【Java基础】05-输入输出(上)
输入输出——上
-
- 异常
-
-
- 非检查型异常举例
- 检查型异常举例
-
- 异常处理
- I/O流
-
- 流的分类
- 字符流
- 字节流
- printf() 方法
- 字节类型处理流 Scanner
- 一个完成文本文件复制的例子
- 写入文本
-
- 使用 FileWriter 类写入文件
- 使用处理流 BufferedWriter
- 读取文本
-
- BufferedReader 类读入
- 使用 Reader 抽象类的方法 read()
- 一个复制文本文件的实例
- 写二进制文件
- 读二进制文件
异常
在 Java 中根据错误严重程度的不同,可以将其分为错误和异常。错误是程序无法处理的,所有错误继承自 Error 类;异常是程序可以捕获和处理的,所有异常继承自 Exception 类。
异常分为两种:
- 非检查型异常:
- 继承自 RuntimeException
- 不希望程序捕获,在方法体之中也不需要处理,编译器也不进行检查。
- 例如引用为空异常,如果使用引用的时候都认为写代码检查是否为空,代码就会变得很繁琐和冗长。
- 检查型异常
- 这是我们需要捕获处理的,编译器也必须进行检查。
非检查型异常举例
- ArithmeticException:整数除法中除数为 0
- NullPointerException:访问的对象还没有实例化
- NegativeArraySizeException:创建数组时元素个数是负数
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:访问数组元素时,数组下标越界
检查型异常举例
- ArrayStoreException:程序试图向数组中存取错误类型的数据
- FileNotFoundException:试图存取一个并不存在的文件
- IOException:通常的 I/O 错误
异常处理
异常处理的例子:
class MyException extends RuntimeException{
public MyException(){
super("This is a MyException!");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
@Override
public void printStackTrace() {
super.printStackTrace();
}
}
public class Exp1 {
public void tryException(){
throw new java.lang.RuntimeException("Error!");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] s = {
"Hello", "OK", "Good"};
try {
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}catch (java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Have printed exception");
}
Exp1 ep = new Exp1();
try{
ep.tryException();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Done");
}
try{
throw new MyException();
}catch (MyException e){
System.out.println("MyException");
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (RuntimeException e){
System.out.println("RuntimeException");
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果如下:
Hello
OK
Good
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
Have printed exception
java.lang.RuntimeException: Error!
Done
MyException
com.company.chap5.MyException: This is a MyException!
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
at com.company.chap5.Exp1.main(Exp1.java:30)
java.lang.RuntimeException: Error!
at com.company.chap5.Exp1.tryException(Exp1.java:23)
at com.company.chap5.Exp1.main(Exp1.java:41)
com.company.chap5.MyException: This is a MyException!
at com.company.chap5.Exp1.main(Exp1.java:50)
catch 只会对声明第一个异常处理,所以一般将子类异常写在前面,将父类异常写在后面。而且我们可以写自己的异常类,但是构造方法里面要调用父类的构造方法。
I/O流
流的分类
- 按照流的分工可以分为节点流和处理流,节点流负责原始读入输出,处理流负责处理节点流的流数据
- 按照流的内容可以分为面向字节的流和面向字符的流
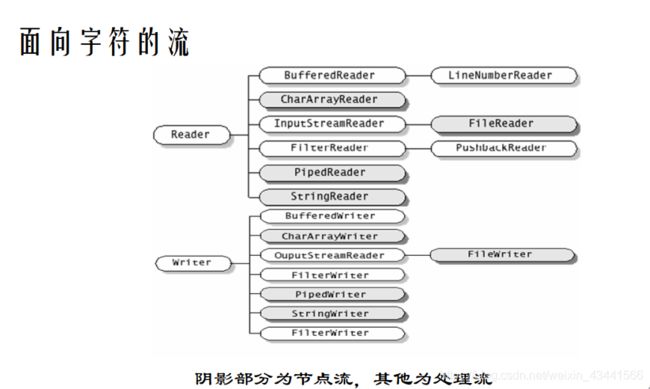
字符流
面向字符的流负责处理字符数据;所有负责处理字符流的类都继承自 Reader 和 Writer 类。面向字节的流负责处理一般的数据;负责处理字节流的类都继承自 InputeStream 和 OutputStream。它们都在 java.io 包里面
面向字符的流针对字符进行过优化,一般 Java 内部字符是 16 位的 unicode 编码,可以同个字符流和外部的 UTF 或者 ASCII 等编码进行转换。
面向字符的流主要是处理文本文件,可以用 FileReader 和 FileWriter 来作为读写文件的节点流,再用处理流处理。
- 节点流:(读)CharArrayReader, PipeReader, StringReader, FileReader; (写)CharArrayWriter, PipeWriter, StringWriter, FileWriter
- 处理流:(读)BufferedReader, LineNumberReader, InputStreamReader, FilterReader, PushbackReader; (写)BufferedWriter, OutputStreamWriter, FilterWriter
字节流
字节流可以处理包括非文本在内的信息。
标准输入输出字节节点流对象
System 类的静态成员变量。
包括:
- System.in: InputStream 类型,标准输入流,默认对应键盘输入
- System.out:OutputStream 类型,标准输出流,默认对应显示器输出
- System.err:OutputStream 类型,标准错误输出流,默认对应显示器输出
可以将标准输入输出流重新定向,达到从别的来源输入或者输出信息的目的。
printf() 方法
可以实现类似于C语言中格式化输出
System.out.printf("%-12s is %2d long", name, l); //-表示靠左排列
System.out.printf("value=%2.2F", value);
Java 里使用 %n 表示跨平台的换行。
字节类型处理流 Scanner
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = s.nextInt();
通过这种方法可以通过标准输入输出流对象读入各种数据类型的数据,类似的还有 nextByte(), nextDouble(), nextFloat(), nextInt(), nextLine(), nextLong(), nextShort()。
这种方法常用在程序设计竞赛里面读入数据。
一个完成文本文件复制的例子
import java.io.*;
public class Exp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String readPath = "./doc/src.txt";
String writePath = "./doc/rst.out";
BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(readPath));
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(writePath));
System.setIn(in); System.setOut(out); System.setErr(out);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while((s = br.readLine())!=null) System.out.println(s);
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
这就完成了将 src.txt 文件复制为 rst.out 文件。InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamReader 是字符流和字节流的桥梁,可以将字节流数据转化为字符流数据。
写入文本
使用 FileWriter 类写入文件
public class Exp3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String fileName = "./doc/hello.txt";
try{
File fw = new FileWriter(fileName));
fw.write("Hello!\n");
fw.write("This is a new line!\n");
fw.write("The end!\n");
fw.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Writing error: "+ fileName);
}
}
}
\n 在 Java 中不具有跨平台的特性,所以不同平台打开 hello.txt 可能会显示异常。
以上方法写入的时候会将原文本文件清空,如果想在原来的文本上追加内容,可以使用重载的构造方法 FileWriter(filePath, true) ,这里的 true 表示在文件后面添加。
使用处理流 BufferedWriter
当需要将文件写入很多内容的时候,可以使用带缓冲的流 BufferedWriter ,可以提高写入效率。FileWriter 和 BufferedWriter 的方法几乎一样,但是BufferedWriter 类多了一个 newLine 方法可以表示跨平台的换行。
public class Exp3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String fileName = "./doc/hello.txt";
try{
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
bw.write("Hello!");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("This is a new line!");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("The end!");
bw.newLine();
bw.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Writing error: "+ fileName);
}
}
}
读取文本
BufferedReader 类读入
BufferedReader 类是带缓冲的处理流,同时可以使用 readLine() 方法,做到一行行读取,如果读到文件尾,则返回 null,否则返回这一行的内容的字符串对象的引用。BufferedReader, BufferedWriter 继承自Reader。
使用 Reader 抽象类的方法 read()
继承自抽象类 Reader 的类都继承了其 read() 方法,可以逐个字符读取文件。read() 方法返回 unicode 码的大小,可以通过强制类型转换为字符类型,如果读取到文件尾,则返回 -1。FileReader, FileWriter 继承自 Reader 类的子类 InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamReader 。
下面的例子可以实现将文本文件的内容输出到显示器上
import java.io.*;
public class Exp4 {
public void bufferedRead(){
String fileName = "./doc/hello.txt", line;
try{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
while((line=in.readLine()) != null){
// 如果到文件尾则返回 null
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem reading in "+fileName);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void readerRead(){
String fileName = "./doc/hello.txt";
int c;
try{
FileReader in = new FileReader(fileName);
while((c=in.read()) != -1){
// 如果读到文件尾则返回 -1
System.out.print((char)c);
}
in.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem reading in "+fileName);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new Exp4().bufferedRead();
new Exp4().readerRead();
}
}
一个复制文本文件的实例
import javax.management.OperationsException;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.Buffer;
class CopyMaker{
String srcName, dstName;
BufferedReader src;
BufferedWriter dst;
String line;
private boolean openFiles(){
try{
src = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcName));
}catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Problem opening " + srcName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
try{
dst = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dstName));
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem opening " + dstName);
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean copyFiles() {
try {
while ((line = src.readLine()) != null) {
dst.write(line);
dst.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Problem reading or writing");
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean closeFiles(){
boolean rst = true;
try{
src.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem closing " + srcName);
e.printStackTrace();
rst = false;
}
try{
dst.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem closing" + dstName);
e.printStackTrace();
rst = false;
}
return rst;
}
public boolean copy(String source, String destination){
srcName = source; dstName = destination;
return openFiles() && copyFiles() && closeFiles();
}
}
public class Exp5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length == 2) new CopyMaker().copy(args[0], args[1]);
else System.out.println("Please Enter right File names");
}
}
此时在执行 class 文件的时候就可以输入希望被复制的文件和复制后文件的所在路径,完成复制。这边最后 copy() 方法是否成功返回的是 openFiles(), copyFiles(), closeFiles() 的结果相与,Java会按照顺序依次执行 openFiles(), copyFiles(), closeFiles(),最后将结果相遇后返回。
写二进制文件
二进制文件写入流包括公共父类抽象类 OutputStream,和它的派生类 FileOutputStream, BufferedOutputStream, DataOutputStream 等。其中 FileOutputStrem 是节点流,另外连个是处理流。
DataOutputStream 类有 size() 方法,可以统计累计写入的字节数。


使用带缓冲的输出流 BufferedOutputStream 可以提高速度
一个使用的例子如下:
import java.io.*;
public class Exp6 {
public void dataStreamWriteInt() throws IOException {
String fileName = "./doc/data1.dat";
int value0=255, value1=0, value2=-1;
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName));
out.writeInt(value0);
out.writeInt(value1);
out.writeInt(value2);
out.close();
// 结果为 0000 00ff 0000 0000 ffff ffff
}
public void bufferedStreamWriteTypes() throws IOException{
String fileName = "./doc/mixedTypes.dat";
DataOutputStream dataOut = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName)));
dataOut.writeInt(0);
System.out.println(dataOut.size()+" bytes written");
dataOut.writeDouble(31.2);
System.out.println(dataOut.size()+" bytes written");
dataOut.writeBytes("JAR");
System.out.println(dataOut.size()+" bytes written");
dataOut.close();
}
public void writeOneByte() throws IOException{
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./doc/tryonce.dat"));
out.writeByte(-1); out.close();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("./doc/tryonce.dat"));
int a = in.readByte(); // 虽然只存储了低 8 位,但是这里会为高位补 0。
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a)); // 转为 16 进制表示
System.out.println(a); // 输出 a
in.skip(-1); // 回退 1 字节以便重新读入。
a = in.readUnsignedByte();
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a));
System.out.println(a);
in.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
new Exp6().dataStreamWriteInt();
new Exp6().bufferedStreamWriteTypes();
new Exp6().writeOneByte();
}
}
运行结果如下:
4 bytes written
12 bytes written
15 bytes written
ffffffff
-1
ff
255
读二进制文件
用于读为二进制文件的输入流包括公共的抽象父类 InputStream 和子类如 FileInputStream, DataInputStream, BufferedInputStream。其中 FileInputStream是 节点流,其它子类是处理流。
DataOutputStream 提供了写入一个 int 型数值低 8 位到输出流的方法—— writeByte();DataInputStream 提供了读入一个字节到一个 int 型数值的第八位,这样就可以通过字节流读取文本文件。
多种读取方式,最后有一个用字节流完成文件复制的例子
import java.io.*;
public class Exp6 {
public void dataStreamReadInt() {
String fileName = "./doc/data1.dat";
int sum=0;
try{
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName)));
try{
while(true) sum += in.readInt();
}catch (EOFException eof){
System.out.println("Sum: "+sum);
in.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Problem reading "+fileName);
}
}
public void streamReadDocument(){
String fileName = "./doc/hello.txt";
try{
FileInputStream s = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int c;
while((c=s.read())!=-1) System.out.write(c); // read 读取一个字节
// write 会将低八位写入标准输出设备——显示器
s.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void streamCopy(String[] args){
DataInputStream in;
DataOutputStream out;
if(args.length !=2){
System.out.println("Please enter file names");
return;
}
try{
in = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(args[0])));
out = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(args[1])));
try{
int data;
while(true){
data = in.readUnsignedByte();
out.writeByte(data);
}
}catch (EOFException eof){
out.close();
in.close();
return;
}
}catch (FileNotFoundException fe){
System.out.println("Problem opening files");
}catch (IOException ioe){
System.out.println("IO problems");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
new Exp6().dataStreamReadInt();
new Exp6().streamReadDocument();
new Exp6().streamCopy(args);
}
}
结果如下:
Sum: 254
Hello!
This is a new line!
The end!