深入学习Redis_(一)五种基本数据类型、RedisTemplate、RedisCache、缓存雪崩等
文章目录
- 一、Redis简介
- 二、Redis的五种基本数据类型
-
- String
- Hash
- List
- Set
- Zset
- 三、Redis pom依赖、yml配置
-
- 配置文件 application.yml 的配置:
- 四、RedisTemplate 的使用方式
-
- 添加配置类 RedisCacheConfig.java
- 五、使用 Spring Cache 集成 Redis
-
- 缓存注解
-
- @Cacheable
- @CachePut
- @CacheEvict
- User
- UserService
- UserServiceImpl
- 测试类
- 六、缓存和数据库数据一致性问题
- 七、Redis 缓存雪崩
-
- 缓存穿透
- 缓存击穿
- 下一章
一、Redis简介
Redis 是 C 语言开发的一个开源的(遵从 BSD 协议)高性能键值对(key-value)的内存数据库,可以用作数据库、缓存、消息中间件等。Redis是一种 NoSQL(not-only sql,泛指非关系型数据库)的数据库。
Redis 作为一个内存数据库:
1.性能优秀,数据在内存中,读写速度非常快,支持并发 10W QPS。
2.单进程单线程,是线程安全的,采用 IO 多路复用机制。
3.丰富的数据类型,支持字符串(strings)、散列(hashes)、列表(lists)、集合(sets)、有序集合(sorted sets)等。
4.支持数据持久化。
5.可以将内存中数据保存在磁盘中,重启时加载。
6.主从复制,哨兵,高可用。
7.可以用作分布式锁。
8.可以作为消息中间件使用,支持发布订阅。
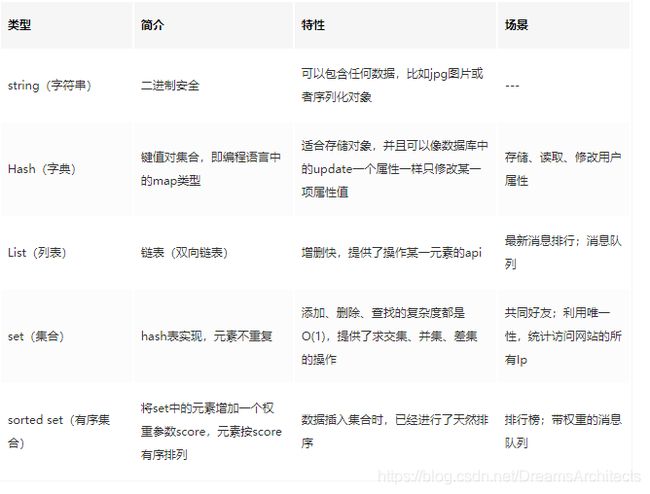
二、Redis的五种基本数据类型
String
String 是 Redis 最基本的类型,一个 Key 对应一个 Value。Value 不仅是 String,也可以是数字。String 类型是二进制安全的,意思是 Redis 的 String 类型可以包含任何数据,比如 jpg 图片或者序列化的对象。String 类型的值最大能存储 512M。
String应用场景 :
常规key-value缓存应用; 常规计数:微博数,粉丝数等。
Hash
Hash是一个键值(key-value)的集合。Redis 的 Hash 是一个 String 的 Key 和 Value 的映射表,Hash 特别适合存储对象。常用命令:hget,hset,hgetall 等。
Hash应用场景 : 存储用户信息,商品信息等等
List
List 列表是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边) 常用命令:lpush、rpush、lpop、rpop、lrange(获取列表片段)等。
另
外可以通过 lrange 命令,就是从某个元素开始读取多少个元素,可以基于 list 实现分页查询,这个很棒的一个功 能,基于 redis 实现简单的高性能分页,可以做类似微博那种下拉不断分页的东西(一页一页的往下走),性能高。
应用场景:List 应用场景非常多,也是 Redis 最重要的数据结构之一,比如 微博的关注列表,粉丝列表都可以用 List 结构来实现。
数据结构:List 就是链表,可以用来当消息队列用。Redis 提供了 List 的 Push 和 Pop 操作,还提供了操作某一段的 API,可以直接查询或者删除某一段的元素。
实现方式:Redis List 的是实现是一个双向链表,既可以支持反向查找和遍历,更方便操作,不过带来了额外的内存开销。
Set
Set 是 String 类型的无序集合。集合是通过 hashtable 实现的。Set 中的元素是没有顺序的,而且是没有重复的。常用命令:sdd、spop、smembers、sunion 等。
Redis Set 对外提供的功能和 List 一样是一个列表,特殊之处在于 Set 是自动去重的。当你需要存储一个列表数据,又不希望出现重复数据时,set是一个很好的选择,并且set提供了判断某个成员是否在 一 个set集合内的重要接口,这个也是list所不能提供的。可以基于 set 轻易实现交集、并集、差集的操作。
应用场景:
比如在微博应用中,可以将一个用户所有的关注人存在一个集合中,将其所有粉丝存在一个集合。Redis可以非常 方 便的实现如共同关注、共同粉丝、共同喜好等功能。这个过程也就是求交集的过程
Zset
Zset 和 Set 一样是 String 类型元素的集合,且不允许重复的元素。常用命令:zadd、zrange、zrem、zcard 等。
Sorted Set 可以通过用户额外提供一个优先级(score)的参数来为成员排序,并且是插入有序的,即自动排序。当你需要一个有序的并且不重复的集合列表,那么可以选择 Sorted Set 结构。
和 Set 相比,Sorted Set关联了一个 Double 类型权重的参数 Score,使得集合中的元素能够按照 Score 进行有序排列,Redis 正是通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。
使用场景:
在直播系统中,实时排行信息包含直播间在线用户列表,各种礼物排行榜,弹幕消息(可以理解为按消息维度 的消息排行榜)等信息,适合使用 Redis 中的 SortedSet 结构进行存储。
实现方式:Redis Sorted Set 的内部使用 HashMap 和跳跃表(skipList)来保证数据的存储和有序,HashMap 里放的是成员到 Score 的映射。而跳跃表里存放的是所有的成员,排序依据是 HashMap 里存的 Score,使用跳跃表的结构可以获得比较高的查找效率,并且在实现上比较简单。
SpringBoot使用RedisTemplate简单操作Redis的五种数据类型
三、Redis pom依赖、yml配置
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
spring-boot-starter-data-redis:在 Spring Boot 2.x 以后底层不再使用 Jedis,而是换成了 Lettuce。
commons-pool2:用作 Redis 连接池,如不引入启动会报错。
spring-session-data-redis:Spring Session 引入,用作共享 Session。
配置文件 application.yml 的配置:
server:
port: 8082
servlet:
session:
timeout: 30ms
spring:
cache:
type: redis
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password:
# redis默认情况下有16个分片,这里配置具体使用的分片,默认为0
database: 0
lettuce:
pool:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负数表示没有限制),默认8
max-active: 100
四、RedisTemplate 的使用方式
默认情况下的模板只能支持 RedisTemplate
添加配置类 RedisCacheConfig.java
package com.lsh.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureAfter;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @author :LiuShihao
* @date :Created in 2021/2/18 9:52 上午
* @desc :配置类 RedisCacheConfig
* 默认情况下的模板只能支持 RedisTemplate,也就是只能存入字符串,所以自定义模板很有必要。
*/
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
public class RedisCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisCacheTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
System.out.println("RedisTemplate加载...");
RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com/fasterxml/jackson/core/JsonProcessingException
// template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
五、使用 Spring Cache 集成 Redis
Spring Cache 具备很好的灵活性,不仅能够使用 SPEL(spring expression language)来定义缓存的 Key 和各种 Condition,还提供了开箱即用的缓存临时存储方案,也支持和主流的专业缓存如 EhCache、Redis、Guava 的集成。
缓存注解
核心是三个注解:
@Cachable
@CachePut
@CacheEvict
@Cacheable
示例:
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id")
根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存:
Key:缓存的 Key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SPEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则按照方法的所有参数进行组合。
Value:缓存的名称,必须指定至少一个(如 @Cacheable (value=‘user’)或者 @Cacheable(value={‘user1’,‘user2’}))
Condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SPEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存。
@CachePut
示例:
@CachePut(value ="user", key = "#user.id")
根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用。参数描述见上。
@CacheEvict
示例:
@CacheEvict(value="user", key = "#id")
根据条件对缓存进行清空:
Key:同上。
Value:同上。
Condition:同上。
allEntries:是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存。
beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存。缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存。
用缓存要注意,启动类要加上一个注解开启缓存:@EnableCaching
package com.lsh;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
/**
* @author :LiuShihao
* @date :Created in 2021/2/1 8:41 下午
* @desc :
*/
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringDataApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringDataApplication.class);
}
}
User
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(){
}
public User(int id,String name,int age){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
UserService
public interface UserService {
User save(User user);
void delete(int id);
User get(Integer id);
}
UserServiceImpl
package com.lsh.service.impl;
import com.lsh.entity.User;
import com.lsh.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author :LiuShihao
* @date :Created in 2021/2/1 9:08 下午
* @desc :
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private static Map<Integer, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
userMap.put(1, new User(1, "刘德华", 25));
userMap.put(2, new User(2, "李焕英", 26));
userMap.put(3, new User(3, "唐人街探案", 24));
}
/**
* 存入缓存
* @param user
* @return
*/
@CachePut(value ="user", key = "#user.id")
@Override
public User save(User user) {
userMap.put(user.getId(), user);
log.info("进入save方法,当前存储对象:{}", user.toString());
return user;
}
/**
* 删除缓存
* @param id
*/
@CacheEvict(value="user", key = "#id")
@Override
public void delete(int id) {
userMap.remove(id);
log.info("进入delete方法,删除成功");
}
/**
* 获得缓存
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id")
@Override
public User get(Integer id) {
log.info("进入get方法,当前获取对象:{}", userMap.get(id)==null?null:userMap.get(id).toString());
return userMap.get(id);
}
}
测试类
package com.lsh.repository;
import com.lsh.entity.User;
import com.lsh.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/**
* @author :LiuShihao
* @date :Created in 2021/2/18 9:52 上午
* @desc :
*/
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisCacheTemplate;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1001);
user.setName("张三");
user.setBirthday("2021-02-18");
redisCacheTemplate.opsForValue().set("userkey", user.toString() );
String user1 = redisCacheTemplate.opsForValue().get("userkey");
log.info("当前获取对象:{}", user1);
}
@Test
public void testCaCheAdd() {
User user = new User(4, "唐仁", 30);
userService.save(user);
}
@Test
public void testCaCheGet() {
User user1 = userService.get(1);
User user2 = userService.get(2);
User user3 = userService.get(3);
User user4 = userService.get(4);
System.out.println(user1);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user3);
System.out.println(user4);
}
@Test
public void testCaCheDel() {
userService.delete(4);
}
}
六、缓存和数据库数据一致性问题
分布式环境下非常容易出现缓存和数据库间数据一致性问题,针对这一点,如果项目对缓存的要求是强一致性的,那么就不要使用缓存。
我们只能采取合适的策略来降低缓存和数据库间数据不一致的概率,而无法保证两者间的强一致性。
合适的策略包括合适的缓存更新策略,更新数据库后及时更新缓存、缓存失败时增加重试机制。
七、Redis 缓存雪崩
一般缓存都是定时任务去刷新,或者查不到之后去更新缓存的,定时任务刷新就有一个问题。
举个栗子:如果首页所有 Key 的失效时间都是 12 小时,中午 12 点刷新的,我零点有个大促活动大量用户涌入,假设每秒 6000 个请求,本来缓存可以抗住每秒 5000 个请求,但是缓存中所有 Key 都失效了。
此时 6000 个/秒的请求全部落在了数据库上,数据库必然扛不住,真实情况可能 DBA(数据库管理员) 都没反应过来直接挂了。
解决方法:
处理缓存雪崩简单,在批量往 Redis 存数据的时候,把每个 Key 的失效时间都加个随机值就好了,这样可以保证数据不会再同一时间大面积失效。
setRedis(key, value, time+Math.random()*10000);
如果 Redis 是集群部署,将热点数据均匀分布在不同的 Redis 库中也能避免全部失效。
或者设置热点数据永不过期,有更新操作就更新缓存就好了(比如运维更新了首页商品,那你刷下缓存就好了,不要设置过期时间),电商首页的数据也可以用这个操作,保险。
缓存穿透
缓存穿透是指缓存和数据库中都没有的数据,而用户(黑客)不断发起请求。
解决方案:
- 查询返回的数据为空,仍把这个空结果进行缓存,但过期时间会比较短;
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter):将所有可能存在的数据哈希到一个足够大的 bitmap 中,一个一定不存在的数据 会被这个 bitmap 拦截掉,从而避免了对 DB 的查询。
缓存击穿
缓存击穿,跟缓存雪崩有点像,但是又有一点不一样,缓存雪崩是因为大面积的缓存失效,打崩了 DB。
而缓存击穿不同的是缓存击穿是指一个 Key 非常热点,在不停地扛着大量的请求,大并发集中对这一个点进行访问,当这个 Key 在失效的瞬间,持续的大并发直接落到了数据库上,就在这个 Key 的点上击穿了缓存。
解决方法:
- 设置热点数据永不过期,物理不过期,但逻辑过期(后台异步线程去刷新)。
- 加上互斥锁:当缓存失效时,不立即去load db,先使用如Redis的setnx去设置一个互斥锁,当操作成功返回时再进行load db的操作并回设缓存,否则重试get缓存的方法。
public static String getData(String key) throws InterruptedException {
//从Redis查询数据
String result = getDataByKV(key);
//参数校验
if (StringUtils.isBlank(result)) {
try {
//获得锁
if (reenLock.tryLock()) {
//去数据库查询
result = getDataByDB(key);
//校验
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(result)) {
//插进缓存
setDataToKV(key, result);
}
} else {
//睡一会再拿
Thread.sleep(100L);
result = getData(key);
}
} finally {
//释放锁
reenLock.unlock();
}
}
return result;
}
下一章
深入学习Redis_(二)淘汰策略、持久化机制、主从复制、哨兵模式等