HTML与CSS进阶
「查漏补缺」HTML与CSS进阶
前言
本文主要介绍H5新增内容以及CSS3中的新特性。在H5方面主要介绍拓展了哪些内容,CSS3方面介绍动画及转换。
H5新增内容
「1. 什么是HTML5」
-
定义:HTML5定义了HTML标准的最新版本,是对HTML的第五次重大修改,号称下一代的HTML。
-
两个概念:
-
- 是一个新版本的HTML语言,定义了新的标签、特性和属性
- 拥有一个强大的技术集,这些技术集是指:HTML5、CSS3、JavaScript,这也是广义上的HTML5。
「2. HTML5拓展了哪些内容」
- 语义化标签
- 本地存储
- 兼容特性
- 2D、3D
- 动画、过渡
- CSS3特性
- 性能与集成
「3. HTML5的现状」
绝大多数新的属性,都已经被浏览器所支持,最新版本的浏览器已经开始陆续支持最新的特性,总的来说:HTML5已经是大势所趋。
HTML5新增标签
「1. 什么是语义化」
语义化是指用HTML写出符合内容的结构化(内容语义化),选择合适的标签(代码语义化),能够便于开发者阅读和写出更优雅的代码的同时让浏览器的爬虫和机器很好地解析。
「2. 新增了哪些语义化标签」
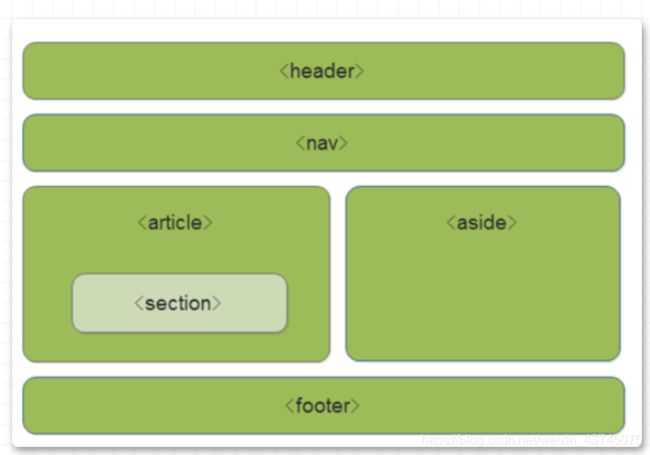
header— 头部标签nav— 导航标签article— 内容标签section— 块级标签aside— 侧边栏标签footer— 尾部标签
-
多媒体标签有两个,分别是音频 audio和视频video。
-
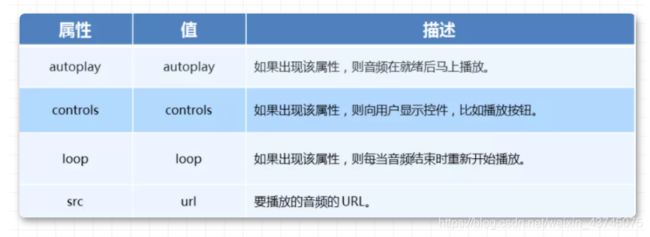
audio 标签说明 -
- 可以在不使用标签的情况下,也能够原生的支持音频格式文件的播放,
- 但是:播放的格式是有限的。
-
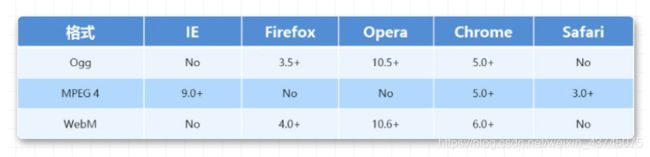
audio支持的音频格式
- audio 的参数
<audio controls>
<!-- 注意:在 chrome 浏览器中已经禁用了 autoplay 属性 -->
<!-- <audio src="./media/snow.mp3" controls autoplay></audio> -->
<!--
因为不同浏览器支持不同的格式,所以我们采取的方案是这个音频准备多个文件 -->
<source src="myAudio.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
<source src="myAudio.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
<p>Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio. Here is
a <a href="myAudio.mp4">link to the audio</a> instead.</p>
</audio>
「4. 新增多媒体视频标签」
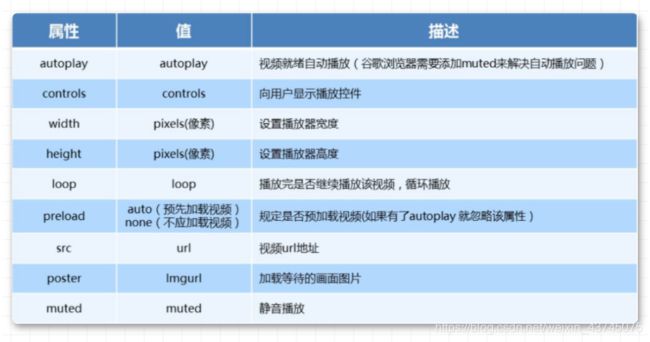
- video视频标签目前支持三种格式
- 语法格式
<video src="./media/video.mp4" controls="controls"></video>
- video的参数
- video代码演示
<body>
<!-- <video src="./media/video.mp4" controls="controls"></video> -->
<!-- 谷歌浏览器禁用了自动播放功能,如果想自动播放,需要添加 muted 属性 -->
<video controls="controls" autoplay muted loop poster="./media/pig.jpg">
<source src="./media/video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="./media/video.ogg" type="video/ogg">
</video>
</body>
-
多媒体标签总结 -
- 音频标签和视频标签使用基本一致
- 多媒体标签在不同浏览器下情况不同,存在兼容性问题
- 谷歌浏览器把音频和视频标签的自动播放都禁止了
- 谷歌浏览器中视频添加muted属性就可以自己播放了
- 注意:重点记住使用方法及自动播放即可,其他属性在使用时查找对应的手册
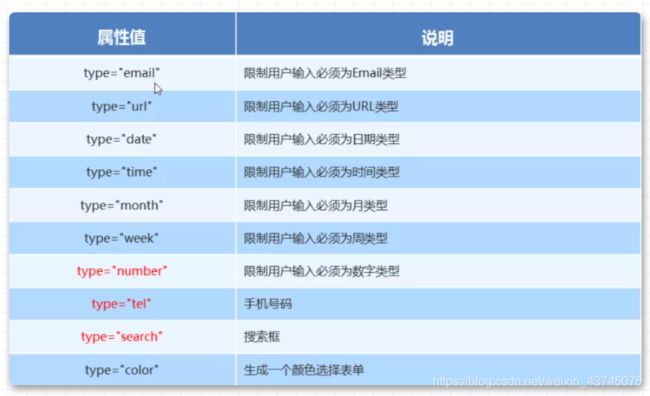
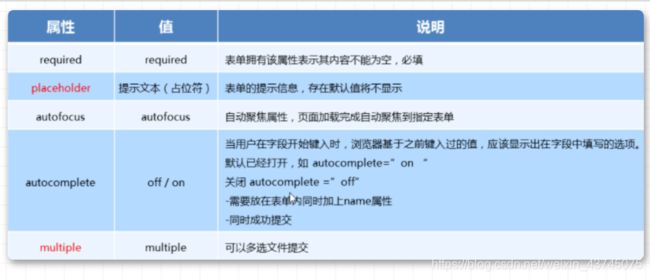
「5. 新增input标签」
CSS3新增
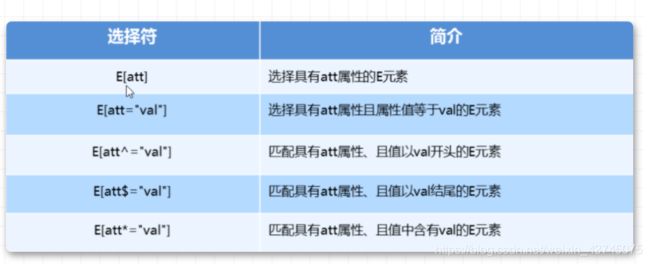
「1. CSS3属性选择器」
button {
cursor: pointer;
}
button[disabled] {
cursor: default;
}
input[type=search] {
color: skyblue;
}
span[class^=black] {
color: lightgreen;
}
span[class$=black] {
color: lightsalmon;
}
span[class*=black] {
color: lightseagreen;
}
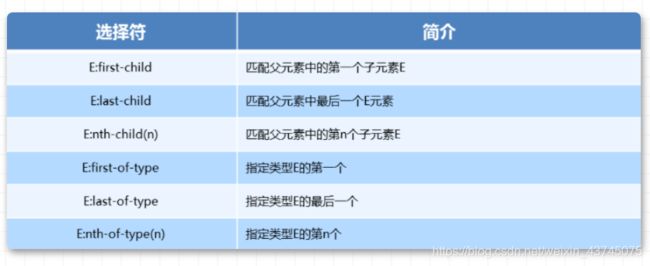
「2. 结构伪类选择器」
ul li:first-child {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
ul li:last-child {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
ul li:nth-child(3) {
background-color: aqua;
}
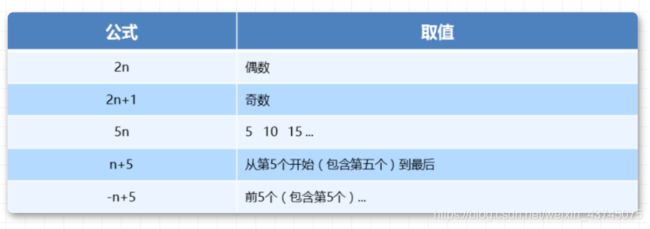
- nth-child(n) 参数n详解
- 注意:本质上就是选中第几个子元素
- n 可以是数字、关键字、公式
- n 如果是数字,就是选中第几个
- 常见的关键字有
even偶数、odd奇数- 常见的公式如下(如果 n 是公式,则从 0 开始计算)
- 但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
<style>
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(even) {
background-color: aquamarine;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
/*n 是公式,从 0 开始计算 */
ul li:nth-child(n) {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n) {
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n + 1) {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/* 选择第 0 5 10 15, 应该怎么选 */
ul li:nth-child(5n) {
background-color: orangered;
}
/* n + 5 就是从第5个开始往后选择 */
ul li:nth-child(n + 5) {
background-color: peru;
}
/* -n + 5 前五个 */
ul li:nth-child(-n + 5) {
background-color: tan;
}
</style>
-
nth-child与nth-of-type区别 -
nth-child选择父元素里面的第几个子元素,不管是第几个类型nth-of-type选择指定类型的元素
<style>
div :nth-child(1) {
background-color: lightblue;
}
div :nth-child(2) {
background-color: lightpink;
}
div span:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
div span:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: #fff;
}
</style>
「3. 伪元素选择器」
-
伪元素选择器注意事项
-
before和after必须有content属性before在内容前面,after 在内容后面before和after创建的是一个元素,但是属于行内元素- 创建出来的元素在
Dom中查找不到,所以称为伪元素 - 伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为 1
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid lightcoral;
}
div::after,
div::before {
width: 20px;
height: 50px;
text-align: center;
display: inline-block;
}
div::after {
content: '德';
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
div::before {
content: '道';
background-color: mediumaquamarine;
}
</style>
伪元素字体图标
p {
position: relative;
width: 220px;
height: 22px;
border: 1px solid lightseagreen;
margin: 60px;
}
p::after {
content: '\ea50';
font-family: 'icomoon';
position: absolute;
top: -1px;
right: 10px;
}
「4. 2D 转换之translate」
-
2D转换
-
- 2D转换是改变标签在二维平面上的位置和形状
- 移动:translate
- 旋转:rotate
- 缩放:scale
-
translate语法
-
- x就是X轴上水平移动
- y就是y轴上水平移动
transform: translate(x, y)
transform: translateX(n)
transfrom: translateY(n)
-
重点知识点
-
- 2D的移动主要是指水平、垂直方向上的移动
- translate最大的优点就是不影响其他元素的位置
- translate中的100%单位,是相对于本身的宽度和高度来进行计算的
- 行内标签没有效果
div {
background-color: lightseagreen;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* 平移 */
/* 水平垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 100px); */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 0) */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(0, 100px) */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translateX(100px); */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
transform: translateY(100px);
/*百分比用法*/
transform: translateY(100%);
}
让一个盒子水平垂直居中
div {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
/* 1. 我们tranlate里面的参数是可以用 % */
/* 2. 如果里面的参数是 % 移动的距离是 盒子自身的宽度或者高度来对比的 */
/* 这里的 50% 就是 50px 因为盒子的宽度是 100px */
/* transform: translateX(50%); */
}
p {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
/1.* margin-top: -100px;
margin-left: -100px; */
/2.* translate(-50%, -50%)
盒子往上走自己高度的一半 */
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
span {
/* translate 对于行内元素是无效的 */
transform: translate(300px, 300px);
}
「5. 2D 转换之rotate」
-
rotate 旋转
-
- 2D旋转指的是让元素在二维平面内顺时针或者逆时针旋转
/* 单位是:deg */
img:hover {
transform: rotate(360deg)
}
-
rotate语法
-
rotate里面跟度数,单位是deg- 角度为正时,顺时针,角度为负时,逆时针
- 默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心点
-
设置元素旋转的中心的(transform-origin)
transform-origin: x y;
-
注意 -
- 后面的参数 x 和 y 用空格隔开
- x y 默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心(50% 50%),等价于center center
- 还可以给x y 设置像素或者方位名词(top、bottom、left、right、center)
「6. 2D 转换之scale」
- scale的作用:用来控制元素的放大与缩小
transform: scale(x, y)
-
知识要点: -
- 注意,x与y之间用逗号进行分隔
transform: scale(1, 1): 宽高都放大一倍,相当于没有放大transform: scale(2, 2): 宽和高都放大了二倍transform: scale(2): 如果只写了一个参数,第二个参数就和第一个参数一致transform:scale(0.5, 0.5): 缩小scale最大的优势:可以设置转换中心点缩放,默认以中心点缩放,而且不影响其他盒子
div:hover {
/* 注意,数字是倍数的含义,所以不需要加单位 */
/* transform: scale(2, 2) */
/* 实现等比缩放,同时修改宽与高 */
/* transform: scale(2) */
/* 小于 1 就等于缩放*/
transform: scale(0.5, 0.5)
}
「7. 2D 转换综合写法以及顺序问题」
知识要点
- 同时使用多个转换,其格式为
transform: translate() rotate() scale() - 顺序会影响到转换的效果(先旋转会改变坐标轴方向)
- 当我们同时有位置或者其他属性的时候,要将位移放到最前面
div:hover {
transform: translate(200px, 0) rotate(360deg) scale(1.2)
}
动画(animation)
**「动画」**是CSS3中最具颠覆性的特征之一,可通过设置多个节点来精确的控制一个或者一组动画,从而实现复杂的动画效果。
「动画的使用」
- 先定义动画
- 再调用定义好的动画
/*1. 定义动画*/
@keyframes 动画名称 {
0% {
width: 100px;
}
100% {
width: 200px
}
}
div {
/* 调用动画 */
animation-name: 动画名称;
/* 持续时间 */
animation-duration: 持续时间;
}
「动画序列」
- 0% 是动画的开始,100 % 是动画的完成,这样的规则就是动画序列
- 在 @keyframs中规定某项 CSS 样式,就由创建当前样式逐渐改为新样式的动画效果
- 动画是使元素从一个样式逐渐变化为另一个样式的效果,可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数
- 用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用
from和to,等同于 0% 和 100%
「动画常见属性」
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aquamarine;
/* 动画名称 */
animation-name: move;
/* 动画花费时长 */
animation-duration: 2s;
/* 动画速度曲线 */
animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;
/* 动画等待多长时间执行 */
animation-delay: 2s;
/* 规定动画播放次数 infinite: 无限循环 */
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
/* 是否逆行播放 */
animation-direction: alternate;
/* 动画结束之后的状态 */
animation-fill-mode: forwards;
}
div:hover {
/* 规定动画是否暂停或者播放 */
animation-play-state: paused;
}
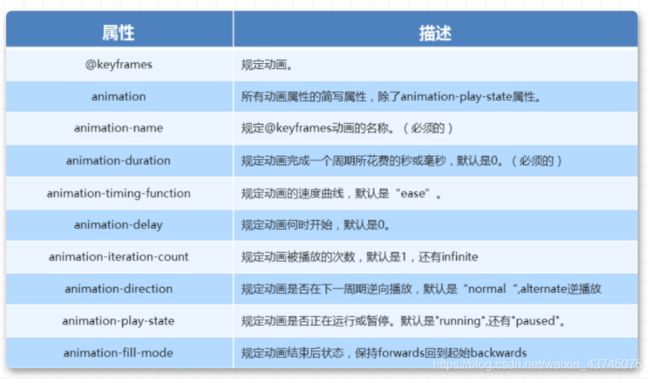
「动画简写方式」
/* animation: 动画名称 持续时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向 起始与结束状态 */
animation: name duration timing-function delay iteration-count direction fill-mode
知识要点
- 简写属性里面不包含
animation-paly-state - 暂停动画
animation-paly-state: paused; 经常和鼠标经过等其他配合使用 - 要想动画走回来,而不是直接调回来:
animation-direction: alternate - 盒子动画结束后,停在结束位置:
animation-fill-mode: forwards
animation: move 2s linear 1s infinite alternate forwards;
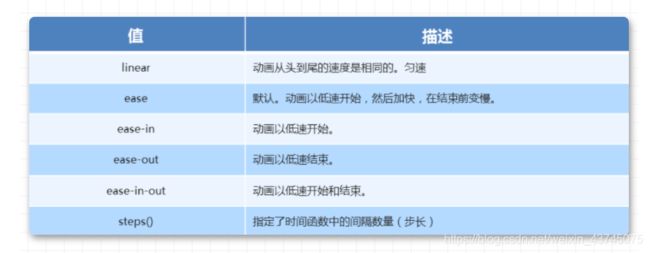
「速度曲线细节」
animation-timing-function: 规定动画的速度曲线,默认是ease
/*打字机效果*/
div {
width: 0px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
background-color: aquamarine;
animation: move 4s steps(24) forwards;
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
width: 0px;
}
100% {
width: 480px;
}
}
CSS 过渡transition
通过过渡transition,可以让web前端开发人员不需要javascript就可以实现简单的动画交互效果。
深入理解CSS过渡transition
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/5347930.html
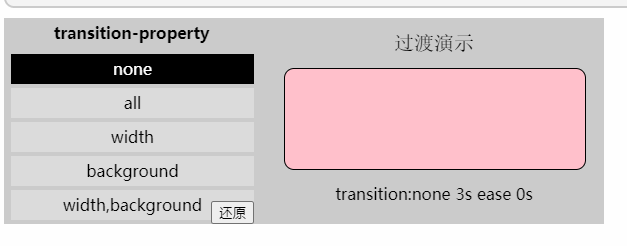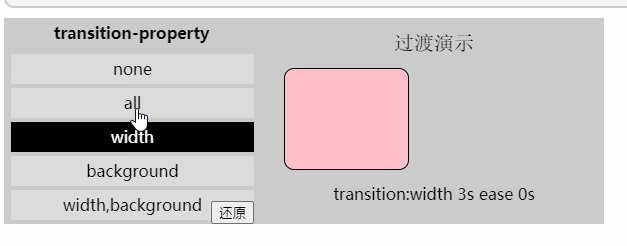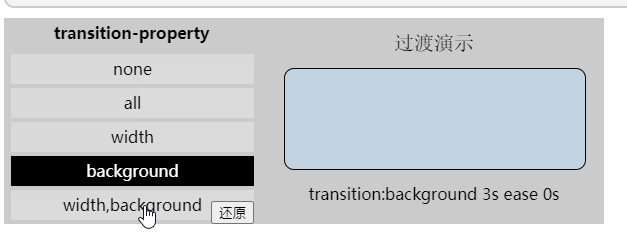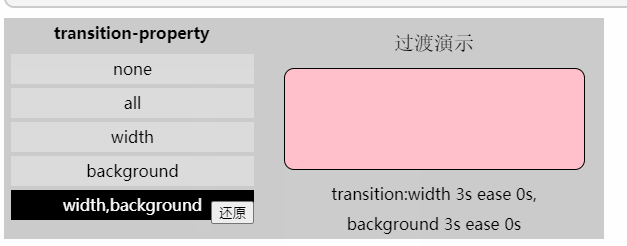
「定义」过渡transition是一个复合属性,包括transition-property、transition-duration、transition-timing-function、transition-delay这四个子属性。通过这四个子属性的配合来完成一个完整的过渡效果。
transition-property: 过渡属性(默认值为all)
transition-duration: 过渡持续时间(默认值为0s)
transiton-timing-function: 过渡函数(默认值为ease函数)
transition-delay: 过渡延迟时间(默认值为0s)
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
transition-duration: 3s;
/* 以下三值为默认值,稍后会详细介绍 */
transition-property: all;
transition-timing-function: ease;
transition-delay: 0s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
~~~html
"test">
「复合属性」 过渡transition的这四个子属性只有是必需且不能为0。其中,和都是时间。当两个时间同时出现时,第一个是,第二个是;当只有一个时间时,它是,而为默认值0s
-
注意:
-
- transition的这四个子属性之间不能用逗号隔开,只能用空格隔开。因为逗号隔开的代表不同的属性(transition属性支持多值,多值部分稍后介绍);而空格隔开的代表不同属性的四个关于过渡的子属性。
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*代表持续时间为2s,延迟时间为默认值0s*/
transition;2s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
"test">
延迟时间delay 案例
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*代表持续时间为1s,延迟时间为2s*/
transition: 1s 2s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
"test">
「过渡属性」
- 值: none | all | [,]
- 初始值: all
- 应用于: 所有元素
- 继承性: 无
none: 没有指定任何样式
all: 默认值,表示指定元素所有支持transition-property属性的样式
: 可过渡的样式,可用逗号分开写多个样式
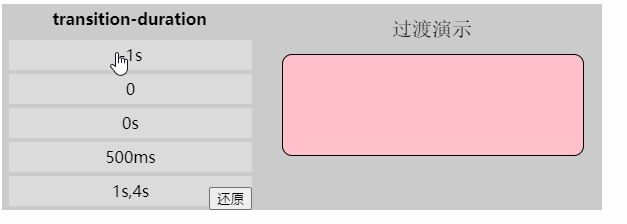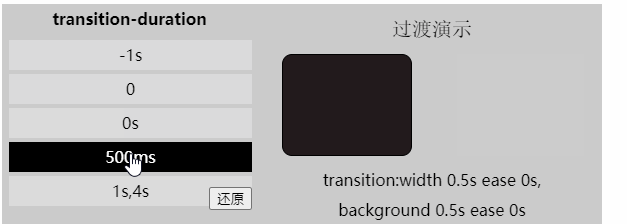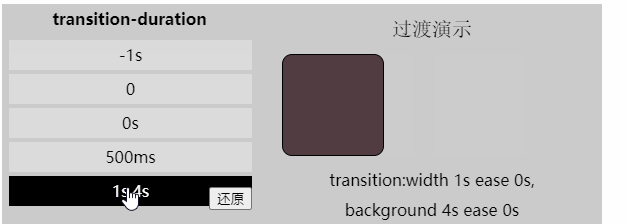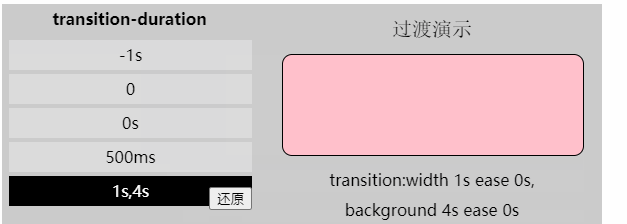
「过渡持续时间」
- 值: [,]*
- 初始值: 0s
- 应用于: 所有元素
- 继承性: 无
- [注意]该属性不能为负值
- [注意]若该属性为0s则为默认值,若为0则为无效值。所以必须带单位
- [注意]该值为单值时,即所有过渡属性都对应同样时间;该值为多值时,过渡属性按照顺序对应持续时间
/*DEMO中的过渡属性值*/
transition-property: width,background;
过渡时间函数用于定义元素过渡属性随时间变化的过渡速度变化效果
- 值: [,]*
- 初始值: ease
- 应用于: 所有元素
- 继承性: 无
「取值」 过渡时间函数共三种取值,分别是关键字、steps函数和bezier函数
「关键字」 其实是bezier函数或steps函数的特殊值
ease: 开始和结束慢,中间快。
linear: 匀速。
ease-in: 开始慢。
ease-out: 结束慢。
ease-in-out: 和ease类似,但比ease幅度大。
3D转换
认识3D转换
「3D的特点」 近大远小,物体和面遮挡不可见
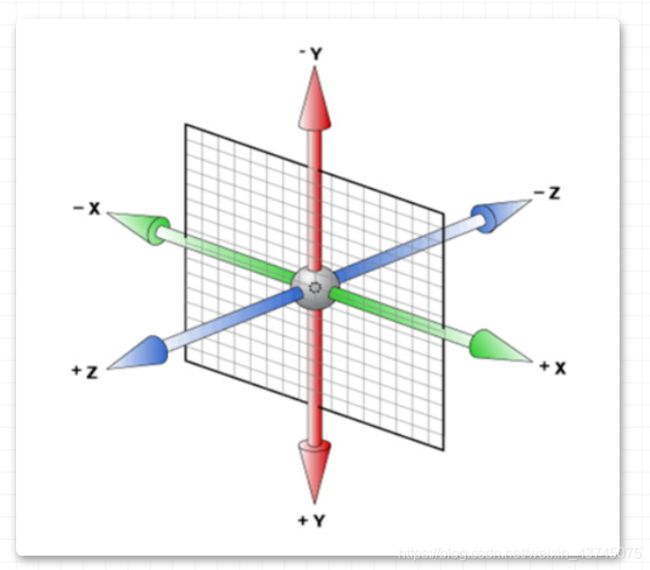
「三维坐标系」
- x 轴:水平向右 –
注意:x 轴右边是正值,左边是负值 - y 轴:垂直向下 –
注意:y 轴下面是正值,上面是负值 - z 轴:垂直屏幕 –
注意:往外边的是正值,往里面的是负值
3D转换
1. 3D 转换知识要点
3D位移:translate3d(x, y, z)3D旋转:rotate3d(x, y, z)透视:perspctive3D呈现transfrom-style
2. 3D 移动translate3d
3D移动就是在2D移动的基础上多加了一个可以移动的方向,就是 z 轴方向transform: translateX(100px):仅仅是在 x 轴上移动transform: translateY(100px):仅仅是在 y 轴上移动transform: translateZ(100px):仅仅是在 z 轴上移动transform: translate3d(x, y, z):其中x、y、z 分别指要移动的轴的方向的距离注意:x, y, z 对应的值不能省略,不需要填写用 0 进行填充
transform: translate3d(100px, 100px, 100px)
/* 注意:x, y, z 对应的值不能省略,不需要填写用 0 进行填充 */
transform: translate3d(100px, 100px, 0)
透视perspective
-
知识点讲解
-
- 如果想要网页产生
3D效果需要透视(理解成3D物体投影的2D平面上) - 实际上模仿人类的视觉位置,可视为安排一只眼睛去看
- 透视也称为视距,所谓的视距就是人的眼睛到屏幕的距离
- 距离视觉点越近的在电脑平面成像越大,越远成像越小
- 透视的单位是像素
- 如果想要网页产生
-
知识要点
-
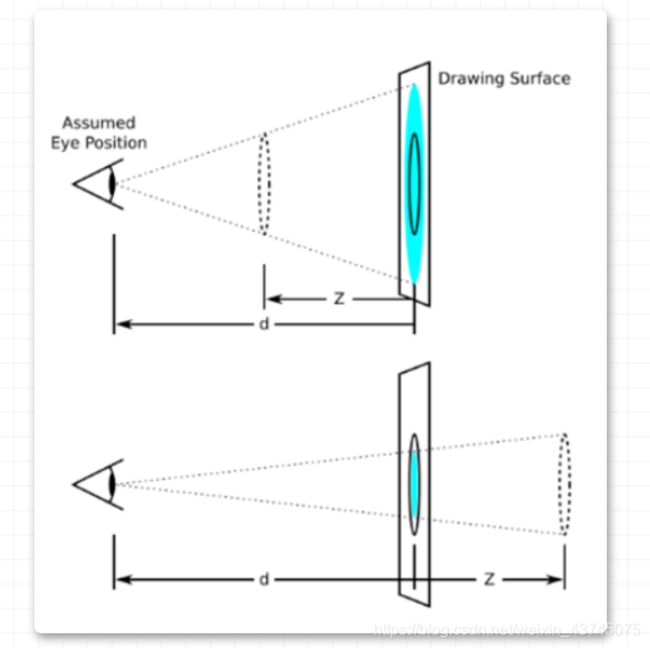
- 透视需要写在被视察元素的父盒子上面
- 注意下方图片
- d:就是视距,视距就是指人的眼睛到屏幕的距离
- z:就是 z 轴,z 轴越大(正值),我们看到的物体就越大
body {
/*透视需要写在被视察元素的父盒子上面 */
perspective: 1000px;
}
translateZ与perspective的区别
perspecitve给父级进行设置视距的,translateZ给 子元素进行设置不同的大小
3D 旋转rotateX
3D 旋转指可以让元素在三维平面内沿着 x 轴、y 轴、z 轴 或者自定义轴进行旋转
-
语法: -
- transform: rotateX(45deg) – 沿着 x 轴正方向旋转 45 度
- transform: rotateY(45deg) – 沿着 y 轴正方向旋转 45 度
- transform: rotateZ(45deg) – 沿着 z 轴正方向旋转 45 度
- transform: rotate3d(x, y, z, 45deg) – 沿着自定义轴旋转 45 deg 为角度
-
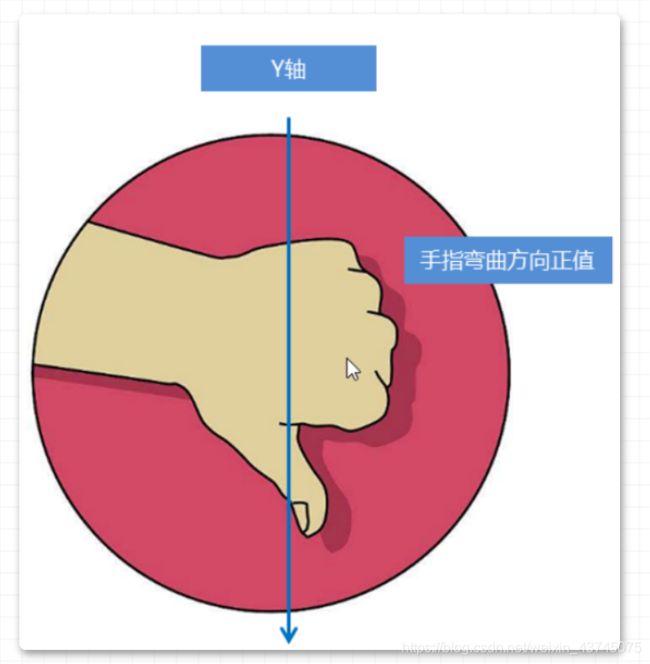
左手法则: -
- 左手的手拇指指向 x 轴的正方向
- 其余手指的弯曲方向就是该元素沿着 x 轴旋转的方向
div {
/*透视写在被视察元素的父盒子上面 */
perspective: 300px;
}
/*被观察元素*/
img {
display: block;
margin: 100px auto;
transition: all 1s;
}
img:hover {
transform: rotateX(-45deg)
}
3D 旋转rotateY
-
左手法则: -
- 左手的拇指指向 y 轴的正方向
- 其余的手指弯曲方向就是该元素沿着 y 轴旋转的方向(正值)
div {
perspective: 500px;
}
img {
display: block;
margin: 100px auto;
transition: all 1s;
}
img:hover {
transform: rotateY(180deg)
}
3D 旋转rotateZ
div {
perspective: 500px;
}
img {
display: block;
margin: 100px auto;
transition: all 1s;
}
img:hover {
transform: rotateZ(180deg)
}
「rotate3d」
-
transform: rotate3d(x, y, z, deg) – 沿着自定义轴旋转 deg 为角度
-
x, y, z 表示旋转轴的矢量,是标识你是否希望沿着该轴进行旋转,最后一个标识旋转的角度
-
- transform: rotate3d(1, 1, 0, 180deg) – 沿着对角线旋转 45deg
- transform: rotate3d(1, 0, 0, 180deg) – 沿着 x 轴旋转 45deg
div {
perspective: 500px;
}
img {
display: block;
margin: 100px auto;
transition: all 1s;
}
img:hover {
transform: rotate3d(1, 1, 0, 180deg)
}
3D呈现transform-style
- 控制子元素是否开启三维立体环境
transform-style: flat代表子元素不开启3D立体空间,默认的transform-style: preserve-3d子元素开启立体空间- 代码写给父级,但是影响的是子盒子
<body>
<div class="box">
<div>div>
<div>div>
div>
body>
<style>
body {
perspective: 500px;
}
.box {
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
margin: 100px auto;
transition: all 2s;
/* 让子元素保持3d立体空间环境 */
transform-style: preserve-3d;
}
.box:hover {
transform: rotateY(60deg);
}
.box div {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: pink;
}
.box div:last-child {
background-color: purple;
transform: rotateX(60deg);
}
style>