李航《统计学习方法》第2版 第2章课后习题答案
习题2.1
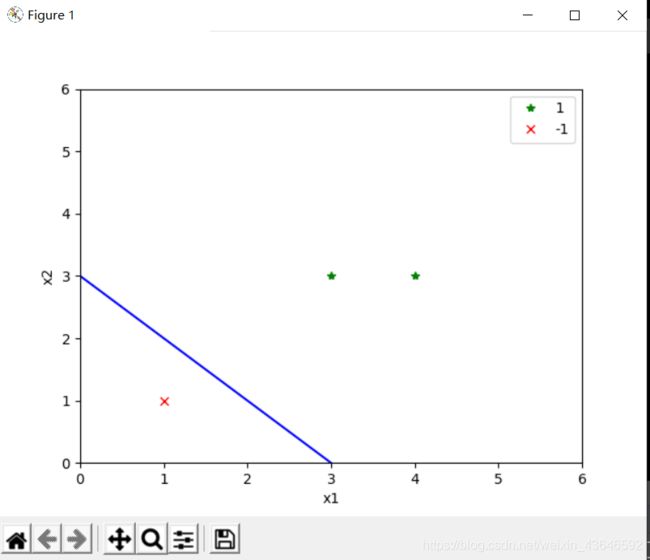
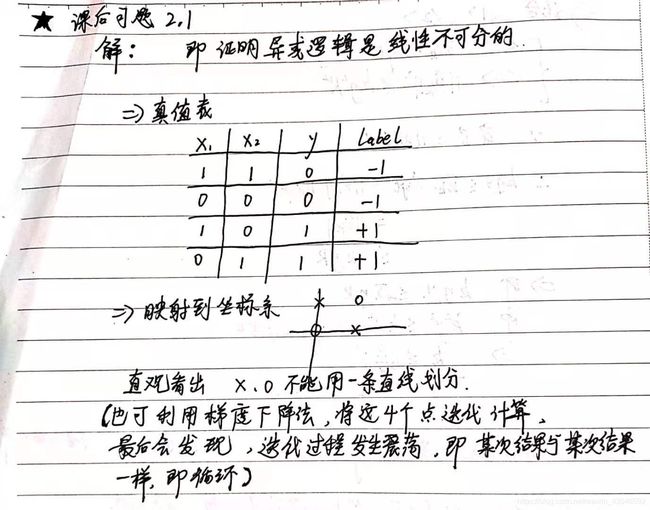
题目:Minsky与Papert指出:感知机因为是线性模型,所以不能表示复杂的函数,如异或(XOR),验证感知机为什么不能表示异或。
习题2.2
题目:模仿例题2.1,构建从训练数据集求解感知机模型的例子。
解:这里用python代码分别实现一下感知机学习算法的原始形式与对偶形式
原始形式:
"""
感知机(原始形式):实现书本P40页 例题2.1
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class MyPerceptron():
def __init__(self):
# 因为w的维度与x一致,所以先不定义为固定维度
self.w = None
self.b = 0
self.lr = 1
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
self.w = np.zeros(x_train.shape[1])
i=0
while i < x_train.shape[0]:
x = x_train[i]
y = y_train[i]
#若为误分类点则更新参数,重新遍历样本集
if y*(np.dot(self.w,x) + self.b) <= 0:
self.w = self.w + self.lr * np.dot(y,x)
self.b = self.b + self.lr * y
i=0
else:
i += 1
def draw(X, w, b):
# 生产分离超平面上的两点
X_new = np.array([0,6])
y_predict = -(b + w[0] * X_new) / w[1]
# 绘制训练数据集的散点图
plt.plot(X[:2, 0], X[:2, 1], "g*", label="1")
plt.plot(X[2:, 0], X[2:, 1], "rx", label="-1")
# 绘制分离超平面
plt.plot(X_new, y_predict, "b-")
# 设置两坐标轴起止值
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 6])
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def main():
x_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([1, 1, -1])
Perceptron = MyPerceptron()
Perceptron.fit(x_train, y)
draw(x_train, Perceptron.w, Perceptron.b)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
对偶形式:
"""
感知机(对偶形式):实现书本P40页 例题2.1
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class MyPerceptron():
def __init__(self):
# 因为w的维度与x一致,所以先不定义为固定维度
self.a = None
self.w = None
self.b = 0
self.lr = 1
def fit(self, x_train, y_train, Gram_Matrix):
self.a = np.zeros(x_train.shape[0])
i=0
while i < x_train.shape[0]:
x = x_train[i]
y = y_train[i]
#若为误分类点则更新参数,重新遍历样本集
if y*(np.sum(self.a*y_train*Gram_Matrix[:,i])+self.b) <= 0:
self.a[i] = self.a[i] + self.lr
self.b = self.b + self.lr*y
i = 0
else:
i += 1
#因为看公式可以知道y_train与self.a是对应位置相乘,他们与x_train是矩阵乘法
#所以将x_train转换为矩阵(array中的*代表对应位置相乘,而mat中的*为矩阵乘法)
self.w = y_train * self.a * np.mat(x_train)
#这里修改下w维度,为了和原始形式程序中的draw函数统一
self.w = np.squeeze(np.array(self.w))
def draw(X, w, b):
# 生产分离超平面上的两点
X_new = np.array([0,6])
y_predict = -(b + w[0] * X_new) / w[1]
# 绘制训练数据集的散点图
plt.plot(X[:2, 0], X[:2, 1], "g*", label="1")
plt.plot(X[2:, 0], X[2:, 1], "rx", label="-1")
# 绘制分离超平面
plt.plot(X_new, y_predict, "b-")
# 设置两坐标轴起止值
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 6])
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def main():
x_train = np.array([[3, 3], [4, 3], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([1, 1, -1])
#生成Gram矩阵
Gram_Matrix = np.zeros(shape=(3,3))
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
Gram_Matrix[i][j] = np.dot(x_train[i], x_train[j].T)
Perceptron = MyPerceptron()
Perceptron.fit(x_train, y, Gram_Matrix)
draw(x_train, Perceptron.w, Perceptron.b)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
结果:
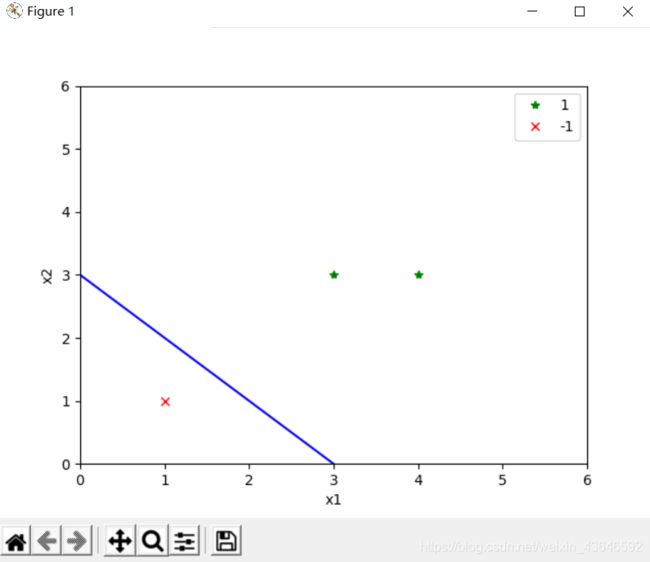
(感知机学习算法存在无穷多个解,这些解既依赖于初值的选择,也依赖于迭代过程中误分类点的选择顺序。)
习题2.3
题目:证明以下定理:样本集线性可分的充分必要条件是正实例点集所构成的凸壳与负实例点集所构成的凸壳互不相交。

新手一枚,如果有错,评论区帮忙指正谢谢大佬们,thanks~