;
}
public void setRate(double rate) {
this.rate = rate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SalesEmployee [monthSales=" + monthSales + ", rate=" + rate + ", name=" + name + ", month=" + month + "]";
}
}
TestCompany.java
package com.nesoft.javase.practice;
public class TestCompany {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SalariedEmployee emp0=new SalariedEmployee(10000, "lisi", 7);
SalesEmployee emp1=new SalesEmployee(200000,0.1,"zhangsan",6);
HourlyEmployee emp2=new HourlyEmployee(40, 240, "wangwu",5);
ColaEmployee[] emps= {
emp0,emp1,emp2};
for(ColaEmployee e:emps) {
Company.getResult(e);
}
}
}
工具类
3、分别在控制台输入字符串和子字符串,并计算字符串中子字符串出现的次数。 [选做题]
第一种做法
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入源字符串:");
String source=sc.nextLine(); // eqyurqiujeqipikkoeq
System.out.println("请输入子字符串:");
String dest=sc.nextLine(); // eq
// int num=0;
// int index=0;
// for(int i=0;i
// if((index=source.indexOf(dest))!=-1) {
// source=source.substring(index+dest.length());
// num++;
// }
// }
// System.out.println(num);
第二种做法
int num=0;//统计
int index=0;//开始查询的索引
for(int i=0;i<source.length();i++) {
if((index=source.indexOf(dest, index))!=-1) {
num++;
index=index+dest.length();
}else {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}
2、编写一个程序,实现从命令行参数输入一字符串,统计该字符串中字符“e”出现的次数。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一串字符串:");
String str = sc.nextLine();
STR(str);
}
private static void STR(String str) {
String str1 = "e";
int a = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < str.length();i++){
if (str.charAt(i) == 'e'){
a++;
}
}
System.out.println("字符串中e出现"+a+"次");
}
}
4、编写一个程序,实现从命令行参数输入一字符串,统计该字符串中字母出现的次数。
Scanner aa=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个回文数");
String str=aa.nextLine();
if(str.equals(new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString())) {
System.out.println("是回文数");
}else {
System.out.println("不是回文数");
}