opencv图像处理之图像变换(傅里叶变换)
文章目录
-
-
- 1.原理
- 2.Numpy中的傅里叶变换
- 3.opencv中的傅里叶变换
- 3.DFT性能优化
- 4.查看不同算子是低通还是高通
-
1.原理
- 傅里叶变换经常被用来分析不同滤波器的频率特性。我们可以使用2D 离散傅里叶变换(
DFT) 分析图像的频域特性。实现DFT 的一个快速算法被称为快速傅里叶变换(FFT)。 - 对于一个正弦信号: x ( t ) = A s i n ( 2 π f t ) x(t)=Asin(2πft) x(t)=Asin(2πft), 它的频率为 f f f,如果把这个信号转到它的频域表示,我们会在频率 f f f中看到一个峰值。如果我们的信号是由采样产生的离散信号好组成,我们会得到类似的频谱图,只不过前面是连续的,现在是离散。你可以把图像想象成沿着两个方向采集的信号。所以对图像同时进行X 方向和Y 方向的傅里叶变换,我们就会得到这幅图像的频域表示(频谱图)。
- 更直观一点,对于一个正弦信号,如果它的幅度变化非常快,我们可以说他是高频信号,如果变化非常慢,我们称之为低频信号。你可以把这种想法应用到图像中。图像哪里的幅度变化非常大呢?边界点或者噪声。所以我们说边界和噪声是图像中的
高频分量(注意这里的高频是指变化非常快,而非出现的次数多)。如果没有如此大的幅度变化我们称之为低频分量。
2.Numpy中的傅里叶变换
代码速记:
- np.fft.fft2()
- np.fft.fftshift()
- np.fft.ifftshift()
- np.fft.ifft2()
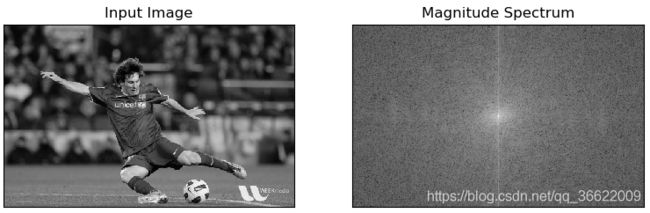
(1)构建频谱图实战:
def numpy_fft(self):
#【1】转灰度图
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#【2】fft2:对信号进行频率转换,输出结果是一个复杂的数组。
#第二个参数是可选的, 决定输出数组的大小。
#输出数组的大小和输入图像大小一样。如果输出结果比输入图像大,输入图像就需要在进行FFT前填充为0。
#如果输出结果比输入图像小的话,输入图像就会被裁剪。
f = np.fft.fft2(img)
#【3】fftshift
fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f)#上面得到的结果中,频率为0的部分(直流分量)在输出图像的左上角
#让它(直流分量)在输出图像的中心,我们还需要将结果沿两个方向平移 N/2
#【4】构建频谱图
#20*log(|fshift|)
magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(np.abs(fshift))
#画图
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Magnitude Spectrum'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
(2)对频谱图的操作:高通滤波(HPF)、重建图像(即找到逆DFT):
def numpy_fft_abs(self):
#对原图进行傅里叶变换
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
f = np.fft.fft2(img)
fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f)
#在频域对图像进行一些操作:
#【1】高通滤波:
#使用一个60x60 的矩形窗口对图像进行掩模操作从而去除低频分量
rows, cols = img.shape
crow, ccol = int(rows / 2), int(cols / 2)
fshift[crow - 30:crow + 30, ccol - 30:ccol + 30] = 0
#【2】重建图像:逆傅里叶变换
f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift)#逆平移:使直流分量回到左上角
img_back = np.fft.ifft2(f_ishift)#进行FFT逆变换
img_back = np.abs(img_back)# 取绝对值
#画图
plt.subplot(131), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(132), plt.imshow(img_back, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Image after HPF'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(133), plt.imshow(img_back)
plt.title('Result in JET'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
- 结果表明,高通滤波是一种边缘检测操作。这是我们在图像梯度章节中看到的。这也表明大部分图像数据都存在于频谱的低频区域。
- 最后一张JET 颜色(颜色表为jet(蓝色…红色)。不同颜色用来代表高程、振幅等信息)的图像,会看到一些不自然的东西,有些条带状的结构,这被成为振铃效应。这是由于我们使用矩形窗口做掩模造成的。这个掩模被转换成正弦形状时就会出现这个问题。所以一般我们不适用矩形窗口滤波。最好的选择是高斯窗口。
3.opencv中的傅里叶变换
代码速记:
- cv2.dft()
- cv2.idft()
- cv2.magnitude()
(1)离散傅里叶变换:
def dft(self):
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
dft = cv2.dft(np.float32(img), flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
#构建频谱图
magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(cv2.magnitude(dft_shift[:, :, 0], dft_shift[:, :, 1]))
#画图
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Magnitude Spectrum'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
def reverse_dft(self):
#对原图像进行 DFT
img = cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
dft = cv2.dft(np.float32(img), flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
#在频域上:低通滤波(其实就是图像模糊)
rows, cols = img.shape
crow, ccol = int(rows / 2), int(cols / 2)
mask = np.zeros((rows, cols, 2), np.uint8)
mask[crow - 30:crow + 30, ccol - 30:ccol + 30] = 1
fshift = dft_shift * mask
#重建图像:逆 DFT
f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift)
img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift)
img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:, :, 0], img_back[:, :, 1])
#画图
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(img_back, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Magnitude Spectrum'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()

OpenCV 中的函数cv2.dft() 和cv2.idft() 要比Numpy 快。但是Numpy 函数更加用户友好。
3.DFT性能优化
- cv2.getOptimalDFTSize()
当数组的大小为某些值时DFT 的性能会更好。当数组的大小是2 的指数时DFT 效率最高。当数组的大小是2,3,5 的倍数时效率也会很高。所以如果你想提高代码的运行效率时,你可以修改输入图像的大小(补0)。对于OpenCV 你必须自己手动补0。但是Numpy,你只需要指定FFT 运算的大小,它会自动补0。那我们怎样确定最佳大小呢?OpenCV 提供了一个函数:cv2.getOptimalDFTSize()。它可以同时被cv2.dft() 和np.fft.fft2() 使用。
img = cv2.imread('messi5.jpg',0)
#图像原始大小
rows,cols = img.shape
print(rows,cols)#342 548
#优化后的图像大小
nrows = cv2.getOptimalDFTSize(rows)
ncols = cv2.getOptimalDFTSize(cols)
print(nrows, ncols)#360 57
#补零
nimg = np.zeros((nrows,ncols))
nimg[:rows,:cols] = img
#Numpy(自己计算时间):
fft1 = np.fft.fft2(img)
fft2 = np.fft.fft2(nimg,[nrows,ncols])
#OpenCV(自己计算时间):
dft1= cv2.dft(np.float32(img),flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
dft2= cv2.dft(np.float32(nimg),flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
4.查看不同算子是低通还是高通
def test_algorithm(self):
mean_filter = np.ones((3, 3))# 均值过滤
x = cv2.getGaussianKernel(5, 10)# 创建一个高斯核
gaussian = x * x.T#矩阵转置
# 不同算子
# scharr:x方向
scharr = np.array([[-3, 0, 3],
[-10, 0, 10],
[-3, 0, 3]])
# sobel:x方向
sobel_x = np.array([[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]])
# sobel:y方向
sobel_y = np.array([[-1, -2, -1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 1]])
# laplacian:
laplacian = np.array([[0, 1, 0],
[1, -4, 1],
[0, 1, 0]])
#不同的过滤器
filters = [mean_filter, gaussian, laplacian, sobel_x, sobel_y, scharr]
filter_name = ['mean_filter', 'gaussian', 'laplacian', 'sobel_x', 'sobel_y', 'scharr_x']
#求不同核作用下的图像的频谱图
fft_filters = [np.fft.fft2(x) for x in filters]
fft_shift = [np.fft.fftshift(y) for y in fft_filters]
mag_spectrum = [np.log(np.abs(z) + 1) for z in fft_shift]
#画图
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1), plt.imshow(mag_spectrum[i], cmap='gray')
plt.title(filter_name[i]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()