【深度学习笔记】task4 网络八股扩展
深度学习- 网络八股扩展
-
- 4.1 搭建网络八股概览
- 4.2 自制数据集,解决本领域问题
- 4.2 数据增强,扩充数据集
- 4.3 断点续训,存取模型
- 4.4 参数提取,把参数存入文本
- 4.6 acc&loss可视化,查看训练效果
- 4.6 应用程序,给图识物
依依旧是跟着曹健老师的课程学习,之前主要是给予所给的训练集和测试集进行训练和测试,这一节中讲授了如何自制数据集以及模型保存的问题,非常有实用价值
- 视频地址
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1B7411L7Qt?p=1 - 原码https://github.com/jlff/tf2_notes
4.1 搭建网络八股概览
4.2 自制数据集,解决本领域问题
原有数据如下,已经有了手写数字图片和txt文件,txt文件中记录了手写图片的文件名和其对应的标签
在这里插入代码片
目标:把图片路径和标签文件输入generateds,generateds函数返回输入特征和标签
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import os
train_path = './mnist_image_label/mnist_train_jpg_60000/'
train_txt = './mnist_image_label/mnist_train_jpg_60000.txt'
x_train_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_x_train.npy'
y_train_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_y_train.npy'
test_path = './mnist_image_label/mnist_test_jpg_10000/'
test_txt = './mnist_image_label/mnist_test_jpg_10000.txt'
x_test_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_x_test.npy'
y_test_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_y_test.npy'
def generateds(path, txt):
f = open(txt, 'r') # 以只读形式打开txt文件
contents = f.readlines() # 读取文件中所有行
f.close() # 关闭txt文件
x, y_ = [], [] # 建立空列表
for content in contents: # 逐行取出
value = content.split() # 以空格分开,图片路径为value[0] , 标签为value[1] , 存入列表
img_path = path + value[0] # 拼出图片路径和文件名
img = Image.open(img_path) # 读入图片
img = np.array(img.convert('L')) # 图片变为8位宽灰度值的np.array格式
img = img / 255. # 数据归一化 (实现预处理)
x.append(img) # 归一化后的数据,贴到列表x
y_.append(value[1]) # 标签贴到列表y_
print('loading : ' + content) # 打印状态提示
x = np.array(x) # 变为np.array格式
y_ = np.array(y_) # 变为np.array格式
y_ = y_.astype(np.int64) # 变为64位整型
return x, y_ # 返回输入特征x,返回标签y_
#测试各个路径是否已经存在
if os.path.exists(x_train_savepath) and os.path.exists(y_train_savepath) and os.path.exists(
x_test_savepath) and os.path.exists(y_test_savepath):
#如果存在直接读取
print('-------------Load Datasets-----------------')
x_train_save = np.load(x_train_savepath)
y_train = np.load(y_train_savepath)
x_test_save = np.load(x_test_savepath)
y_test = np.load(y_test_savepath)
x_train = np.reshape(x_train_save, (len(x_train_save), 28, 28))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test_save, (len(x_test_save), 28, 28))
else:
#如果不存在调用generate函数制作数据集
print('-------------Generate Datasets-----------------')
x_train, y_train = generateds(train_path, train_txt)
x_test, y_test = generateds(test_path, test_txt)
print('-------------Save Datasets-----------------')
x_train_save = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), -1))
x_test_save = np.reshape(x_test, (len(x_test), -1))
np.save(x_train_savepath, x_train_save)
np.save(y_train_savepath, y_train)
np.save(x_test_savepath, x_test_save)
np.save(y_test_savepath, y_test)
##搭建神经网络模型
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
##设置神经网络训练参数
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
##神经网络训练
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=5, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1)
model.summary()
4.2 数据增强,扩充数据集
对图像的增强就是对图像的简单形变,tf2给出了数据增强函数

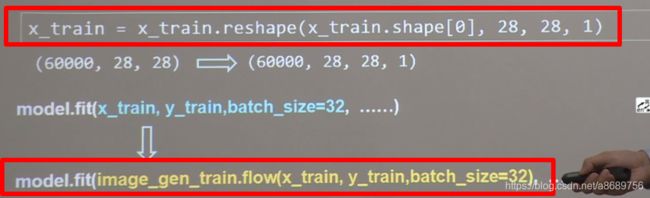
在进行数据增强前需要对图片进行reshpe变成四维数据的
如手写数字数据集由(60000,28,28)变成了(60000,28,28,1),其中的1代表单通道,即灰度值
另一个改动之处就是在fit时
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], 28, 28, 1) # 给数据增加一个维度,从(60000, 28, 28)reshape为(60000, 28, 28, 1)
image_gen_train = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1. / 1., # 如为图像,分母为255时,可归至0~1
rotation_range=45, # 随机45度旋转
width_shift_range=.15, # 宽度偏移
height_shift_range=.15, # 高度偏移
horizontal_flip=False, # 水平翻转
zoom_range=0.5 # 将图像随机缩放阈量50%
)
image_gen_train.fit(x_train)
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
model.fit(image_gen_train.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32), epochs=5, validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
validation_freq=1)
model.summary()
4.3 断点续训,存取模型
- 读取模型:
load_weights(路径文件名)
具体应用:1定义存放的路径和文件名命名为ckpt文件,通过判断是否已经有索引表(如果存储模型,那么会同步生产索引表)来判断是否保存过模型, 如果已经保存过,那么久读取出来
- 保存模型:使用tensorflow给出的回调函数
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath=路径文件名,
save_weights_only=True/False,#是否值保留模型参数
save_best_only=True/False,#是否只保留最优结果
history=model.fit(callbacks=[cp_callback])#执行训练过程时候加入callbacks选型记录到history中
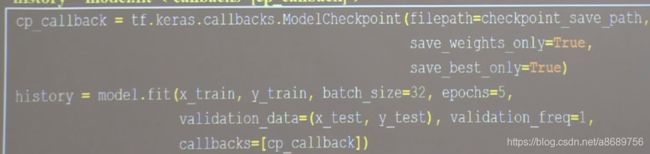
第一次运行后会保存模型,等第二次运行的时候会加载原来的模型继续在原来的模型上进行提升(不是不再训练了哦~)
##导入相关包
import tensorflow as tf
import os
##导入数据集
mnist=tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test)=mnist.load_data()
x_train=x_train/255
x_test=x_test/255
##构建神经网络
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
##设置神经网络训练参数
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
##设置断点续存
checkpoint_save_path='./checkpoint/mnist.ckpt'
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path+'.index'):
print('---------load the model-------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback=tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_best_only=True,
save_weights_only=True)
##模型训练
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,
batch_size=32,
epochs=5,
validation_data=(x_test,y_test),
validation_freq=1,
callbacks=[cp_callback])
##打印结果
model.summary()
4.4 参数提取,把参数存入文本
- 提取可训练参数
model.train_variables 返回模型中可训练的参数
- 设置print输出格式
np.set_printoptions(threshold=超过多少省略显示)
import numpy as np #
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
print(model.trainable_variables)
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
对于上面的例子,结果太长不写了
4.6 acc&loss可视化,查看训练效果
history=model.fit(训练集数据,训练集标签,batch_size=,epochs=,validation_split=用作测试数据的比例,validation_data=测试集,validation_freq=测试频率)
可以用history.history提取
训练集loss:loss
测试集loss:val_loss
训练集准确率:sparse_categorival_accuracy
测试集准确率:val_sparse_categorival_accuracy
在上面的例子上进行提取
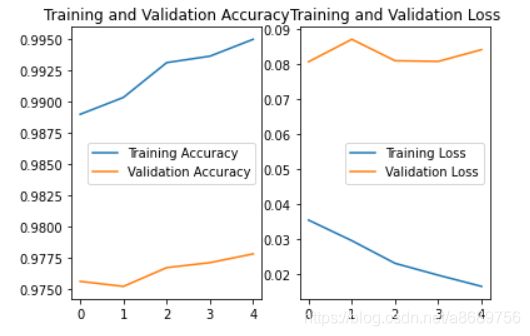
#绘制acc和loss曲线
#提取到的是五次迭代的结果
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) #将图像分为一行两列
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend()#画出图例
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
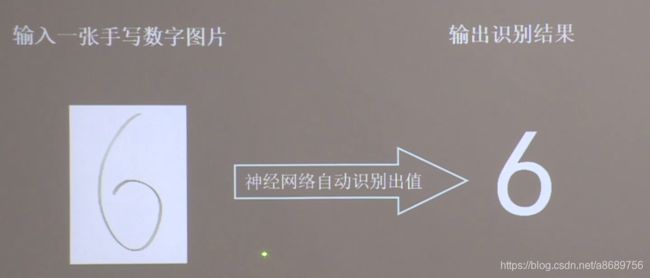
4.6 应用程序,给图识物
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
model_save_path='./checkpoint/mnist.ckpt'
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')])
model.load_weights(model_save_path)
#输入图像个数
preNum = int(input("input the number of test pictures:"))
for i in range(preNum):
image_path = input("the path of test picture:")
img = Image.open(image_path)
img = img.resize((28, 28), Image.ANTIALIAS)#因为训练的时候是28*28的图片,而输入是任意的图片,因此需要先resize
#Image.NEAREST :低质量
# Image.BILINEAR:双线性
# Image.BICUBIC :三次样条插值
# Image.ANTIALIAS:高质量
img_arr = np.array(img.convert('L'))#转化为灰度图
img_arr = 255 - img_arr#输入程序的图片是白底黑字,但是训练的模型是黑底白字的,因此需要进行转换
###也可以将其编码成黑白的高对比度图,代码吐下
# for i in range(28):
# for j in range(28):
# if img_arr[i][j]<200:
# img_arr[i][j]=255
# else:
# img_arr[i][j]=0
img_arr = img_arr / 255.0#归一化
print("img_arr:",img_arr.shape)
x_predict = img_arr[tf.newaxis, ...]#添加维度,即从28*28变成了1*28*28三维数据
print("x_predict:",x_predict.shape)
result = model.predict(x_predict)
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
print('\n')
tf.print(pred)