目录
一、pytest简介
1.1运行成功则在命令行显示 类名+.
1.1.1CaculateAdd.py类(定义了add()和jian() 两个方法)
1.1.2TestPytestHtmlDemo.py类(pytest运行demo:注意是Test开头)
1.1.3运行几个成功类名后面就几个.
1.1.4运行错误的展示F
1.1.5运行几个错误 类名后就展示几个F
1.2Pytest生成自带的html测试报告
1.2.1运行代码如下:
1.2.2打开123.html
1.3 pytest -x的使用等
-x出现一条测试用例失败就退出测试
-v: 丰富信息模式, 输出更详细的用例执行信息
-s:显示print内容
-q: 简化结果信息,不会显示每个用例的文件名
二、allure开源测试报告
2.1安装allure
2.1.1配置allure,环境变量path配置:新增allure的bin目录下的路径
三、pytest和alluredir的生成测试报告json
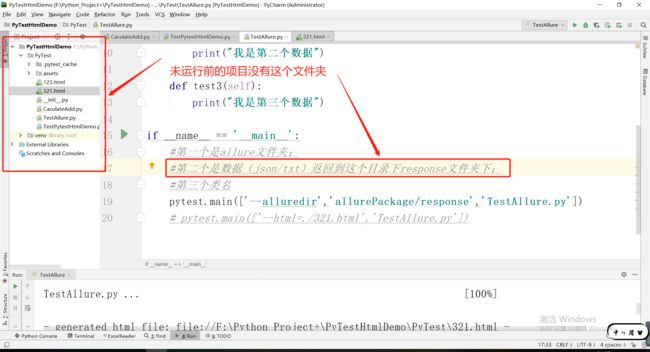
3.1运行前
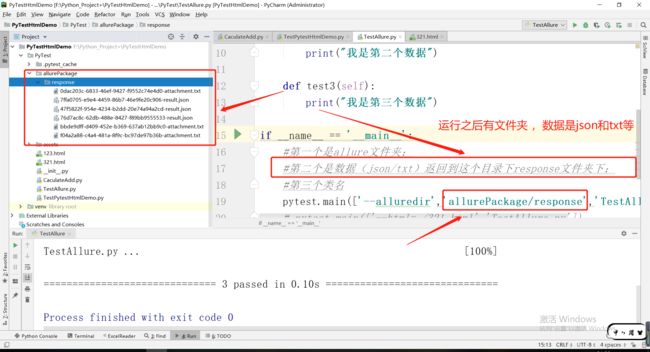
3.2运行后(多了allurePackage/response文件夹)
3.3Pytest和allure结合生成html格式的测试报告
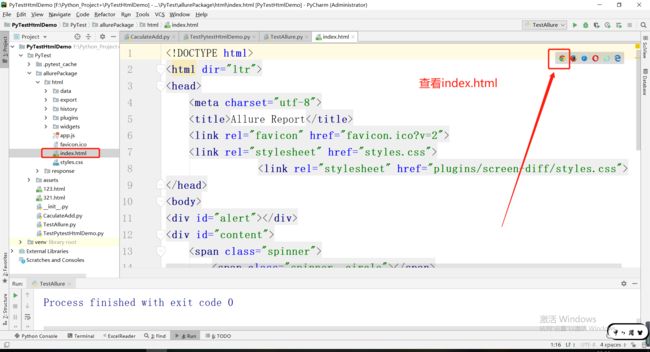
3.4index.html页面Allure测试报告
四、Allure常用的几个特性
4.1 @allure.feature使用
4.4with allure.step("用户登录"): # 用于描述测试步骤,将会输出到报告中 allure.attach("GUOYING","用户名") # 用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据,截图等
一、pytest简介
**需要安装pytest和pytest-html(生成html测试报告) **
**pip install pytest 和 pip install pytest-html **
**命名规则 **
**Pytest单元测试中的类名和方法名必须是以test开头,执行中只能找到test开头的类和方法,比unittest更加严谨 **
unittest:Setup>> setupclass teardown teardownclass
Pytest的setup, setup_class和teardown, teardown_class函数(和unittest执行效果一样) 运行于测试方法的始末,
**setup,teardown :即:运行一次测试函数会运行一次setup和teardown **
setup_class,teardown_class:运行于测试方法的始末,但是不管有多少测试函数都只执行一次setup_class和 teardown_class
1.1运行成功则在命令行显示 类名+.
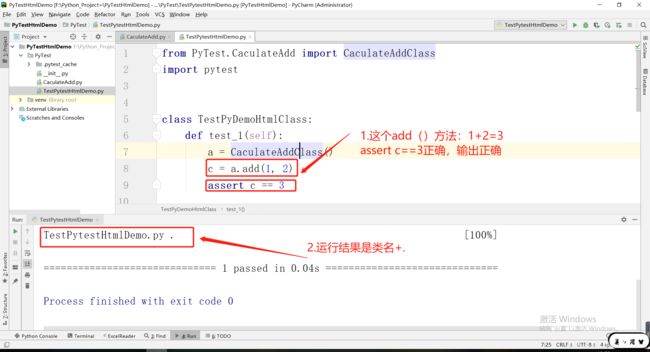
1.1.1CaculateAdd.py类(定义了add()和jian() 两个方法)
class CaculateAddClass:
def add(self,a,b):
c = a+b
return c
def jian(self,a,b):
d = a-b
return d
1.1.2TestPytestHtmlDemo.py类(pytest运行demo:注意是Test开头)
from PyTest.CaculateAdd import CaculateAddClassimport pytest
class TestPyDemoHtmlClass:
def test_1(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
c = a.add(1, 2)
assert c == 3
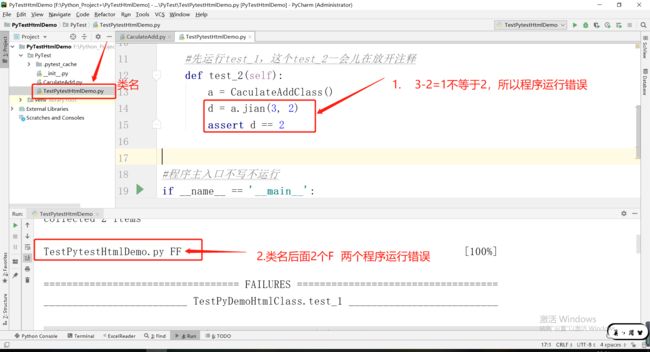
#先运行test_1,这个test_2一会儿在放开注释
# def test_2(self):
# a = CaculateAddClass()
# d = a.jian(3, 2)
# assert d == 1
#程序主入口不写不运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['TestPytestHtmlDemo.py'])#['类名']运行这个类
运行结果:(因为1+2=3,assert c==3,符合程序运行结果,正确)
. 点号,表示用例通过
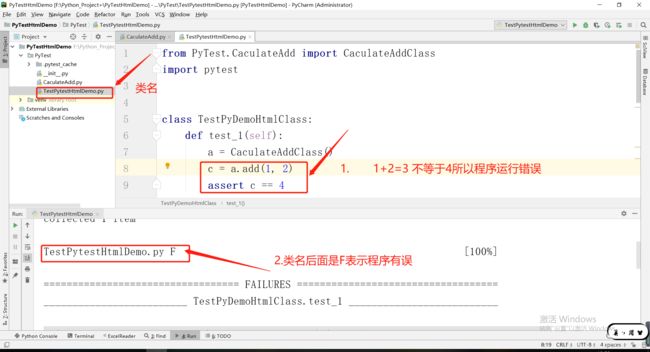
F 表示失败 Failure
E 表示用例中存在异常 Error
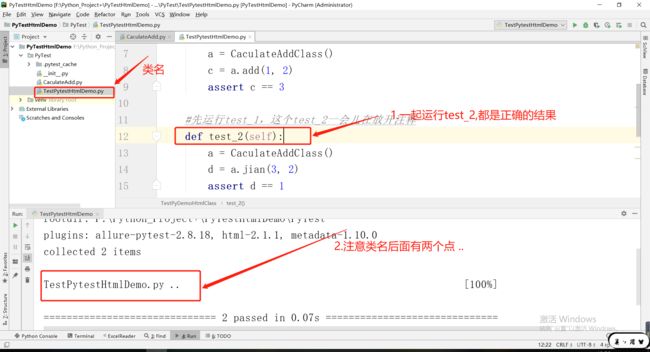
1.1.3运行几个成功类名后面就几个.
from PyTest.CaculateAdd import CaculateAddClassimport pytest
class TestPyDemoHtmlClass:
def test_1(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
c = a.add(1, 2)
assert c == 3
def test_2(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
d = a.jian(3, 2)
assert d == 1
#程序主入口不写不运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['TestPytestHtmlDemo.py'])#['类名']运行这个类
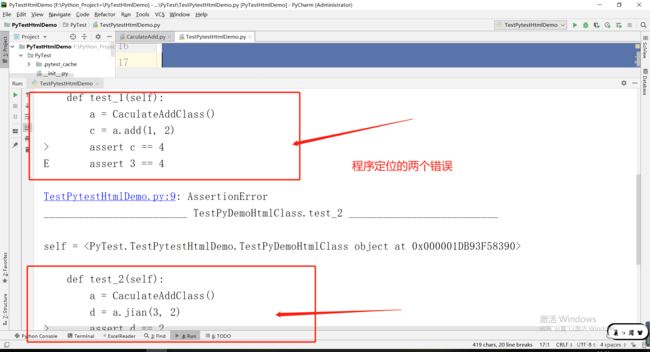
1.1.4运行错误的展示F
from PyTest.CaculateAdd import CaculateAddClassimport pytest
class TestPyDemoHtmlClass:
def test_1(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
c = a.add(1, 2)
assert c == 4
#先运行test_1,这个test_2一会儿在放开注释
# def test_2(self):
# a = CaculateAddClass()
# d = a.jian(3, 2)
# assert d == 1
#程序主入口不写不运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['TestPytestHtmlDemo.py'])#['类名']运行这个类
运行结果:
1.1.5运行几个错误 类名后就展示几个F
1.2Pytest生成自带的html测试报告
1.在Pycharm安装pytest自带的测试报告包:
pip install pytest-html2.直接执行pytest.main() 【自动查找当前目录下,以test_开头的文件或者以_test结尾的py文件】
pytest.main("模块.py") 【运行指定模块下,运行所有test开头的类和测试用例】
**3.python自带的插件 **
pytest.main(["--html=./report.html","test3.py"])
# 程序主入口不写不运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["--html=./report.html", "TestPytestHtmlDemo.py"]) # 第一个参数是html,第二个是['类名']
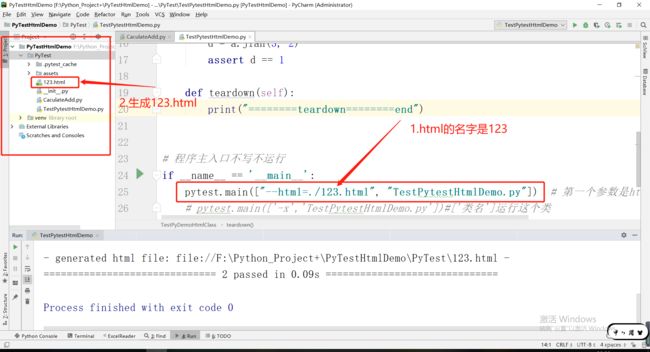
1.2.1运行代码如下:
from PyTest.CaculateAdd import CaculateAddClassimport pytest
class TestPyDemoHtmlClass:
def setup(self):
print("========setup========start")
def test_1(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
c = a.add(1, 2)
assert c == 3
def test_2(self):
a = CaculateAddClass()
d = a.jian(3, 2)
assert d == 1
def teardown(self):
print("========teardown========end")
# 程序主入口不写不运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["--html=./report.html", "TestPytestHtmlDemo.py"]) # 第一个参数是html,第二个是['类名'] # pytest.main(['-x','TestPytestHtmlDemo.py'])#['类名']运行这个类
运行结果:
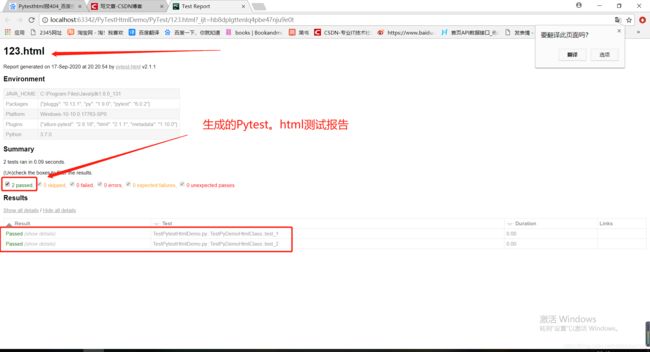
1.2.2打开123.html
1.3 pytest -x的使用等
pytest.main(['-x','--html=./report.html','t12est000.py'])
-x出现一条测试用例失败就退出测试
-v: 丰富信息模式, 输出更详细的用例执行信息
-s:显示print内容
-q: 简化结果信息,不会显示每个用例的文件名
二、allure开源测试报告
** Allure是一款轻量级并且非常灵活的开源测试报告框架。 它支持绝大多数测试框架, 例如TestNG、Pytest、JUint等。它简单易用,易于集成。**
2.1安装allure
首先要在Pycharm安装:allure-pytest是Pytest的一个插件,通过它我们可以生成Allure所需要的用于生成测试报告的数据
allure:
pip install allure-pytest
2.1.1配置allure,环境变量path配置:新增allure的bin目录下的路径
三、pytest和alluredir的生成测试报告json
import pytest class TestAllureClass:
def test1(self):
print("我是第一个数据")
def test2(self):
print("我是第二个数据")
def test3(self):
print("我是第三个数据")
if __name__ == '__main__':
#第一个是allure文件夹;
#第二个是数据(json/txt)返回到这个目录下response文件夹下;
#第三个类名
pytest.main(['--alluredir','allurePackage/response','TestAllure.py'])
# pytest.main(['--html=./321.html','TestAllure.py'])
3.1运行前
3.2运行后(多了allurePackage/response文件夹)
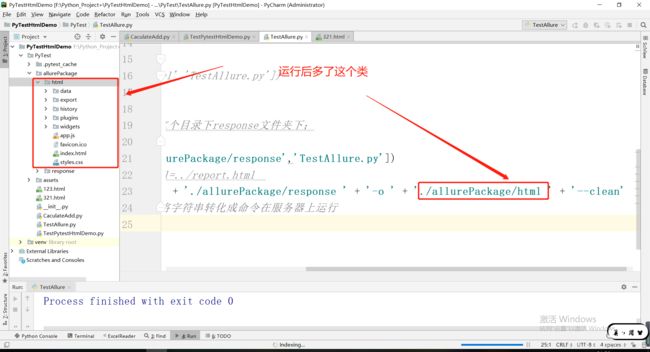
3.3Pytest和allure结合生成html格式的测试报告
pytest.main(['--alluredir','allurePackage/response','TestAllure.py']) ## 将测试报告转为html格式# --html=../report.html
split = 'allure ' + 'generate ' + './allurePackage/response ' + '-o ' + './allurePackage/html ' + '--clean' os.system(split)#system函数可以将字符串转化成命令在服务器上运行
运行前:
运行后:
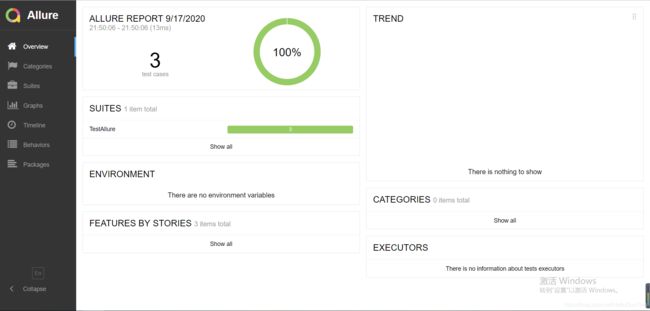
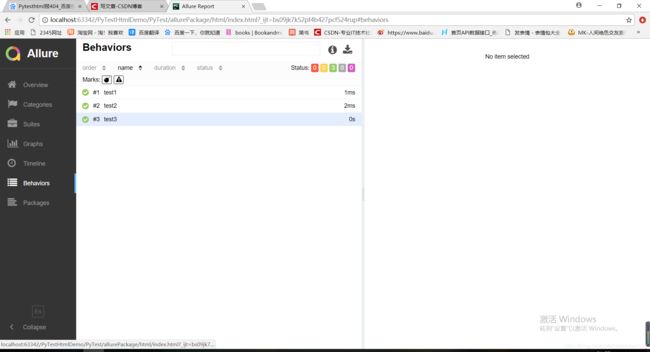
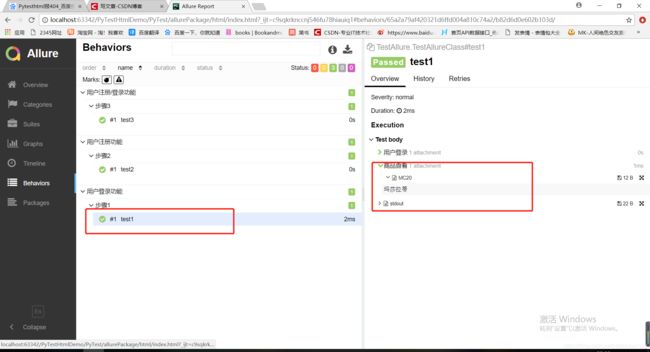
3.4index.html页面Allure测试报告
四、Allure常用的几个特性
@allure.feature # 用于描述被测试产品需求
@allure.story # 用于描述feature的用户场景,即测试需求
with allure.step(): # 用于描述测试步骤,将会输出到报告中
**allure.attach # 用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据,截图等 **
4.1 @allure.feature使用
import pytest,os,allure
class TestAllureClass:
@allure.feature("用户登录功能")
def test1(self):
print("我是第一个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册功能")
def test2(self):
print("我是第二个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册/登录功能")
def test3(self):
print("我是第三个数据")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# pytest.main(['--html=./321.html','TestAllure.py'])
#生成测试报告json
#第一个是allure文件夹;
#第二个是数据(json/txt)返回到这个目录下response文件夹下;
#第三个类名
pytest.main(['--alluredir','allurePackage/response','TestAllure.py']) ## 将测试报告转为html格式# --html=../report.html
split = 'allure ' + 'generate ' + './allurePackage/response ' + '-o ' + './allurePackage/html ' + '--clean' os.system(split)#system函数可以将字符串转化成命令在服务器上运行
运行后:
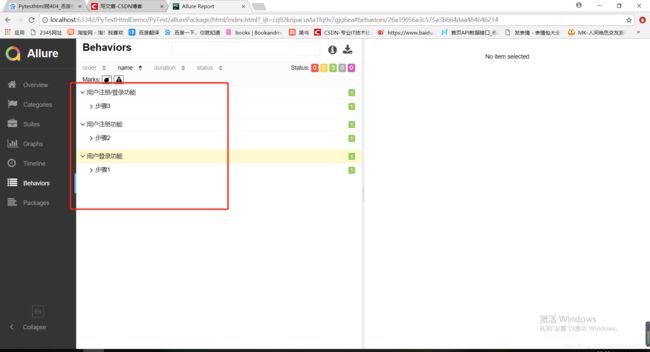
4.2@allure.story
import pytest,os,allure
class TestAllureClass:
@allure.feature("用户登录功能")
@allure.story("步骤1")
def test1(self):
print("我是第一个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册功能")
@allure.story("步骤2")
def test2(self):
print("我是第二个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册/登录功能")
@allure.story("步骤3")
def test3(self):
print("我是第三个数据")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# pytest.main(['--html=./321.html','TestAllure.py'])
#生成测试报告json
#第一个是allure文件夹;
#第二个是数据(json/txt)返回到这个目录下response文件夹下;
#第三个类名
pytest.main(['--alluredir','allurePackage/response','TestAllure.py'])
## 将测试报告转为html格式# --html=../report.html
split = 'allure ' + 'generate ' + './allurePackage/response ' + '-o ' + './allurePackage/html ' + '--clean' os.system(split)#system函数可以将字符串转化成命令在服务器上运行
运行结果:
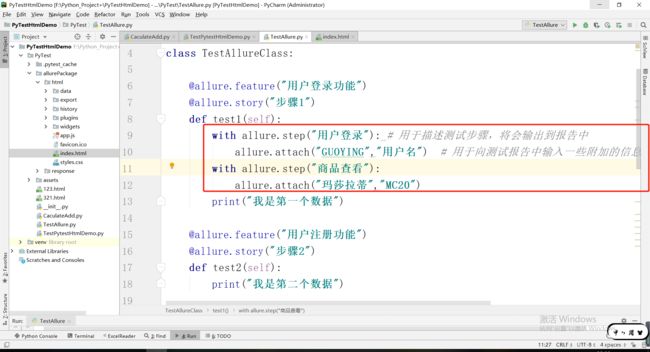
4.4with allure.step("用户登录"): # 用于描述测试步骤,将会输出到报告中
allure.attach("GUOYING","用户名") # 用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据,截图等
import pytest,os,allure
class TestAllureClass:
@allure.feature("用户登录功能")
@allure.story("步骤1")
def test1(self):
with allure.step("用户登录"): # 用于描述测试步骤,将会输出到报告中
allure.attach("GUOYING","用户名") # 用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据,截图等
with allure.step("商品查看"):
allure.attach("玛莎拉蒂","MC20")
print("我是第一个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册功能")
@allure.story("步骤2")
def test2(self):
print("我是第二个数据")
@allure.feature("用户注册/登录功能")
@allure.story("步骤3")
def test3(self):
print("我是第三个数据")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# pytest.main(['--html=./321.html','TestAllure.py'])
#生成测试报告json
#第一个是allure文件夹;
#第二个是数据(json/txt)返回到这个目录下response文件夹下;
#第三个类名
pytest.main(['--alluredir','allurePackage/response','TestAllure.py'])
## 将测试报告转为html格式# --html=../report.html�
split = 'allure ' + 'generate ' + './allurePackage/response ' + '-o ' + './allurePackage/html ' + '--clean'
os.system(split)#system函数可以将字符串转化成命令在服务器上运行
运行结果: