起因是一场周赛的题目 1705. 吃苹果的最大数目
有一棵特殊的苹果树,一连 n 天,每天都可以长出若干个苹果。在第 i 天,树上会长出 apples[i] 个苹果,这些苹果将会在 days[i] 天后(也就是说,第 i + days[i] 天时)腐烂,变得无法食用。也可能有那么几天,树上不会长出新的苹果,此时用 apples[i] == 0 且 days[i] == 0 表示。
你打算每天 最多 吃一个苹果来保证营养均衡。注意,你可以在这 n 天之后继续吃苹果。
给你两个长度为 n 的整数数组 days 和 apples ,返回你可以吃掉的苹果的最大数目。
示例:
apples = [1,2,3,5,2], days = [3,2,1,4,2]
- 第一天,你吃掉第一天长出来的苹果。
- 第二天,你吃掉一个第二天长出来的苹果。
- 第三天,你吃掉一个第二天长出来的苹果。过了这一天,第三天长出来的苹果就已经腐烂了。
- 第四天到第七天,你吃的都是第四天长出来的苹果。
描述中的第四天到第七天吃的都是第四天的苹果,我以为是记录当前剩余苹果的贪心,实际应该是
- 第四天,吃掉一个第四天长出的苹果。
- 第五天,第四天的四个苹果保质三天,第五天的两个苹果保质两天,吃掉一个第五天的苹果
- 第六天,第四天的四个苹果保质两天,第五天的一个苹果保质一天,吃掉一个第五天的苹果
- 第七天,第四天的四个苹果保质一天,吃掉一个第四天苹果
- 第八天,第四天的三个苹果保质零天,没的吃。
做题
要优先吃快要坏掉的苹果,分为三步:
var eatenApples = function(apples, days) {
let aLen = apples.length
let eat = 0
let queue = [] // 按照好坏程度排序的苹果队列
let i = 0 // 当前是第几天
// todo
// 1、把今天的苹果收起来
// 2、把坏掉的苹果扔掉
// 3、吃一个
return eat
};1、收苹果
// 收苹果时需要把当天的苹果放入合适位置
// 以保证 queue 是按照从坏到好的顺序
if(i < aLen && apples[i]) {
let j = queue.length - 1
while(j >= 0 && ((i + days[i]) < (queue[j] + days[queue[j]]))) {
// queue不为空 且 当前天的苹果的保质期 < queue倒序中的苹果的保质期
queue[j + 1] = queue[j]
j--
}
queue[j + 1] = i
}2、扔坏苹果
while(
queue.length > 0 &&
(apples[queue[0]] <= 0 || i >= (queue[0] + days[queue[0]]))
// 第一坏的位置没苹果了 或者 第一坏的位置已经过保质期了
) queue.shift()3、吃
if(queue.length > 0) {
apples[queue[0]]--
eat++
}已经可以过了,但是只击败了56%,原因在于我们优先队列的实现方式是简单数组,每次插入和 shift() 的时候都是 O(n) 的复杂度,接下来就是使用二叉堆来实现一个优先队列。
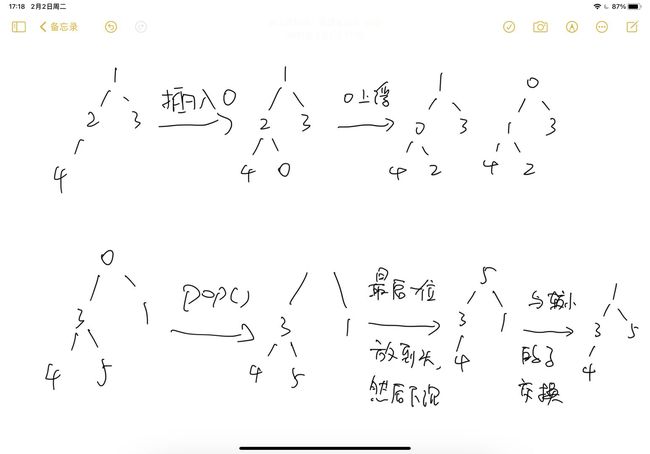
二叉堆
二叉堆本质是完全二叉树,分为最大堆和最小堆,最大堆就是任意一个父节点,都大于他的子节点的值,最小堆同理,任意一个父节点都小于他的子节点的值。
二叉堆的根节点叫做堆顶,最大堆的根节点是堆的最大元素,最小堆的根节点是堆的最小元素。
二叉堆的操作包括:插入节点,删除节点,构建二叉堆,这三种操作又都是基于节点的上浮和下沉
下面使用数组来简单实现一个最小二叉堆
function BinaryHeap() {
this.list = []
}
BinaryHeap.prototype = {
push(data) {
this.list.push(data)
this._moveUp()
},
pop() {
const data = this.list[0]
this.list[0] = this.list[this.list.length - 1]
this.list.pop()
this._moveDown(0)
return data
},
// 节点上浮
_moveUp() {
let childIndex = this.list.length - 1
let parentIndex = (childIndex - 1) >>> 1
let temp = this.list[childIndex]
while(childIndex > 0 && temp < this.list[parentIndex]) {
this.list[childIndex] = this.list[parentIndex]
childIndex = parentIndex
parentIndex = (parentIndex - 1) >>> 1
}
this.list[childIndex] = temp
},
// 节点下沉
_moveDown(index) {
let parent = index
let temp = this.list[parent]
let child = 2 * parent + 1
while(child < this.list.length) {
if(child < this.list.length - 1 && this.list[child + 1] < this.list[child]) {
// 如果有两个子节点, 将父节点下沉到更小的节点的位置
child++
}
if(this.list[child] < temp) {
this.list[parent] = this.list[child]
parent = child
child = 2 * parent + 1
} else {
break
}
}
this.list[parent] = temp
}
}二叉堆的push和pop都是 logn 的复杂度,类比二分查找,大家都是 logn,能不能用二分代替嘞,不能。
因为二叉堆的 logn 是 查 + 替换, 二分查找的 logn 只有查,替换是 n,所以不能。
应用
下面使用二叉堆来改写代码,只需要把我们实现的二叉堆中是否上浮和下沉的对比条件修改一下,重复代码就不占篇幅了,大概代码如下
function BinaryHeap(compareArr) {
this.list = []
this.compareArr = compareArr
}
BinaryHeap.prototype = {
lessThan(index1, index2) {
return (index1 + this.compareArr[index1]) < (index2 + this.compareArr[index2])
},
first() {
return this.list[0]
},
length() {
return this.list.length
},
push(data) {
// ...
},
pop() {
// ...
},
_moveUp() {
// ...
while(childIndex > 0 && this.lessThan(temp, this.list[parentIndex])) {
// ...
}
// ...
},
_moveDown(index) {
// ...
while(child < this.list.length) {
if(child < this.list.length - 1 && this.lessThan(this.list[child + 1],this.list[child])) {
child++
}
if(this.lessThan(this.list[child], temp)) {
// ...
} else {
break
}
}
this.list[parent] = temp
}
}
var eatenApples = function(apples, days) {
let aLen = apples.length
let eat = 0
let queue = new BinaryHeap(days)
let i = 0
while(i < aLen || queue.length > 0) {
if(i < aLen && apples[i]) {
queue.push(i)
}
while(
queue.length() > 0 &&
(apples[queue.first()] <= 0 || (queue.first() + days[queue.first()]) <= i)
) queue.pop()
if(queue.length() > 0) {
apples[queue.first()]--
eat++
}
i++
}
return eat
};二叉堆版本的代码和最初的速度对比![]()
图中序号2和3是二叉堆版本和线性数组的时间对比,也从击败56%提升到92%
序号1则是速度排在最前面的答案的重新提交,但是有一个测试用例不通过,可能是补充用例之前的提交。
最后的代码看起来确实很长,但是把二叉堆单拎出来,阅读起来可能更清晰一点。