数字图像处理(六):小波变换
- 小波变换的引入
-
- FT 傅里叶变换
- STFT 短时傅里叶变换
- Wavelet 小波
- Wavelet transform 小波变换
-
- 特性
- 滤波器组
- 应用
-
- 边缘检测
- 图像平滑
- 图像渐进重构
- 函数代码
-
- wavefilter.m
- wavework.m
- wave2gray.m
- wavecut.m
- wavecopy.m
- wavepaste.m
- wavefast.m
- wavezero.m
- waveback.m
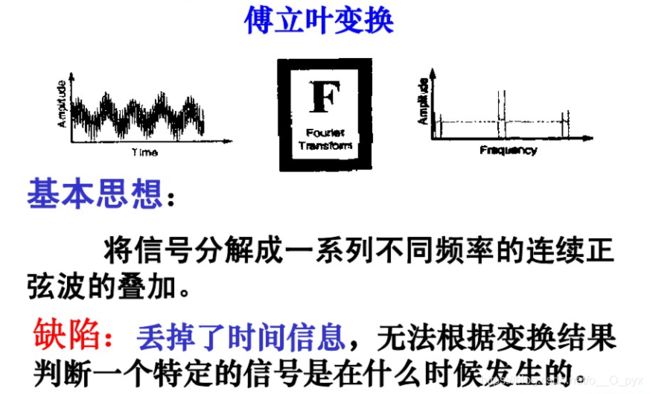
小波变换的引入
FT 傅里叶变换
STFT 短时傅里叶变换
给信号加窗,反应信号局部(一段时间的)特征。
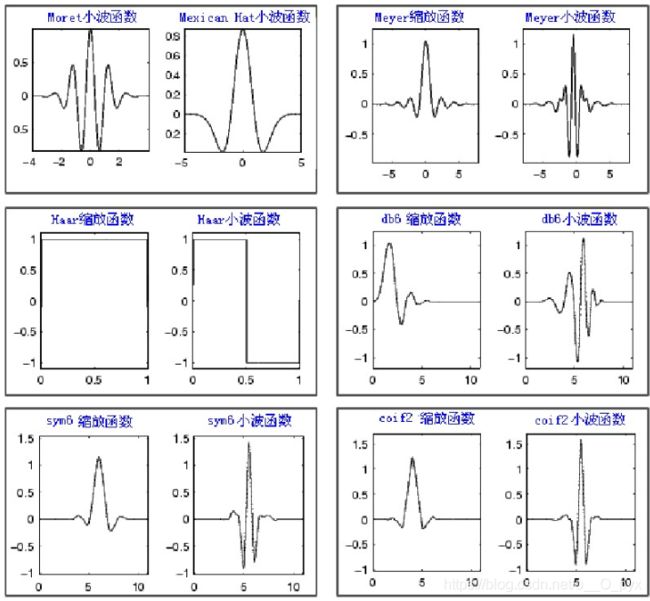
Wavelet 小波
- 变化频率和振幅、持续时间有限
- 波形可以不规则、不对称
- 整个时间范围里幅度平均值为零
- 比较正弦波
Wavelet transform 小波变换
特性
可分离性、尺度可变性、平移性
多分辨率的一致性
正交性
滤波器组
Wφ:尺度j处的滤波器系数
H、V、D:水平、垂直、对角线细节系数

应用
边缘检测
图像平滑
wavezero
图像渐进重构
函数代码
%% 编码
cod_t = wcodemat(tempf, nbcol);%图像编码矩阵
cod_cA1 = wcodemat(cA1, nbcol);%近似
cod_cH1 = wcodemat(cH1, nbcol);%水平
cod_cV1 = wcodemat(cV1, nbcol);%垂直
cod_cD1 = wcodemat(cD1, nbcol);%对角
wavefilter.m
function [varargout] = wavefilter(wname, type)
%WAVEFILTER Create wavelet decomposition and reconstruction filters.
% [VARARGOUT] = WAVEFILTER(WNAME, TYPE) returns the decomposition
% and/or reconstruction filters used in the computation of the
% forward and inverse FWT (fast wavelet transform).
%
% EXAMPLES:
% [ld, hd, lr, hr] = wavefilter('haar') Get the low and highpass
% decomposition (ld, hd)
% and reconstruction
% (lr, hr) filters for
% wavelet 'haar'.
% [ld, hd] = wavefilter('haar','d') Get decomposition filters
% ld and hd.
% [lr, hr] = wavefilter('haar','r') Get reconstruction
% filters lr and hr.
%
% INPUTS:
% WNAME Wavelet Name
% ---------------------------------------------------------
% 'haar' or 'db1' Haar
% 'db4' 4th order Daubechies
% 'sym4' 4th order Symlets
% 'bior6.8' Cohen-Daubechies-Feauveau biorthogonal
% 'jpeg9.7' Antonini-Barlaud-Mathieu-Daubechies
%
% TYPE Filter Type
% ---------------------------------------------------------
% 'd' Decomposition filters
% 'r' Reconstruction filters
%
% See also WAVEFAST and WAVEBACK.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/10/13 01:09:39 $
% Check the input and output arguments.
error(nargchk(1, 2, nargin));
if (nargin == 1 & nargout ~= 4) |e799bee5baa6e79fa5e98193e4b893e5b19e31333330333563 (nargin == 2 & nargout ~= 2)
error('Invalid number of output arguments.');
end
if nargin == 1 & ~ischar(wname)
error('WNAME must be a string.');
end
if nargin == 2 & ~ischar(type)
error('TYPE must be a string.');
end
% Create filters for the requested wavelet.
switch lower(wname)
case {
'haar', 'db1'}
ld = [1 1]/sqrt(2); hd = [-1 1]/sqrt(2);
lr = ld; hr = -hd;
case 'db4'
ld = [-1.059740178499728e-002 3.288301166698295e-002 ...
3.084138183598697e-002 -1.870348117188811e-001 ...
-2.798376941698385e-002 6.308807679295904e-001 ...
7.148465705525415e-001 2.303778133088552e-001];
t = (0:7);
hd = ld; hd(end:-1:1) = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
lr = ld; lr(end:-1:1) = ld;
hr = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
case 'sym4'
ld = [-7.576571478927333e-002 -2.963552764599851e-002 ...
4.976186676320155e-001 8.037387518059161e-001 ...
2.978577956052774e-001 -9.921954357684722e-002 ...
-1.260396726203783e-002 3.222310060404270e-002];
t = (0:7);
hd = ld; hd(end:-1:1) = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
lr = ld; lr(end:-1:1) = ld;
hr = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
case 'bior6.8'
ld = [0 1.908831736481291e-003 -1.914286129088767e-003 ...
-1.699063986760234e-002 1.193456527972926e-002 ...
4.973290349094079e-002 -7.726317316720414e-002 ...
-9.405920349573646e-002 4.207962846098268e-001 ...
8.259229974584023e-001 4.207962846098268e-001 ...
-9.405920349573646e-002 -7.726317316720414e-002 ...
4.973290349094079e-002 1.193456527972926e-002 ...
-1.699063986760234e-002 -1.914286129088767e-003 ...
1.908831736481291e-003];
hd = [0 0 0 1.442628250562444e-002 -1.446750489679015e-002 ...
-7.872200106262882e-002 4.036797903033992e-002 ...
4.178491091502746e-001 -7.589077294536542e-001 ...
4.178491091502746e-001 4.036797903033992e-002 ...
-7.872200106262882e-002 -1.446750489679015e-002 ...
1.442628250562444e-002 0 0 0 0];
t = (0:17);
lr = cos(pi * (t + 1)) .* hd;
hr = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
case 'jpeg9.7'
ld = [0 0.02674875741080976 -0.01686411844287495 ...
-0.07822326652898785 0.2668641184428723 ...
0.6029490182363579 0.2668641184428723 ...
-0.07822326652898785 -0.01686411844287495 ...
0.02674875741080976];
hd = [0 -0.09127176311424948 0.05754352622849957 ...
0.5912717631142470 -1.115087052456994 ...
0.5912717631142470 0.05754352622849957 ...
-0.09127176311424948 0 0];
t = (0:9);
lr = cos(pi * (t + 1)) .* hd;
hr = cos(pi * t) .* ld;
otherwise
error('Unrecognizable wavelet name (WNAME).');
end
% Output the requested filters.
if (nargin == 1)
varargout(1:4) = {
ld, hd, lr, hr};
else
switch lower(type(1))
case 'd'
varargout = {
ld, hd};
case 'r'
varargout = {
lr, hr};
otherwise
error('Unrecognizable filter TYPE.');
end
end
wavework.m
function [varargout] = wavework(opcode, type, c, s, n, x)
%WAVEWORK is used to edit wavelet decomposition structures.
% [VARARGOUT] = WAVEWORK(OPCODE, TYPE, C, S, N, X) gets the
% coefficients specified by TYPE and N for access or modification
% based on OPCODE.
%
% INPUTS:
% OPCODE Operation to perform
% --------------------------------------------------------------
% 'copy' [varargout] = Y = requested (via TYPE and N)
% coefficient matrix
% 'cut' [varargout] = [NC, Y] = New decomposition vector
% (with requested coefficient matrix zeroed) AND
% requested coefficient matrix
% 'paste' [varargout] = [NC] = new decomposition vector with
% coefficient matrix replaced by X
%
% TYPE Coefficient category
% --------------------------------------------
% 'a' Approximation coefficients
% 'h' Horizontal details
% 'v' Vertical details
% 'd' Diagonal details
%
% [C, S] is a wavelet toolbox decomposition structure.
% N is a decomposition level (Ignored if TYPE = 'a').
% X is a two-dimensional coefficient matrix for pasting.
%
% See also WAVECUT, WAVECOPY, and WAVEPASTE.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.6 $ $Date: 2003/11/21 15:00:18 $
error(nargchk(4, 6, nargin));
if (ndims(c) ~= 2) | (size(c, 1) ~= 1)
error('C must be a row vector.');
end
if (ndims(s) ~= 2) | ~isreal(s) | ~isnumeric(s) | (size(s, 2) ~= 2)
error('S must be a real, numeric two-column array.');
end
elements = prod(s, 2); % Coefficient matrix elements.
if (length(c) < elements(end)) | ...
~(elements(1) + 3 * sum(elements(2:end - 1)) >= elements(end))
error(['[C S] must form a standard wavelet decomposition ' ...
'structure.']);
end
if strcmp(lower(opcode(1:3)), 'pas') & nargin < 6
error('Not enough input arguments.');
end
if nargin < 5
n = 1; % Default level is 1.
end
nmax = size(s, 1) - 2; % Maximum levels in [C, S].
aflag = (lower(type(1)) == 'a');
if ~aflag & (n > nmax)
error('N exceeds the decompositions in [C, S].');
end
switch lower(type(1)) % Make pointers into C.
case 'a'
nindex = 1;
start = 1; stop = elements(1); ntst = nmax;
case {
'h', 'v', 'd'}
switch type
case 'h', offset = 0; % Offset to details.
case 'v', offset = 1;
case 'd', offset = 2;
end
nindex = size(s, 1) - n; % Index to detail info.
start = elements(1) + 3 * sum(elements(2:nmax - n + 1)) + ...
offset * elements(nindex) + 1;
stop = start + elements(nindex) - 1;
ntst = n;
otherwise
error('TYPE must begin with "a", "h", "v", or "d".');
end
switch lower(opcode) % Do requested action.
case {
'copy', 'cut'}
y = repmat(0, s(nindex, :));
y(:) = c(start:stop); nc = c;
if strcmp(lower(opcode(1:3)), 'cut')
nc(start: stop) = 0; varargout = {
nc, y};
else
varargout = {
y};
end
case 'paste'
if prod(size(x)) ~= elements(end - ntst)
error('X is not sized for the requested paste.');
else
nc = c; nc(start:stop) = x(:); varargout = {
nc};
end
otherwise
error('Unrecognized OPCODE.');
end
wave2gray.m
function w = wave2gray(c, s, scale, border)
%WAVE2GRAY Display wavelet decomposition coefficients.
% W = WAVE2GRAY(C, S, SCALE, BORDER) displays and returns a
% wavelet coefficient image.
% EXAMPLES:
% wave2gray(c, s); Display w/defaults.
% foo = wave2gray(c, s); Display and return.
% foo = wave2gray(c, s, 4); Magnify the details.
% foo = wave2gray(c, s, -4); Magnify absolute values.
% foo = wave2gray(c, s, 1, 'append'); Keep border values.
%
% INPUTS/OUTPUTS:
% [C, S] is a wavelet decomposition vector and bookkeeping
% matrix.
%
% SCALE Detail coefficient scaling
%--------------------------------------------------------------------
% 0 or 1 Maximum range (default)
% 2, 3... Magnify default by the scale factor
% -1, -2... Magnify absolute values by abs(scale)
%
% BORDER Border between wavelet decompositions
%--------------------------------------------------------------------
% 'absorb' Border replaces image (default)
% 'append' Border increases width of image
%
% Image W: ------- ------ -------------- -------------------
% | | | |
% | a(n) | h(n) | |
% | | | |
% ------- ------ h(n-1) |
% | | | |
% | v(n) | d(n) | | h(n-2)
% | | | |
% ------- ------ --------------
% | | |
% | v(n-1) | d(n-1) |
% | | |
% -------------- -------------- -------------------
% | |
% | v(n-2) | d(n-2)
% | |
%
% Here, n denotes the decomposition step scale and a, h, v, d are
% approximation, horizontal, vertical, and diagonal detail
% coefficients, respectively.
% Check input arguments for reasonableness.
error(nargchk(2, 4, nargin));
if (ndims(c) ~= 2) | (size(c, 1) ~= 1)
error('C must be a row vector.'); end
if (ndims(s) ~= 2) | ~isreal(s) | ~isnumeric(s) | (size(s, 2) ~= 2)
error('S must be a real, numeric two-column array.'); end
elements = prod(s, 2);
if (length(c) < elements(end)) | ...
~(elements(1) + 3 * sum(elements(2:end - 1)) >= elements(end))
error(['[C S] must be a standard wavelet ' ...
'decomposition structure.']);
end
if (nargin > 2) & (~isreal(scale) | ~isnumeric(scale))
error('SCALE must be a real, numeric scalar.');
end
if (nargin > 3) & (~ischar(border))
error('BORDER must be character string.');
end
if nargin == 2
scale =1; % Default scale.
end
if nargin < 4
border = 'absorb'; % Default border.
end
% Scale coefficients and determine pad fill.
absflag = scale < 0;
scale = abs(scale);
if scale == 0
scale = 1;
end
[cd, w] = wavecut('a', c, s); w = mat2gray(w);
cdx = max(abs(cd(:))) / scale;
if absflag
cd = mat2gray(abs(cd), [0, cdx]); fill = 0;
else
cd = mat2gray(cd, [-cdx, cdx]); fill = 0.5;
end
% Build gray image one decomposition at a time.
for i = size(s, 1) - 2:-1:1
ws = size(w);
h = wavecopy('h', cd, s, i);
pad = ws - size(h); frontporch = round(pad / 2);
h = padarray(h, frontporch, fill, 'pre');
h = padarray(h, pad - frontporch, fill, 'post');
v = wavecopy('v', cd, s, i);
pad = ws - size(v); frontporch = round(pad / 2);
v = padarray(v, frontporch, fill, 'pre');
v = padarray(v, pad - frontporch, fill, 'post');
d = wavecopy('d', cd, s, i);
pad = ws - size(d); frontporch = round(pad / 2);
d = padarray(d, frontporch, fill, 'pre');
d = padarray(d, pad - frontporch, fill, 'post');
% Add 1 pixel white border.
switch lower(border)
case 'append'
w = padarray(w, [1 1], 1, 'post');
h = padarray(h, [1 0], 1, 'post');
v = padarray(v, [0 1], 1, 'post');
case 'absorb'
w(:, end) = 1; w(end, :) = 1;
h(end, :) = 1; v(:, end) = 1;
otherwise
error('Unrecognized BORDER parameter.');
end
w = [w h; v d]; % Concatenate coefs.
end
if nargout == 0
imshow(w); % Display result.
end
wavecut.m
function [nc,y]=wavecut(type,c,s,n)
%wavecut在小波重构结构是零系数
%当它的细节或近似值矩阵已经被定义为0,返回一个新的重构向量。
%输入:
%类型 系数类型
%'a' 近似值系数
%'h' 水平细节
%'v' 垂直细节
%'d' 对角线细节
%[c,s]是一个小波数据结构。n是指定的重构水平(type='a'则忽略)。
error(nargchk(3,4,narargin));
if nargin==4
[nc,y]=wavework('cut',type,c,s,n);
else
[nc,y]=wavework('cut',type,c,s);
end
wavecopy.m
function y = wavecopy(type, c, s, n)
%WAVECOPY Fetches coefficients of a wavelet decomposition structure.
% Y = WAVECOPY(TYPE, C, S, N) returns a coefficient array based on
% TYPE and N.
%
% INPUTS:
% TYPE Coefficient category
% -------------------------------------
% 'a' Approximation coefficients
% 'h' Horizontal details
% 'v' Vertical details
% 'd' Diagonal details
%
% [C, S] is a wavelet data structure.
% N specifies a decomposition level (ignored if TYPE = 'a').
%
% See also WAVEWORK, WAVECUT, and WAVEPASTE.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.4 $ $Date: 2003/10/13 01:20:41 $
error(nargchk(3, 4, nargin));
if nargin == 4
y = wavework('copy', type, c, s, n);
else
y = wavework('copy', type, c, s);
end
wavepaste.m
%wavepaste源程序
function nc=wavepaste(type,c,s,n,x)
%wavepaste是在小波重构结构是投入的系数
%粘贴x之后返回一个新的重构结构
%输入:
%类型 系数类型
%'a' 近似值系数
%'h' 水平细节
%'v' 垂直细节
%'d' 对角线细节
%[c,s]是一个小波数据结构。
%n是指定的重构水平(type='a'则忽略)。
%x是二维近似值或者细节系数矩阵
error(nargchk(5,5,nargin))
nc=wavework('paste',type,c,s,n,x);
wavefast.m
function [c, s] = wavefast(x, n, varargin)
%WAVEFAST Perform multi-level 2-dimensional fast wavelet transform.
% [C, L] = WAVEFAST(X, N, LP, HP) performs a 2D N-level FWT of
% image (or matrix) X with respect to decomposition filters LP and
% HP.
%
% [C, L] = WAVEFAST(X, N, WNAME) performs the same operation but
% fetches filters LP and HP for wavelet WNAME using WAVEFILTER.
%
% Scale parameter N must be less than or equal to log2 of the
% maximum image dimension. Filters LP and HP must be even. To
% reduce border distortion, X is symmetrically extended. That is,
% if X = [c1 c2 c3 ... cn] (in 1D), then its symmetric extension
% would be [... c3 c2 c1 c1 c2 c3 ... cn cn cn-1 cn-2 ...].
%
% OUTPUTS:
% Matrix C is a coefficient decomposition vector:
%
% C = [ a(n) h(n) v(n) d(n) h(n-1) ... v(1) d(1) ]
%
% where a, h, v, and d are columnwise vectors containing
% approximation, horizontal, vertical, and diagonal coefficient
% matrices, respectively. C has 3n + 1 sections where n is the
% number of wavelet decompositions.
%
% Matrix S is an (n+2) x 2 bookkeeping matrix:
%
% S = [ sa(n, :); sd(n, :); sd(n-1, :); ... ; sd(1, :); sx ]
%
% where sa and sd are approximation and detail size entries.
%
% See also WAVEBACK and WAVEFILTER.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/10/13 01:14:17 $
% Check the input arguments for reasonableness.
error(nargchk(3, 4, nargin));
if nargin == 3
if ischar(varargin{
1})
[lp, hp] = wavefilter(varargin{
1}, 'd');
else
error('Missing wavelet name.');
end
else
lp = varargin{
1}; hp = varargin{
2};
end
fl = length(lp); sx = size(x);
if (ndims(x) ~e799bee5baa6e997aee7ad94e58685e5aeb931333337383235= 2) | (min(sx) < 2) | ~isreal(x) | ~isnumeric(x)
error('X must be a real, numeric matrix.');
end
if (ndims(lp) ~= 2) | ~isreal(lp) | ~isnumeric(lp) ...
| (ndims(hp) ~= 2) | ~isreal(hp) | ~isnumeric(hp) ...
| (fl ~= length(hp)) | rem(fl, 2) ~= 0
error(['LP and HP must be even and equal length real, ' ...
'numeric filter vectors.']);
end
if ~isreal(n) | ~isnumeric(n) | (n < 1) | (n > log2(max(sx)))
error(['N must be a real scalar between 1 and ' ...
'log2(max(size((X))).']);
end
% Init the starting output data structures and initial approximation.
c = []; s = sx; app = double(x);
% For each decomposition ...
for i = 1:n
% Extend the approximation symmetrically.
[app, keep] = symextend(app, fl);
% Convolve rows with HP and downsample. Then convolve columns
% with HP and LP to get the diagonal and vertical coefficients.
rows = symconv(app, hp, 'row', fl, keep);
coefs = symconv(rows, hp, 'col', fl, keep);
c = [coefs(:)' c]; s = [size(coefs); s];
coefs = symconv(rows, lp, 'col', fl, keep);
c = [coefs(:)' c];
% Convolve rows with LP and downsample. Then convolve columns
% with HP and LP to get the horizontal and next approximation
% coeffcients.
rows = symconv(app, lp, 'row', fl, keep);
coefs = symconv(rows, hp, 'col', fl, keep);
c = [coefs(:)' c];
app = symconv(rows, lp, 'col', fl, keep);
end
% Append final approximation structures.
c = [app(:)' c]; s = [size(app); s];
%-------------------------------------------------------------------%
function [y, keep] = symextend(x, fl)
% Compute the number of coefficients to keep after convolution
% and downsampling. Then extend x in both dimensions.
keep = floor((fl + size(x) - 1) / 2);
y = padarray(x, [(fl - 1) (fl - 1)], 'symmetric', 'both');
%-------------------------------------------------------------------%
function y = symconv(x, h, type, fl, keep)
% Convolve the rows or columns of x with h, downsample,
% and extract the center section since symmetrically extended.
if strcmp(type, 'row')
y = conv2(x, h);
y = y(:, 1:2:end);
y = y(:, fl / 2 + 1:fl / 2 + keep(2));
else
y = conv2(x, h');
y = y(1:2:end, :);
y = y(fl / 2 + 1:fl / 2 + keep(1), :);
end
wavezero.m
function [nc, g8] = wavezero(c, s, l, wname)
%WAVEZERO Zeroes wavelet transform detail coefficients.
% [NC, G8] = WAVEZERO(C, S, L, WNAME) zeroes the level L detail
% coefficients in wavelet decomposition structure [C, S] and
% computes the resulting inverse transform with respect to WNAME
% wavelets.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.4 $ $Date: 2003/10/13 01:31:35 $
[nc, foo] = wavecut('h', c, s, l);
[nc, foo] = wavecut('v', nc, s, l);
[nc, foo] = wavecut('d', nc, s, l);
i = waveback(nc, s, wname);
g8 = im2uint8(mat2gray(i));
figure; imshow(g8);
waveback.m
function [varargout] = waveback(c, s, varargin)
%WAVEBACK Performs a multi-level two-dimensional inverse FWT.
% [VARARGOUT] = WAVEBACK(C, S, VARARGIN) computes a 2D N-level
% partial or complete wavelet reconstruction of decomposition
% structure [C, S].
%
% SYNTAX:
% Y = WAVEBACK(C, S, 'WNAME'); Output inverse FWT matrix Y
% Y = WAVEBACK(C, S, LR, HR); using lowpass and highpass
% reconstruction filters (LR and
% HR) or filters obtained by
% calling WAVEFILTER with 'WNAME'.
%
% [NC, NS] = WAVEBACK(C, S, 'WNAME', N); Output new wavelet
% [NC, NS] = WAVEBACK(C, S, LR, HR, N); decomposition structure
% [NC, NS] after N step
% reconstruction.
%
% See also WAVEFAST and WAVEFILTER.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/10/13 01:29:36 $
% Check the input and output arguments for reasonableness.
error(nargchk(3, 5, nargin));
error(nargchk(1, 2, nargout));
if (ndims(c) ~= 2) | (size(c, 1) ~= 1)
error('C must be a row vector.');
end
if (ndims(s) ~= 2) | ~isreal(s) | ~isnumeric(s) | (size(s,2) ~= 2)
error('S must be a real, numeric two-column array.');
end
elements = prod(s, 2);
if (length(c) < elements(end)) | ...
~(elements(1) + 3 * sum(elements(2:end - 1)) >= elements(end))
error(['[C S] must be a standard wavelet ' ...
'decomposition structure.']);
end
% Maximum levels in [C, S].
nmax = size(s, 1) - 2;
% Get third input parameter and init check flags.
wname = varargin{
1}; filterchk = 0; nchk = 0;
switch nargin
case 3
if ischar(wname)
[lp, hp] = wavefilter(wname, 'r'); n = nmax;
else
error('Undefined filter.');
end
if nargout ~= 1
error('Wrong number of output arguments.');
end
case 4
if ischar(wname)
[lp, hp] = wavefilter(wname, 'r');
n = varargin{
2}; nchk = 1;
else
lp = varargin{
1}; hp = varargin{
2};
filterchk = 1; n = nmax;
if nargout ~= 1
error('Wrong number of output arguments.');
end
end
case 5
lp = varargin{
1}; hp = varargin{
2}; filterchk = 1;
n = varargin{
3}; nchk = 1;
otherwise
error('Improper number of input arguments.');
end
fl = length(lp);
if filterchk % Check filters.
if (ndims(lp) ~= 2) | ~isreal(lp) | ~isnumeric(lp) ...
| (ndims(hp) ~= 2) | ~isreal(hp) | ~isnumeric(hp) ...
| (fl ~= length(hp)) | rem(fl, 2) ~= 0
error(['LP and HP must be even and equal length real, ' ...
'numeric filter vectors.']);
end
end
if nchk & (~isnumeric(n) | ~isreal(n)) % Check scale N.
error('N must be a real numeric.');
end
if (n > nmax) | (n < 1)
error('Invalid number (N) of reconstructions requested.');
end
if (n ~= nmax) & (nargout ~= 2)
error('Not enough output arguments.');
end
nc = c; ns = s; nnmax = nmax; % Init decomposition.
for i = 1:n
% Compute a new approximation.
a = symconvup(wavecopy('a', nc, ns), lp, lp, fl, ns(3, :)) + ...
symconvup(wavecopy('h', nc, ns, nnmax), ...
hp, lp, fl, ns(3, :)) + ...
symconvup(wavecopy('v', nc, ns, nnmax), ...
lp, hp, fl, ns(3, :)) + ...
symconvup(wavecopy('d', nc, ns, nnmax), ...
hp, hp, fl, ns(3, :));
% Update decomposition.
nc = nc(4 * prod(ns(1, :)) + 1:end); nc = [a(:)' nc];
ns = ns(3:end, :); ns = [ns(1, :); ns];
nnmax = size(ns, 1) - 2;
end
% For complete reconstructions, reformat output as 2-D.
if nargout == 1
a = nc; nc = repmat(0, ns(1, :)); nc(:) = a;
end
varargout{
1} = nc;
if nargout == 2
varargout{
2} = ns;
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------%
function z = symconvup(x, f1, f2, fln, keep)
% Upsample rows and convolve columns with f1; upsample columns and
% convolve rows with f2; then extract center assuming symmetrical
% extension.
y = zeros([2 1] .* size(x)); y(1:2:end, :) = x;
y = conv2(y, f1');
z = zeros([1 2] .* size(y)); z(:, 1:2:end) = y;
z = conv2(z, f2);
z = z(fln - 1:fln + keep(1) - 2, fln - 1:fln + keep(2) - 2);