SQL查询总结
查询
- 聚合查询
-
- 聚合函数
- GROUP BY 子句
-
- 多次分组聚合
- HAVING
- 联合查询
-
- 内连接
- 外连接
- 自连接
- 子查询
-
- [NOT] IN
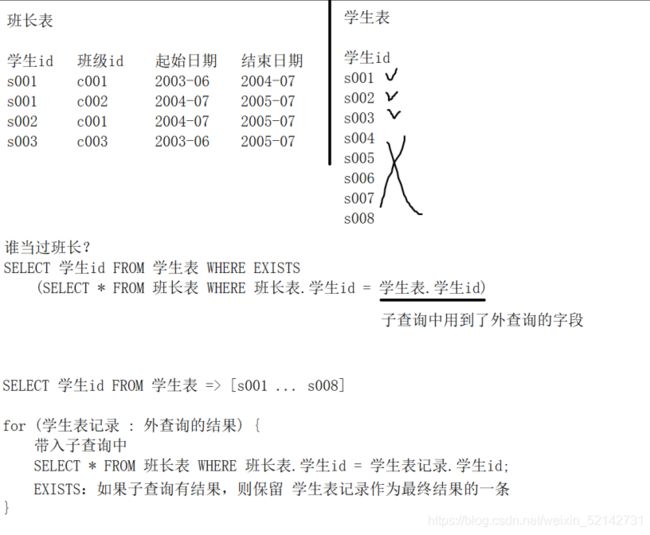
- [NOT] EXISTS
SQL基础语句查询为:
SELECT * FROM student;
聚合查询
聚合函数
常见的聚合函数有:MAX、MIN、AVG、COUNT、SUM
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| COUNT | 返回查询到数据的数量 |
| MIN | 返回查询到数据的最小值 |
| MAX | 返回查询到数据的最大值 |
| AVG | 返回查询到数据的平均值 |
| SUM | 返回查询到数据的总和 |
需要注意的是:min/max/avg/sum 只能用于数值类型的字段
- count
select count(*) from student;
select count(0) from student;
select count(姓名) from student;
select count(分数) from student;
null 不参与计数
- sum
select sum(分数) from student;
- avg
select avg(分数) from student;
- max
select max(分数) from student;
- min
select min(分数) from student;
GROUP BY 子句
select 中使用group by子句可以对指定列进行分组查询。需要满足:使用group by 进行分组查询时,select 指定的字段必须是“分组依据字段”,其他字段若想出现在select中,则必须包含在聚合函数中。
例如:
select 班级,count(*) from 表 group by 班级;
错误用法:
select 姓名 from 表 group by 班级;
或:
select 姓名 班级 count(*) from 表 group by 班级;
多次分组聚合
例如:
select 年级,班级,count(*) from 表 group by 年级,班级;
这样查询,会根据年级,班级两次分组
HAVING
group by 子句进行分组后,需要对分组结果在进行条件过滤的时候,不能使用where语句,而需要使用having
注意:where发生在聚合前、having发生在聚合之后
例如:
select 姓名 , count(*) from 表
where 时间 between '2020-04-01' and '2020-04-30'
group by 姓名;
select 年级,班级,count(*)
from 表
group by 年级,班级
Having count(*) > 2;
联合查询
在实际情况中,我们不可能只查询一张表的数据,所以需要多表联合查询。
多表查询是对多张表的数据取笛卡尔积(没有条件的联表结果,是笛卡尔积关系);
所以我们需要联表条件。
内连接
语法:
select 字段 from 表1 别名1 [inner] join 表2 别名2 on 连接条件 and 其他条件;
select 字段 from 表1 别名1 , 表2 别名2 where 连接条件 and 其他条件;
内连接求的是交集
外连接
外连接分为 左外连接和右外连接,左侧的表显示完全就是左联,右边的表显示完全就是右联。
语法:
-- 左联
select 字段 from 表1 left join 表2 on 连接条件;
-- 右联
select 字段 from 表1 right join 表2 on 连接条件;
我们可以理解为:
外连接求的是并集,并且,不推荐使用右链接,可以转为左连接
自连接
自连接指的是在同一张表连接自身查询。
子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql子句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
子查询放在from后,作为数据源在查询,可以理解为:查询出了一张表,然后在此基础上继续查询
例如:
select 学生id
from (select 学生id,书籍id from 表1) [as] 表别名
where ....;
外查询:
子查询出现在from后,必须给出别名!
子查询必须通过小括号()括起来!
子查询可以出现在where条件中,
1、单行单列:
select ... from 表 where 字段 < (select count(*) from 表);
2、单行多列:
select ... from 表 where 字段 = (select id ,name from 表 where .... );
3、单列多行:
select ... from 表 where 字段 = (select id from 表 where .... );
[NOT] IN
– in
select ... from 表 where 字段 in (select id ,name from 表 where .... );
– not in
select ... from 表 where 字段 not in (select id ,name from 表 where .... );