黑马程序员---三天快速入门Python机器学习(第三天)
文章目录
- 四、回归与聚类算法
-
- 4.1 线性回归
-
- 4.1.1 线性回归的原理
- 4.1.2 线性回归的损失和优化原理
- 4.1.3 线性回归API
- 4.1.4 波士顿房价预测
- 4.1.5 梯度下降的扩展:GD、SGD、SAG
- 4.1.6 总结
- 4.2 欠拟合与过拟合
-
- 4.2.1 什么是过拟合与欠拟合
- 4.2.2 原因以及解决方法
- 4.3 线性回归的改进---岭回归
-
- 4.3.1 带有L2正则化的线性回归--岭回归
- 4.4 分类算法--逻辑回归与二分类
-
- 4.4.1 逻辑回归的应用场景
- 4.4.2 逻辑回归的原理
- 4.4.3 逻辑回归API
- 4.4.4 案例:癌症分类预测-良/恶性乳腺癌肿瘤预测
- 4.4.5 分类的评估方法
- 4.5 模型保存和加载
-
- 4.5.1 模型的保存和加载API
- 4.5.2 线性回归的模型保存加载案例
- 4.6 无监督学习:K-means算法
-
- 什么是无监督学习
- 4.6.2 无监督学习包含算法
- 4.6.3 K-means原理
- 4.6.4 K-means API
- 4.6.5 案例:k-means对instacart Market用户聚类
- 4.6.6 K-means性能评估指标
- 4.6.7 K-means总结
四、回归与聚类算法
4.1 线性回归
学习目标:
- 记忆线性回归的原理过程
- 应用LinearRegression或SGDRegressor实现回归预测
- 记忆回归算法的评估标准及其公式
4.1.1 线性回归的原理
1 线性回归应用场景

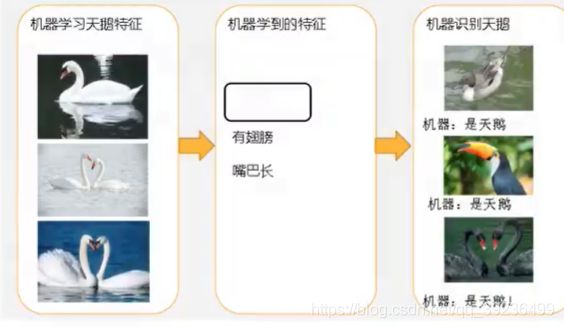
2 什么是线性回归
不同权重加权

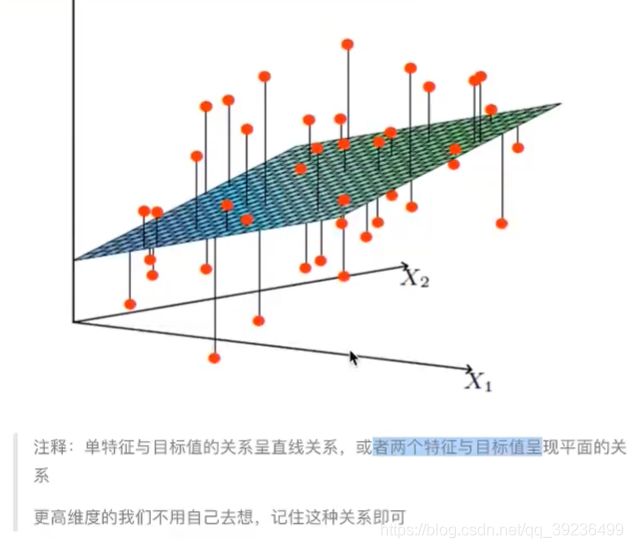
2)线性回归的特征与目标的关系分析
广义线性模型
4.1.2 线性回归的损失和优化原理
- 正规方程:直接求解W
- 梯度下降:试错,改进
正规方程:直接求解W

梯度下降(Gradient Descent)

4.1.3 线性回归API
1)线性回归:
sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
- fit_intercept:是否计算偏置
- LinearRegression.coef_:回归系数
- LinearRegression.intercept_:偏置
2)梯度下降:
sklearn.linear_model.SGDRegressor(loss="squared_loss", fit_intercept=True, learning_rate='invscaling', eta0=0.01
- SGDRegressor类实现了随机梯度下降学习,它支持不同的loss函数和正则化惩罚项来拟合线性回归模型
- loss:损失类型
-
- loss=“squared_loss”:普通最小二乘法
- fit_intercept:是否计算偏置
- learning_rate:string,optional
-
- 学习率填充
-
- ‘constant’:eta=eta0
-
- ‘optimal’:eta=1.0 / (alpha*(t+t0)) [default]
-
- ‘invscaling’:eta=eta0 / pow(t, power_t)
- SGDRegression.coef_:回归系数
- SGDRegression.intercept_:偏置

4.1.4 波士顿房价预测
流程:
1)获取数据集
2)划分数据集
3)特征工程:无量纲化 - 标准化
4)预估器流程:fit() -> 模型,coef_ intercept_
5)模型评估
2 回归性能评估
均方误差(Mean Squared Error)(MSE)评价机制

sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error(y_ture, y_pred)
- 均方误差回归损失
- y_true:真实值
- y_pred:预测值
- return:浮点数结果
3 代码
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
def linner1():
"""
正规方程的优化方法
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据
boston = load_boston()
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=22)
# 3)标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)预估器
estimator = LinearRegression()
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)得出模型
print("正规方程权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("正规方程偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 6)模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("正规方程-均分误差为:\n", error)
return None
def linner2():
"""
梯度下降的优化方法
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据
boston = load_boston()
print("特征数量:\n", boston.data.shape) # 几个特征对应几个权重系数
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=22)
# 3)标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)预估器
estimator = SGDRegressor(learning_rate="constant", eta0=0.001, max_iter=10000)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)得出模型
print("梯度下降权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("梯度下降偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 6)模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("梯度下降-均分误差为:\n", error)
return None
if __name__ == '__main__':
linner1()
linner2()
正规方程权重系数为:
[-0.64817766 1.14673408 -0.05949444 0.74216553 -1.95515269 2.70902585
-0.07737374 -3.29889391 2.50267196 -1.85679269 -1.75044624 0.87341624
-3.91336869]
正规方程偏置为:
22.62137203166228
预测房价:
[28.22944896 31.5122308 21.11612841 32.6663189 20.0023467 19.07315705
21.09772798 19.61400153 19.61907059 32.87611987 20.97911561 27.52898011
15.54701758 19.78630176 36.88641203 18.81202132 9.35912225 18.49452615
30.66499315 24.30184448 19.08220837 34.11391208 29.81386585 17.51775647
34.91026707 26.54967053 34.71035391 27.4268996 19.09095832 14.92742976
30.86877936 15.88271775 37.17548808 7.72101675 16.24074861 17.19211608
7.42140081 20.0098852 40.58481466 28.93190595 25.25404307 17.74970308
38.76446932 6.87996052 21.80450956 25.29110265 20.427491 20.4698034
17.25330064 26.12442519 8.48268143 27.50871869 30.58284841 16.56039764
9.38919181 35.54434377 32.29801978 21.81298945 17.60263689 22.0804256
23.49262401 24.10617033 20.1346492 38.5268066 24.58319594 19.78072415
13.93429891 6.75507808 42.03759064 21.9215625 16.91352899 22.58327744
40.76440704 21.3998946 36.89912238 27.19273661 20.97945544 20.37925063
25.3536439 22.18729123 31.13342301 20.39451125 23.99224334 31.54729547
26.74581308 20.90199941 29.08225233 21.98331503 26.29101202 20.17329401
25.49225305 24.09171045 19.90739221 16.35154974 15.25184758 18.40766132
24.83797801 16.61703662 20.89470344 26.70854061 20.7591883 17.88403312
24.28656105 23.37651493 21.64202047 36.81476219 15.86570054 21.42338732
32.81366203 33.74086414 20.61688336 26.88191023 22.65739323 17.35731771
21.67699248 21.65034728 27.66728556 25.04691687 23.73976625 14.6649641
15.17700342 3.81620663 29.18194848 20.68544417 22.32934783 28.01568563
28.58237108]
正规方程-均分误差为:
20.62751376309541
特征数量:
(506, 13)
梯度下降权重系数为:
[-0.49204282 0.90600442 -0.425408 0.78122193 -1.64479112 2.83475726
-0.13698271 -3.10445426 1.64364102 -0.88718517 -1.70440114 0.86728865
-3.89585718]
梯度下降偏置为:
[22.64133018]
预测房价:
[28.32988027 31.59628165 21.47291021 32.62500214 20.25743881 19.25430704
21.38515208 19.41801029 19.65928761 32.85198424 21.37546131 27.39056689
15.66170121 20.03328423 37.07101073 18.63258981 9.77520186 18.65105864
30.75325523 24.22837635 19.22472715 34.09165 29.44791249 17.56977717
34.7787419 26.45428709 34.22802121 27.29578864 19.32013582 15.73108309
30.8244829 14.45690648 37.39673182 9.17153635 16.4192231 16.95257013
8.02155337 19.91710981 40.38852095 29.15121021 25.24407119 18.010192
39.44673115 6.88236339 21.66834002 25.00581309 20.93463887 20.7354025
16.93857116 26.53856695 9.76725711 27.08260975 30.57506666 16.93015199
9.7853468 35.48002407 31.38771996 22.92251304 17.5887466 21.81266956
23.59614589 23.90931722 20.36883456 38.1178319 25.69501252 19.84073947
14.34417444 6.91806577 42.47139663 21.77826021 16.84647155 22.57258974
40.93987894 21.67674727 36.91202332 27.13881344 21.80877794 20.7595932
25.25423255 23.79657533 31.47394835 20.13480903 23.8995206 31.35105601
27.26683269 21.0353684 29.04765138 21.97300518 26.75012864 18.76796591
25.07915162 23.89632104 20.11003321 18.24837709 15.66456151 18.41027271
24.51065473 16.92998012 20.79986196 26.80312356 20.88746429 18.18470202
24.16520581 23.24517214 20.27485512 36.41503937 16.03109086 22.43965602
32.59510994 33.78438794 20.55420887 25.91441489 23.37496527 17.74240561
21.45360217 21.65660718 27.41255864 25.15738326 23.64996403 14.61343906
15.9240983 3.86335915 29.20453051 20.82989445 22.24521707 28.00451562
28.39269673]
梯度下降-均分误差为:
21.42768961540712
4.1.5 梯度下降的扩展:GD、SGD、SAG
4.1.6 总结
线性回归的损失函数:均方误差
线性回归的优化方法:正规方程、梯度下降
线性回归的性能衡量方法:均方误差
4.2 欠拟合与过拟合
学习目标:
- 说明线性回归(不带正则化)的缺点
- 说明过拟合与欠拟合的原因以及解决方法
问题:训练数据训练的很好啊,误差也不大,为什么在测试集上有问题呢?
过拟合
4.2.1 什么是过拟合与欠拟合
4.2.2 原因以及解决方法
欠拟合原因以及解决方法
- 原因:学习到数据的特征过少
- 解决方法:增加数据的特征数量
过拟合原因以及解决方法 - 原因:学到的特征过多,存在一些嘈杂特征,模型过于复杂
- 解决办法:正则化

1 正则化类别 - L1正则化
- L2正则化,更常用
L2正则化:
L1正则化:
- 作用:可以使得其中一些W的值直接为0,删除这个特征的影响
- LASSO回归
4.3 线性回归的改进—岭回归
学习目标:
- 说明岭回归的原理即与线性回归的不同之处
- 说明正则化对于权重参数的影响
- 说明L1和L2正则化的区别
4.3.1 带有L2正则化的线性回归–岭回归
岭回归,其实也是一种线性回归。只不过在算法建立回归方程时候,加上正则化的限制,从而达到解决过拟合的效果
1 API
sklearn.linear_model.Ridge(alpha=1.0, fit_intercept=True, solver='auto', normalize=False)
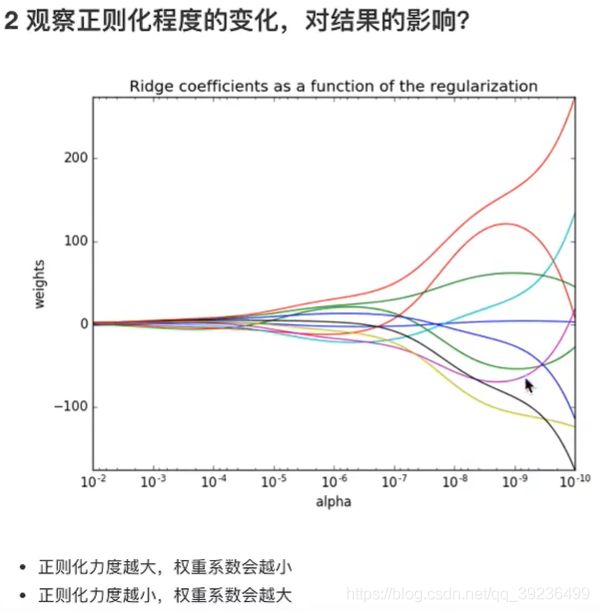
- alpha:正则化力度,取值范围:0-1,1-10
- solver:会根据数据自动选择优化方法
-
- sag:如果数据集、特征都较大,选择该随机梯度下降优化
- normalize:数据是否进行标准化
-
- normalize=False:可以在fit之前调用preprocessing.StandardScaler标准化数据
- Ridge.coef_:回归权重
- Ridge.intercept_:回归偏置

3 波士顿房价预测
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
def linner1():
"""
正规方程的优化方法
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据
boston = load_boston()
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=22)
# 3)标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)预估器
estimator = LinearRegression()
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)得出模型
print("正规方程权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("正规方程偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 6)模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("正规方程-均分误差为:\n", error)
return None
def linner2():
"""
梯度下降的优化方法
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据
boston = load_boston()
print("特征数量:\n", boston.data.shape) # 几个特征对应几个权重系数
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=22)
# 3)标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)预估器
estimator = SGDRegressor(learning_rate="constant", eta0=0.001, max_iter=10000)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)得出模型
print("梯度下降权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("梯度下降偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 6)模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("梯度下降-均分误差为:\n", error)
return None
def linner3():
"""
岭回归
:return:
"""
# 1)获取数据
boston = load_boston()
print("特征数量:\n", boston.data.shape) # 几个特征对应几个权重系数
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=22)
# 3)标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)预估器
estimator = Ridge(alpha=0.5, max_iter=10000) # 可默认参数
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)得出模型
print("岭回归-权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("岭回归-下降偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 6)模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("岭回归-均分误差为:\n", error)
return None
if __name__ == '__main__':
linner1()
linner2()
linner3()
4.4 分类算法–逻辑回归与二分类
学习目标:
- 说明逻辑回归的损失函数
- 说明逻辑回归的优化方法
- 说明sigmoid函数
- 知道逻辑回归的应用场景
- 知道精确率、召回率指标的区别
- 知道F-score指标说明召回率的实际意义
- 说明如何解决样本不均衡情况下的评估
- 了解ROC曲线的意义,说明AUC指标大小
- 应用classificiation_report实现精确率、召回率计算
- 应用roc_auc_score实现指标计算
4.4.1 逻辑回归的应用场景
- 广告点击率:是否会被点击
- 是否为垃圾邮件
- 是否患病
- 金融诈骗
- 虚假账号
以上都是二分类(正例,反例),逻辑回归就是解决二分类的利器
4.4.2 逻辑回归的原理

线性回归的输出就是逻辑回归的输入


3 损失以及优化

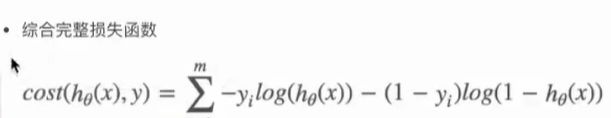

2 优化
同样使用梯度下降优化算法,去减少损失函数的值。这样去更新逻辑回归前面对应算法的权重参数,提升原本属于1类别的概率,降低原本是0类别的概率
4.4.3 逻辑回归API
sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRefression(solver='liblinear', penalty='l2, C=1.0)
4.4.4 案例:癌症分类预测-良/恶性乳腺癌肿瘤预测

流程分析:
1)获取数据:读取的时候加上names
2)数据处理:处理缺失值
3)数据集划分
4)特征工程:无量纲化处理—标准化
5)逻辑回归预估器
6)模型评估
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 1、读取数据
path = "https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data"
column_name = ['Sample code number', 'Clump Thickness', 'Uniformity of Cell Size', 'Uniformity of Cell Shape',
'Marginal Adhesion', 'Single Epithelial Cell Size', 'Bare Nuclei', 'Bland Chromatin',
'Normal Nucleoli', 'Mitoses', 'Class']
data = pd.read_csv(path, names=column_name) #699 rows × 11 columns
# 2、缺失值处理
# 1)替换-》np.nan
data = data.replace(to_replace="?", value=np.nan)
# 2)删除缺失样本
data.dropna(inplace=True) #683 rows × 11 columns
# 3、划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 筛选特征值和目标值
x = data.iloc[:, 1:-1]
y = data["Class"]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y)
# 4、标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# 5、预估器流程
estimator = LogisticRegression()
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 逻辑回归的模型参数:回归系数和偏置
estimator.coef_ # 权重
estimator.intercept_ # 偏置
# 6、模型评估
# 方法1:直接比对真实值和预测值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("y_predict:\n", y_predict)
print("直接比对真实值和预测值:\n", y_test == y_predict)
# 方法2:计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_test, y_test)
print("准确率为:\n", score)
4.4.5 分类的评估方法
1 精确率与召回率
1 混淆矩阵
真的患癌症的,能够被检查出来的概率

2 精确率(Precision)与召回率(Recall)



3 分类评估报告API
sklearn.metrics.classification_report(y_true, y_pred, labels=[], target_names=None)
- y_true:真实目标值
- y_pred:估计器预测目标值
- labels:指定类别对应的数字
- target_names:目标类别名称
- return:每个类别精确率与召回率
# 查看精确率、召回率、F1-score
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
report = classification_report(y_test, y_predict, labels=[2, 4], target_names=["良性", "恶性"])

衡量样本不均衡下的评估:
2 ROC曲线与AUC指标
TPR就是召回率



4 AUC计算API
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score)
- y_true:每个样本的真实类别,必须为0(反例)和1(正例)
- y_score:预测得分,可以是正类的估计概率、置信值或者分类器方法的返回值
# y_true:每个样本的真实类别,必须为0(反例),1(正例)标记
# 将y_test 转换成 0 1
y_true = np.where(y_test > 3, 1, 0)
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
roc_auc_score(y_true, y_predict)
- AUC只能用来评价二分类
- AUC非常适合评价样本在不平衡中的分类器性能
4.5 模型保存和加载
学习目标:
- 应用joblib实现模型的保存于加载
4.5.1 模型的保存和加载API
import joblib
- 保存:joblib.dump(rf, ‘test.pkl’)
- 加载:estimator = joblib.load(‘test.pkl’)
4.5.2 线性回归的模型保存加载案例
4.6 无监督学习:K-means算法
学习目标:
- 说明K-means算法原理
- 说明K-means的性能评估标准轮廓系数
- 说明K-means的优缺点
什么是无监督学习
4.6.2 无监督学习包含算法
聚类:K-means
降维:PCA
4.6.3 K-means原理
4.6.4 K-means API
sklearn.cluster.KMeans(n_cluster=8, init='k-means++')
- n_clusters:开始聚类中心数量
- init:初始化方法,默认为‘k-means++’
- labels_:默认标记的类型,可以和真实值比较(不是值比较)
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
estimator = KMeans(n_clusters=3)
estimator.fit(data_new)
y_predict = estimator.predict(data_new)
4.6.5 案例:k-means对instacart Market用户聚类
1 分析
- 1)降维之后的数据
- 2)预估器流程:k-means聚类
- 3)聚类结果显示
- 4)模型评估
4.6.6 K-means性能评估指标
1 轮廓系数
sklearn.metrics.silhouette_score(X, labels)
- 计算所有样本的平均轮廓系数
- X:特征值
- labels:被聚类标记的目标值
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score
silhouette_score(data_new, y_predict)
4.6.7 K-means总结
特点分析:采用迭代式算法,直观易懂并且非常实用
缺点:容易收敛到局部最优解(多次聚类)
注意:聚类一般坐在分类之前