公平锁与非公平锁是指,多个线程在获取同一把锁的策略,是按照先到先得还是直接竞争。先到先得的策略就是公平锁,排队对所有的线程来说是公平的,直接竞争的策略则是非公平的。

在调用ReenterantLock的构造函数的时候决定是构造一个公平锁还是非公平锁。
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}来看获取锁的过程:
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
lock.lock();点进去看,是调用了sync的lock方法
这里就是对应了我们的公平锁/非公平锁的lock方法。
到这里没有什么大的差异,无非是非公平锁多了一个步骤。cas操作去尝试获取锁,成功了设置owner线程为当前线程。失败了再调用acquire方法获取锁。
那接下来继续看两种锁的acquire方法,两个方法都来到了aqs的acquire方法。
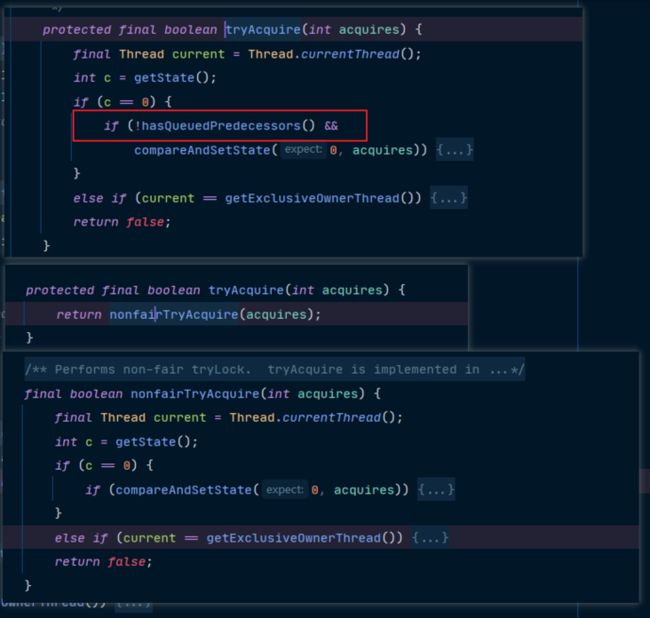
点进去那些方法,所有方法都进入了aqs实现的步骤,只有tryAcquire方法有不同的实现。
进去看,公平锁只是多了 hasQueuedPredecessors这个方法。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) { // 当前锁的状态是无所状态
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && // 判断队列中是否有前驱节点,若果有前驱节点,就不会执行下面的代码,不会去获取锁
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 使用cas尝试获取锁
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 设置owner线程为当前线程
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 持有锁的线程为当前线程
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc); // 更新sate(重入锁的原理)
return true;
}
return false;
}以上分析了公平锁和非公平锁的一个不同。
下面以非公平锁分析加锁的过程
获取锁的过程:
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal * acquire on failure. */final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) // 尝试用cas来获取锁(改变state的值)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); // 设置owner线程为当前线程
else
acquire(1); // 如果锁的状态不为0,被其他线程持有,尝试获取锁
}public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
} tryAcquire(arg)方法是尝试获取锁。
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}原理和上面公平锁的tryAcquire方法一致。
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))方法:
addWaiter方法:
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}创建一个node,入队,并返回该NodeacquireQueued再尝试获取锁
非公平锁解锁的过程:
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) { // 尝试去释放锁
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) // h头结点为空,并且state不等于0
unparkSuccessor(h); // 去唤醒后继节点
return true;
}
return false;
}protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); // 设置owner线程为空
}
setState(c); // 更新state
return free;
}