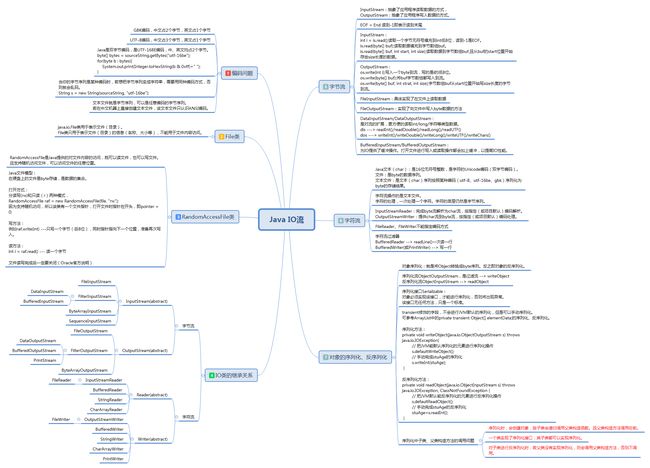
一、Java IO流总览
二、File类
2.1 常用API
package pkg1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @date 2021/4/2
*/
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 了解构造函数,可查看API
File file = new File("d:\\javaio\\cook");
// 设置分隔符,不同系统也可以认识
//File file=new File("d:"+File.separator);
//System.out.println(file.exists());
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
} else {
file.delete();
}
// 是否是一个目录,如果是目录返回true,如果不是目录或目录不存在返回false
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());
// 如果是一个文件
System.out.println(file.isFile());
//File file2 = new File("d:\\javaio\\日记1.txt");
File file2 = new File("d:\\javaio", "日记1.txt");
if (!file2.exists()) {
try {
file2.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
file2.delete();
}
// 常用File对象的api
System.out.println(file);// file.toString()的内容
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file2.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file2.getParent());
System.out.println(file.getParentFile().getAbsolutePath());
}
}
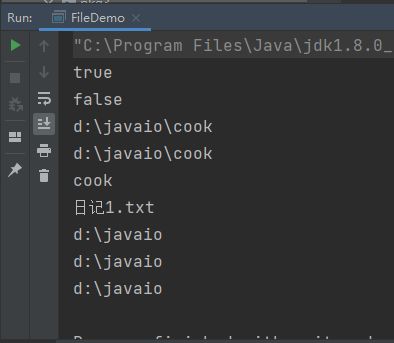
测试结果:
其他API:
package pkg1;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.RandomAccess;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @date 2021/4/7
*/
class FileDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javaio\\example");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
/*String[] fileNames = file.list(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
System.out.println("文件是:"+dir + "\\" + name);
return name.endsWith("java");
}
});
for (String fileName : fileNames != null ? fileNames : new String[0]) {
System.out.println(fileName);
}*/
/*File[] files = file.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
System.out.println("文件是:" + dir + "\\" + name);
return false;
}
});
for (File fileName : files) {
System.out.println(fileName.toString());
}*/
File[] files = file.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
System.out.println(pathname);
return false;
}
});
for (File fileName : files) {
System.out.println(fileName.toString());
}
}
}
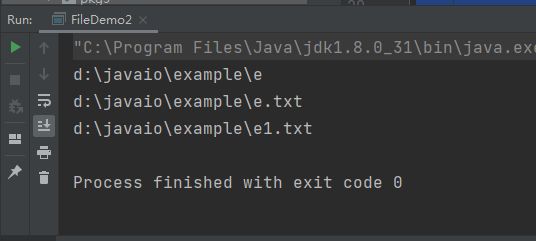
测试:
2.2 遍历目录
package pkg2;
import java.io.File;
/**
* 列出File的一些常用操作,如过滤、遍历
*/
public class FileUtils {
/**
* 列出指定目录(包括其子目录)下的所有文件
*/
public static void listDirectory(File dir) throws IllegalAccessException {
if (!dir.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("目录:" + dir + "不存在");
}
if (!dir.isDirectory()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(dir + "不存在");
}
// list()用于列出当前目录下的子目录(不包含子目录下的内容)和文件。返回的是字符串数组。
/*String[] fileNames = dir.list();
for (String string : fileNames) {
System.out.println(dir + "\\" + string);
}*/
// 若要遍历子目录下的内容,就要构造成File对象进行递归操作。File提供了直接返回File对象的API
File[] files = dir.listFiles();//返回直接子目录(文件)的抽象
/*for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file);
}*/
if (files != null && files.length > 0) {
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// 递归
listDirectory(file);
} else {
System.out.println(file);
}
}
}
}
}
测试类:
package pkg2;
import java.io.File;
public class FileUtilsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
FileUtils.listDirectory(new File("d:javaio"));
}
}
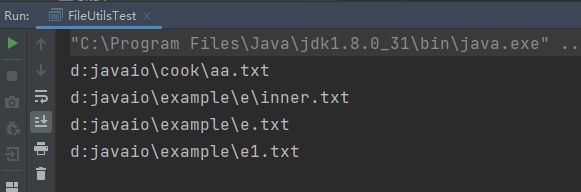
测试结果:
三、RandomAccessFile类
package pkg3;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RafDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 若没有指定路径,则表示相对路径,即项目所在路径。
File demo = new File("demo");
if (!demo.exists()) {
demo.mkdir();
}
File file = new File(demo, "raf.dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
// 查看指针位置
System.out.println(raf.getFilePointer());// 0
raf.writeInt('A');// 只写了一个字节
System.out.println(raf.getFilePointer());
raf.writeInt('B');
int i = 0x7fffffff;
// 用write方法每次只能写一个字节,如果要把i写进去就要写4次
raf.writeInt(i >>> 24);//高8位
raf.writeInt(i >>> 16);
raf.writeInt(i >>> 8);
raf.writeInt(i);// 低8位
System.out.println(raf.getFilePointer());
// 直接写一个int ,与上述4步操作等效
raf.writeInt(i);
String s = "中";
byte[] gbk = s.getBytes("gbk");
raf.write(gbk);
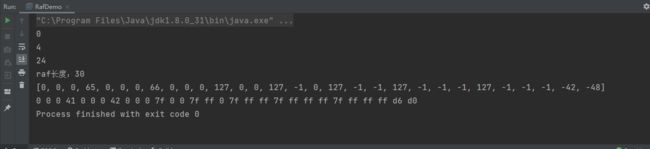
System.out.println("raf长度:" + raf.length());
// 读文件,必须把指针移到头部
raf.seek(0);
// 一次性读取,把文件中的内容都读到字节数组汇总
byte[] buf = new byte[(int) raf.length()];
raf.read(buf);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf));
// 转为字符串
/*String s1=new String(buf,"utf-8");
System.out.println(s1);*/
for (byte b : buf) {
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(b & 0xff) + " ");
}
raf.close();
}
}
测试结果:
四、字节流
4.1 FileInputStream
package pkg4;
import java.io.*;
public class IOUtil {
/**
* 读取指定文件内容, 按照十六进制输出到控制台,
* 且每输出10个byte换行
*
* @param fileName
*/
public static void printHex(String fileName) throws IOException {
// 把文件作为字节流进行操作
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int b;
int i = 1;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
if (b <= 0xf) {
// 单位数前补0
System.out.print("0");
}
// 将整型b转换为16进制表示的字符串
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(b) + " ");
if (i++ % 10 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
fis.close();
}
public static void printHexByByteArray(String fileName) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
/*byte[] buf = new byte[20 * 1024];
//从fis中批量读取字节,放入到buf字节数组中,从第0个位置开始放,最多放buf.length个,返回的是读到的字节个数
int bytes = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length);// 一次性读完,说明字节数组足够大
int j = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < bytes; i++) {
if (buf[i] <= 0xf) {
System.out.print("0");
}
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(buf[i]) + " ");
if (j++ % 10 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}*/
// 当字节数组容量不够,一次读不完时
byte[] buf = new byte[8 * 1024];
int bytes = 0;
int j = 1;
while ((bytes = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length)) != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < bytes; i++) {
// byte是8位,int类型是32位,为了避免数据转换错误,通过&0xff将高24位清零
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(buf[i] & 0xff) + " ");
if (j++ % 10 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
fis.close();
}
/**
* 文件拷贝操作 -> 字节批量读取式拷贝,效率最优
*/
public static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException {
if (!srcFile.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件:" + srcFile + "不存在");
}
if (!srcFile.isFile()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(srcFile + "不是文件");
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
byte[] buf = new byte[8 * 1024];
int b;
while ((b = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, b);
fos.flush();//最好加上这个
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 用带缓冲的字节流,进行文件拷贝,效率居中
*/
public static void copyFileByBuffer(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException {
if (!srcFile.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件:" + srcFile + "不存在");
}
if (!srcFile.isFile()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(srcFile + "不是文件");
}
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
int c;
while ((c = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(c);
// 刷新缓冲区。不能省略,否则无法写入
bos.flush();
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
/**
* 文件拷贝操作 -> 单字节,不带缓冲式拷贝,效率最差
*/
public static void copyFileByByte(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException {
if (!srcFile.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件:" + srcFile + "不存在");
}
if (!srcFile.isFile()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(srcFile + "不是文件");
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
fos.flush();
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
测试类:
package pkg4;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOUtilTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
IOUtil.printHex("d:\\javaio\\FileUtils.java");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.2 FileOutputStream
package pkg5;
import pkg4.IOUtil;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 如果该文件不存在,则直接创建,如果存在,则删除后创建。若要在后面追加内容,参数中加一个true
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("demo/out.dat");
// 写入A的低8位
fos.write('A');
fos.write('B');
// write只能写8位,那么写一个int需要4次,每次8位
int a = 10;
fos.write(a >>> 24);
fos.write(a >>> 16);
fos.write(a >>> 8);
fos.write(a);
byte[] gbk = "中国".getBytes("gbk");
fos.write(gbk);
fos.close();
IOUtil.printHex("demo/out.dat");
}
}
测试类:
package pkg5;
import pkg4.IOUtil;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOUtilTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
IOUtil.copyFile(new File("d:\\javaio\\abc.txt"), new File("d:\\javaio\\abc1.txt"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.3 DataInputStream 、DataOutputStream
输入流:
package pkg6;
import pkg4.IOUtil;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String file = "demo/dos.dat";
IOUtil.printHex(file);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
int i = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(i);
i = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(i);
long l = dis.readLong();
System.out.println(l);
double d = dis.readDouble();
System.out.println(d);
String s = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(s);
dis.close();
}
}
输出流:
package pkg6;
import pkg4.IOUtil;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DosDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String file = "demo/dos.dat";
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
dos.writeInt(10);
dos.writeInt(-10);
dos.writeLong(10l);
dos.writeDouble(10.5);
// 采用utf-8写入
dos.writeUTF("中国");
// 采用utf-16be写入
dos.writeChars("中国");
dos.close();
IOUtil.printHex(file);
}
}
4.4 字节缓冲流
工具类在4.1小节的IOUtil.java中。
测试类:
package pkg7;
import pkg4.IOUtil;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOUtilTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 效率最高
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
IOUtil.copyFile(new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha.mp3"), new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha1.mp3"));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时1:" + (end - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 效率居中
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
IOUtil.copyFileByBuffer(new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha.mp3"), new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha2.mp3"));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时2:" + (end - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 效率最差
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
IOUtil.copyFileByByte(new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha.mp3"), new File("d:\\javaio\\Alpha3.mp3"));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时3:" + (end - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
五、字符流
5.1 InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
package pkg8;
import java.io.*;
public class IsrAndOswDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\javaio\\aa.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//未指定编码格式,即按照项目默认编码操作
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\javaio\\aa.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);//未指定编码格式,即按照项目默认编码操作
/*int c;
while ((c=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)c);
}*/
/*
批量读取。
放入buffer这个字节数组,从第0个位置开始放,最多放buffer.length个,返回读到的字符个数。
*/
char[] buffer = new char[8 * 1024];
int c;
while ((c = isr.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1) {
String s = new String(buffer, 0, c);
System.out.print(s);
/*osw.write(buffer,0,c);
osw.flush();*/
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}
5.2 FileReader、FileWriter
package pkg8;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FrAndFwDemo {
/**
* 注意:FileReader、FileWriter不能指定编码方式
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("d:\\javaio\\aa.txt");
// 指定参数,也可以追加内容:FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append)
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\javaio\\bb.txt");
char[] buffer = new char[8 * 1024];
int c;
while ((c = fr.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1) {
fw.write(buffer, 0, c);
fw.flush();
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
5.3 BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、PrintWriter
package pkg9;
import java.io.*;
public class BrAndBwOrPwDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 对文件进行读写操作
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("d:\\javaio\\aa.txt")));
//BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("d:\\javaio\\cc.txt")));
// PrintWriter可以替换BufferedWriter
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("d:\\javaio\\cc.txt");
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 一次读一行,不能识别换行
System.out.println(line);
/*bw.write(line);
// 手动给出换行
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();*/
pw.println(line);
pw.flush();
}
br.close();
//bw.close();
pw.close();
}
}
6、对象的序列化、反序列化
6.1 transient关键字、序列化、反序列化
实体类:
package pkg10;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String stuNo;
private String stuName;
// 该元素不会 进行JVM默认的序列化,但可以手动序列化
private transient int stuAge;
public Student(String stuNo, String stuName, int stuAge) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.stuAge = stuAge;
}
public String getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(String stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public int getStuAge() {
return stuAge;
}
public void setStuAge(int stuAge) {
this.stuAge = stuAge;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuNo='" + stuNo + '\'' +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", stuAge=" + stuAge +
'}';
}
/**
* 序列化
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException {
// 把JVM能默认序列化的元素进行序列化操作
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 手动完成stuAge的序列化
s.writeInt(stuAge);
}
/**
* 反序列化
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 把JVM默认能反序列化的元素进行反序列化操作
s.defaultReadObject();
// 手动完成stuAge的反序列化
stuAge = s.readInt();
}
}
测试类:
package pkg10;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ObjectSeriaDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String file = "demo/obj.dat";
// 1、对象的序列化
/*ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
Student student = new Student("10001", "张三", 20);
oos.writeObject(student);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
// 2、对象的反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Student stu = (Student) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(stu);
ois.close();
}
}
6.2 序列化、反序列化时,子类、父类构造方法的调用
package pkg11;
import java.io.*;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
public class ObjectSeriaDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 序列化
/*ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Foo2 foo2=new Foo2();
oos.writeObject(foo2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
// 反序列化
/*ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Foo2 foo2= (Foo2) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(foo2);
ois.close();*/
/*ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Bar2 bar2=new Bar2();
oos.writeObject(bar2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
/*ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Bar2 bar2 = (Bar2) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(bar2);
ois.close();*/
/*ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Ccc2 ccc2=new Ccc2();
oos.writeObject(ccc2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("demo/obj1.dat"));
Ccc2 ccc2 = (Ccc2) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(ccc2);
ois.close();
}
}
/**
* 一个类实现了序列化接口,其子类都可以实现序列化。
*/
class Foo implements Serializable {
public Foo() {
System.out.println("foo...");
}
}
class Foo1 extends Foo {
public Foo1() {
System.out.println("foo1...");
}
}
class Foo2 extends Foo1 {
public Foo2() {
System.out.println("foo2...");
}
}
/**
* 对子类对象进行反序列化操作时,
* 如果其父类没有实现序列化接口
* 那么其父类的构造函数会被调用
*/
class Bar {
public Bar() {
System.out.println("Bar...");
}
}
class Bar1 extends Bar implements Serializable {
public Bar1() {
System.out.println("Bar1...");
}
}
class Bar2 extends Bar1 {
public Bar2() {
System.out.println("Bar2...");
}
}
class Ccc {
public Ccc() {
System.out.println("Ccc...");
}
}
class Ccc1 extends Ccc {
public Ccc1() {
System.out.println("Ccc1...");
}
}
class Ccc2 extends Ccc1 implements Serializable {
public Ccc2() {
System.out.println("Ccc2...");
}
}
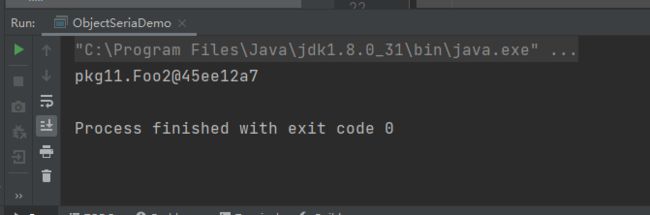
Foo2类反序列化时不打印构造方法:
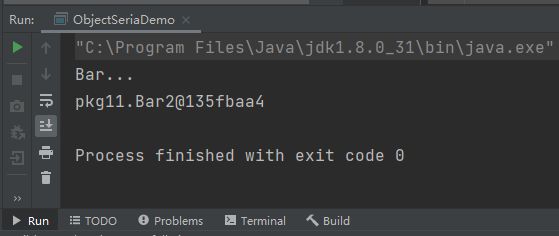
Bar2类反序列化时打印了Bar的构造方法:
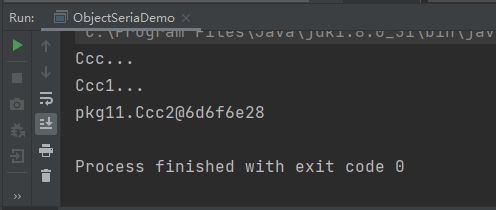
Ccc2类反序列化时打印了Ccc、Ccc1的构造方法:
结论(详见导图标红部分):
对子类对象进行反序列化操作时,如果其父类没有实现序列化接口,那么其父类的构造函数会被调用。
到此这篇关于Java IO流学习总结之文件传输基础的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java IO流文件传输内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!