【Astar寻路算法图解】Java实现
Astar 寻路算法
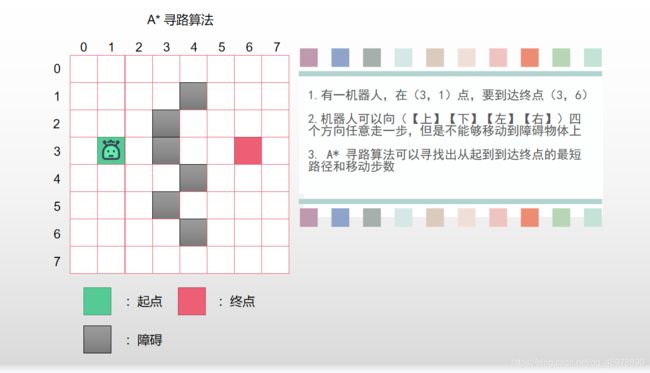
1. 什么是Astar寻路算法
- 拥有一个地图,地图上面有起点和终点
- 一个机器人在起点,希望用最短的距离到达终点
- Astar算法可以用来解决这个问题
2. 算法引入的三个工具
2.1 两个数据结构
- Open表,用来存储当前能够到达的格子,
Open表使用优先队列构建,这样的话Open表就会自动把F值最小的结点放在队首了,poll()方法会自动取队首并且将队首删除
- Close表,用来存储已经到达过的格子
使用一个普通的数组存放即可
2.2 一个公式
- 公式:F = G + H
每一个格子拥有三种属性,即:
-
G:从起点格子走到现在的格子需要花费多少步(已经花了的步数)
-
H:不考虑障碍的情况下,从当前在的格子走到终点需要花费的步数(预估仍然需要花的步数)
3. 算法步骤
步骤如下:
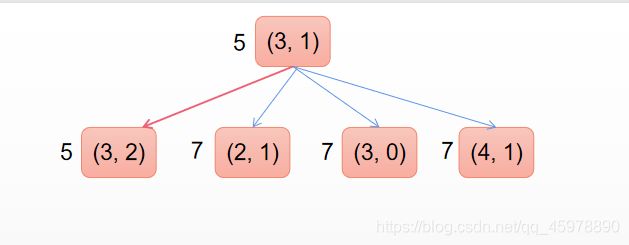
3. 1 第一轮操作
-
在【Open表】中寻找出一个F值最小的结点作为【当前结点】,把这个结点移出【Open表】并且加入到【Close表】中,并且对这个【当前结点】进行检查,看【当前结点】四周是否有能够到达的结点,如果这些能够到达的结点不在Open表中或者Close表中,就把这些能够到达的结点计算出F值后加入到【Open表】中,并且把【当前结点】作为这些结点的父节点

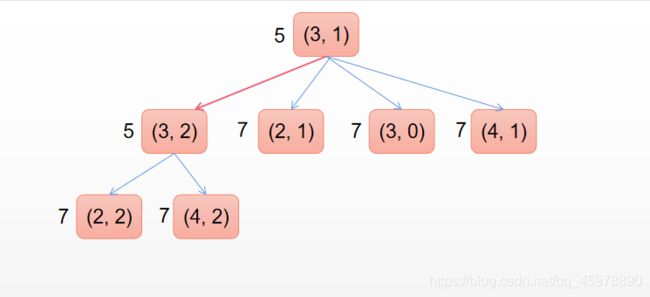
3. 2 第二轮操作
因为当前的【Open表】不为空并且没有找到【end结点】,所以重复第一轮的第二步操作
-
寻找Open表中F值最小的结点当作【当前结点】, 把【当前结点】移出【Open表】并且放入【Close】表,接下来是对【当前结点】进行检查,将能够到达的并且在【Open表】和【Close表】中从来没有出现过的结点添加进【Open表】中,并且把【当前结点】当作能够到达的结点的父结点
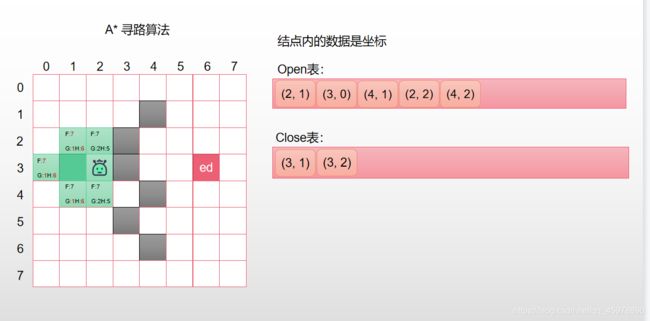
因为(3, 3)是【障碍物】,(3, 1)已经存在于【Close表】中,所以这两个结点都不加入【Open表】中
3. 3 第三轮操作
接下来的方式就是重复以上步骤
- 从【Open】表中寻找F值最小的结点移入【Close表中】并且当作【当前结点】进行检查扩展
- 将能够到达的新结点加入到【Open表】中
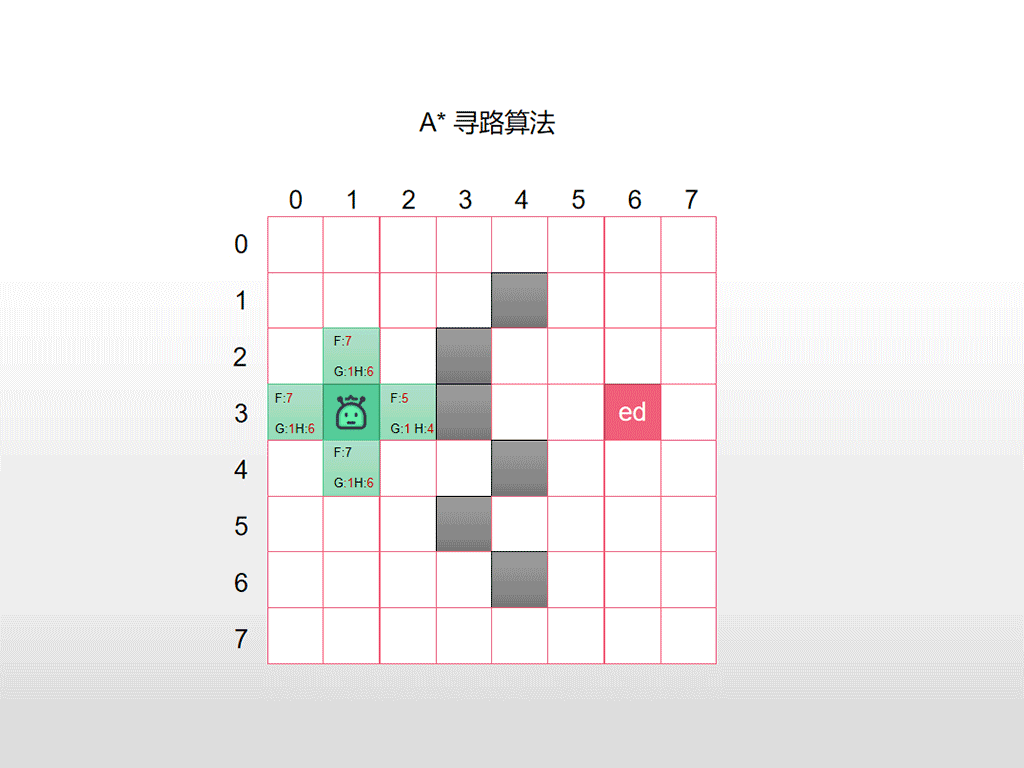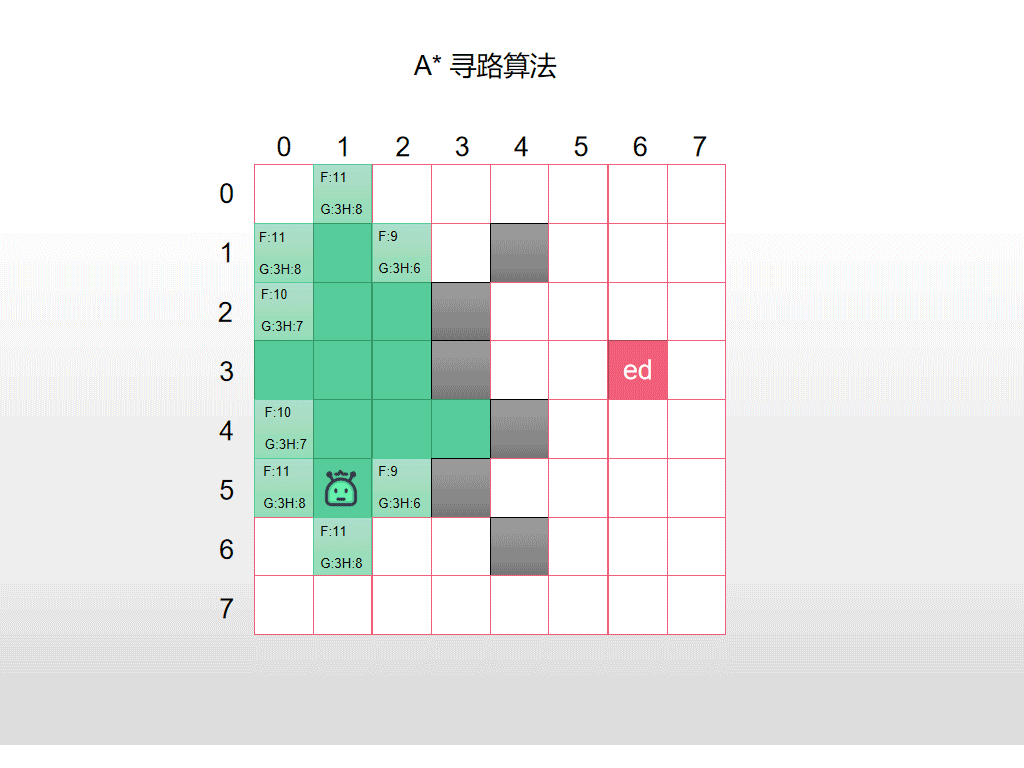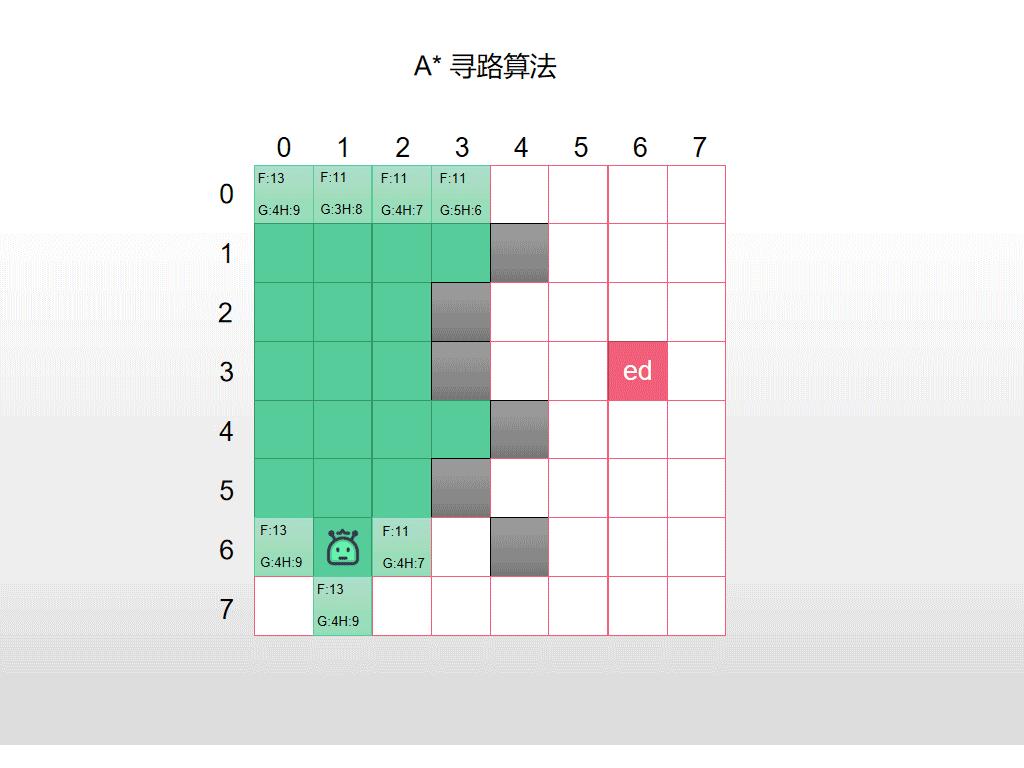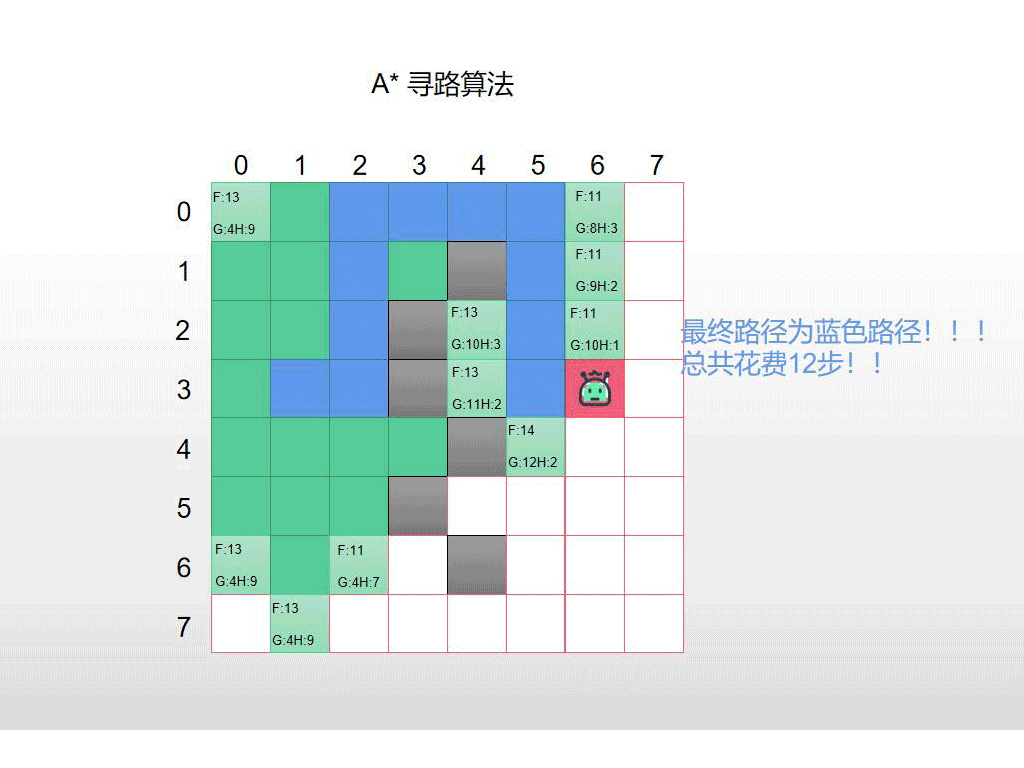
下面是全部的过程的动图示例,仔细看F的值,每次都选择最小的F进行检查和扩展,同时G 和 H的值的变化。
4. 代码实现(Java)
首先对整个算法我们需要整体上的认识
需要一个Node类记录经过的每一个结点的信息,Node类的信息如下:
为了方便数据的处理,所有的成员变量我都public了(不要学我,这好吗?这不好!)
//结点的属性 //因为每个结点都需要存放在优先队列中,所以需要实现Comparable接口 class Node implements Comparable<Node> { public int x; //x坐标 public int y; //y坐标 public int F; //F属性 public int G; //G属性 public int H; //H属性 public Node Father; //此结点的上一个结点 //构造函数 public Node(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } //通过结点的坐标和目标结点的坐标可以计算出F, G, H三个属性 //需要传入这个节点的上一个节点和最终的结点 public void init_node(Node father, Node end) { this.Father = father; if (this.Father != null) { //走过的步数等于父节点走过的步数加一 this.G = father.G + 1; } else { //父节点为空代表它是第一个结点 this.G = 0; } //计算通过现在的结点的位置和最终结点的位置计算H值 this.H = Math.abs(this.x - end.x) + Math.abs(this.y - end.y); this.F = this.G + this.H; } // 用来进行和其他的Node类进行比较重写的方法 @Override public int compareTo(Node o) { return Integer.compare(this.F, o.F); } }
接下来是Solution方法,所有的算法和数据结构都存放在这个方法中
- 首先需要一个地图:
// -1 -> 墙壁, 1 -> 起点 2 -> 终点 public int[][] map = { { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 2, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1}, { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1} };这个map就是上面的地图,由于判断地图是否越界过于麻烦,添加了辅助区域,让我们对【当前结点】进行扩展操作的时候判断扩展是否越界变得简单直观,只要不等于
-1就代表没有越界,而不必判断x坐标和y坐标的范围。
- 有了地图之后我们还需要【Open表】,【Close表】
- 对结点进行扩展添加的时候除了需要判断结点是否合法,还需要判断结点是否在【Open表】和【Close表】中出现过
- 但是由于【Open表】不是可以遍历的数据结构,为了方便使用【Exist表】来记录当前结点是否出现在【Open表】中和【Close表】中
//Open表用来存放能够到达的结点 //Open表会自动把F值最小的结点放在队首 public PriorityQueue<Node> Open = new PriorityQueue<Node>(); //Close表用来存放已经到达的结点 public ArrayList<Node> Close = new ArrayList<Node>(); //Exist表用来存放两张表出现过的结点 public ArrayList<Node> Exist = new ArrayList<Node>();
- 判断一个结点是否出现过(is_exist方法)
public boolean is_exist(Node node) { for (Node exist_node : Exist) { //如果这个结点在Exist中出现过,返回true if (node.x == exist_node.x && node.y == exist_node.y) { return true; } } //没有出现返回false return false; }
- 怎么判断一个结点是否合法(is_valid方法)
public boolean is_valid(int x, int y) { // 如果结点的位置在地图上是-1,则不合法 if (map[x][y] == -1) return false; for (Node node : Exist) { //如果结点出现过,不合法 if (is_exist(new Node(x, y))) { return false; } } //以上情况都没有则合法 return true; }
- 怎么扩展【当前结点】的【上】【下】【左】【右】四个方向的结点(extend_current_node方法)
public ArrayList<Node> extend_current_node(Node current_node) { //获取当前结点的x, y int x = current_node.x; int y = current_node.y; //如果当前结点的邻结点合法,就加入到neighbour_node ArrayList<Node> neighbour_node = new ArrayList<Node>(); if (is_valid(x + 1, y)) { Node node = new Node(x + 1, y); neighbour_node.add(node); } if (is_valid(x - 1, y)) { Node node = new Node(x -1, y); neighbour_node.add(node); } if (is_valid(x, y + 1)) { Node node = new Node(x, y + 1); neighbour_node.add(node); } if (is_valid(x, y - 1)) { Node node = new Node(x, y - 1); neighbour_node.add(node); } //返回合法的邻结点们 return neighbour_node; }
- Astar寻路算法具体实现(astarSearch方法)
public Node astarSearch(Node start, Node end) { //把第一个开始的结点加入到Open表中 this.Open.add(start); this.Exist.add(start); //主循环 while (Open.size() > 0) { //取优先队列顶部元素并且把这个元素从Open表中删除 Node current_node = Open.poll(); //将这个结点加入到Close表中 Close.add(current_node); //对【当前结点】进行扩展,得到一个邻居结点数组 ArrayList<Node> neighbour_node = extend_current_node(current_node); //对这个邻居数组遍历,看是否有目标结点出现 for (Node node : neighbour_node) { if (node.x == end.x && node.y == end.y) { //找到目标结点就返回 //init_node操作把这个邻居结点的父节点设置为当前结点 //并且计算出G, F, H等值 node.init_node(current_node,end); return node; } if (!is_exist(node)) { //没出现过的结点加入到Open表中并且设置父节点 //进行计算对G, F, H 等值 node.init_node(current_node, end); Open.add(node); Exist.add(node); } } } //如果遍历完所有出现的结点都没有找到最终的结点,返回null return null; }
5. 总体代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Astar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] map = {
{
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 2, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1}
};
Node start = new Node(4, 2);
start.Father = null;
Node end = new Node(4, 7);
Solution solution = new Solution();
Node res_node = solution.astarSearch(start, end);
//渲染迷宫
while (res_node != null) {
map[res_node.x][res_node.y] = 11;
res_node = res_node.Father;//迭代操作
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
System.out.printf("%3d", map[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//结点的属性
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public int x; //x坐标
public int y; //y坐标
public int F; //F属性
public int G; //G属性
public int H; //H属性
public Node Father; //此结点的上一个结点
//获取当前结点的坐标
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
//通过结点的坐标可以得到F, G, H三个属性
//需要传入这个节点的上一个节点和最终的结点
public void init_node(Node father, Node end) {
this.Father = father;
if (this.Father != null) {
this.G = father.G + 1;
} else {
//父节点为空代表它是第一个结点
this.G = 0;
}
//计算通过现在的结点的位置和最终结点的位置计算H值
this.H = Math.abs(this.x - end.x) + Math.abs(this.y - end.y);
this.F = this.G + this.H;
}
// 用来进行和其他的Node类进行比较
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return Integer.compare(this.F, o.F);
}
}
class Solution {
//地图 -1 代表墙壁, 1代表起点,2代表终点
public int[][] map = {
{
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 2, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1},
{
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1}
};
// Open表用优先队列
public PriorityQueue<Node> Open = new PriorityQueue<Node>();
//Close表用普通的数组
public ArrayList<Node> Close = new ArrayList<Node>();
//Exist表用来存放已经出现过的结点。
public ArrayList<Node> Exist = new ArrayList<Node>();
public Node astarSearch(Node start, Node end) {
//把第一个开始的结点加入到Open表中
this.Open.add(start);
//把出现过的结点加入到Exist表中
this.Exist.add(start);
//主循环
while (Open.size() > 0) {
//取优先队列顶部元素并且把这个元素从Open表中删除
Node current_node = Open.poll();
//将这个结点加入到Close表中
Close.add(current_node);
//对当前结点进行扩展,得到一个四周结点的数组
ArrayList<Node> neighbour_node = extend_current_node(current_node);
//对这个结点遍历,看是否有目标结点出现
//没有出现目标结点再看是否出现过
for (Node node : neighbour_node) {
if (node.x == end.x && node.y == end.y) {
//找到目标结点就返回
node.init_node(current_node,end);
return node;
}
if (!is_exist(node)) {
//没出现过的结点加入到Open表中并且设置父节点
node.init_node(current_node, end);
Open.add(node);
Exist.add(node);
}
}
}
//如果遍历完所有出现的结点都没有找到最终的结点,返回null
return null;
}
public ArrayList<Node> extend_current_node(Node current_node) {
int x = current_node.x;
int y = current_node.y;
ArrayList<Node> neighbour_node = new ArrayList<Node>();
if (is_valid(x + 1, y))
{
Node node = new Node(x + 1, y);
neighbour_node.add(node);
}
if (is_valid(x - 1, y))
{
Node node = new Node(x -1, y);
neighbour_node.add(node);
}
if (is_valid(x, y + 1))
{
Node node = new Node(x, y + 1);
neighbour_node.add(node);
}
if (is_valid(x, y - 1))
{
Node node = new Node(x, y - 1);
neighbour_node.add(node);
}
return neighbour_node;
}
public boolean is_valid(int x, int y) {
// 如果结点的位置是-1,则不合法
if (map[x][y] == -1) return false;
for (Node node : Exist) {
//如果结点出现过,不合法
// if (node.x == x && node.y == y) {
// return false;
// }
if (is_exist(new Node(x, y))) {
return false;
}
}
//以上情况都没有则合法
return true;
}
public boolean is_exist(Node node)
{
for (Node exist_node : Exist) {
if (node.x == exist_node.x && node.y == exist_node.y) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
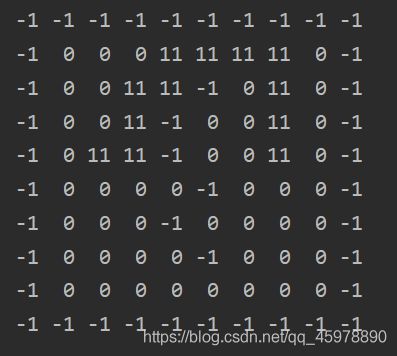
最终输出结果如下: