2021 CCCC天梯赛补题
前言不想看请直接跳过~~~~
前言+检讨:天梯赛我拉垮了,我拖了队伍后腿,我有罪。
分析原因,首先是前一个星期训练量不够,没有跟上队友训练的进度,一些基础的STL的用法使用的也不熟练。
第二,没有把STL用熟,或者是没有真正会用导致比赛时思路有些混乱,打断了思路的连贯性。
第三,把过多时间精力消耗在Debug上,消磨了自己的心态和时间,比如L1-8这道题其实双指针就可以轻松解决的,我非耍小聪明整STL装逼,结果最后调不出来还得再用双指针,分也没拿全,我有罪,拖了全队的后腿。
第四,L2的dfs用的不熟,没有将算法熟练于心像Hello World那些轻松敲出来,反映出近期学习不踏实,有些知识点看似掌握了写了题解,其实换个壳子还是不会。
第五,客观的因素比如电脑死机啥的我就不谈了,就是我水平不够罢了。
今后继续努力!!!
L1前几题太水了,从小干货开始
天梯赛题目目录
- L1-078 吉老师的回归 (15 分)
-
- 思想
- AC代码
- L1-079 天梯赛的善良 (20 分)
-
- 思想
- AC代码
- L1-080 乘法口诀数列 (20 分)
-
- 思想
- Half-AC代码(两个点没过)
- AC代码
- L2-037 包装机 (25 分)
-
- 思想
- AC代码
L1-078 吉老师的回归 (15 分)
输入样例 1:
5 1
L1-1 is a qiandao problem.
L1-2 is so...easy.
L1-3 is Easy.
L1-4 is qianDao.
Wow, such L1-5, so easy.
输出样例 1:
L1-4 is qianDao.
输入样例 2:
5 4
L1-1 is a-qiandao problem.
L1-2 is so easy.
L1-3 is Easy.
L1-4 is qianDao.
Wow, such L1-5, so!!easy.
输出样例 2:
Wo AK le
思想
这道题恶心在哪呢?其实就是输入的时候如果用了scanf注意前面加getchar就完事了。
想法的话这道题很简单,就是在遍历的时候标记哪些题目是跳过的,如果跳不过的题则消耗一次m,如果某次循环m为0,而且此时做的题目无法跳过,那么就直接输出这道题。如果循环结束后m还大于或等于0(可能最后一次简单题消耗掉了),那么就输出Wo AK le。
AC代码
#includeL1-079 天梯赛的善良 (20 分)
10
86 75 233 888 666 75 886 888 75 666
输出样例:
75 3
888 2
思想
这道题水的,暴力完事,只需拿个桶记录最大最小,以及其个数就完事了,每次更新,一次便利即可
AC代码
#includeL1-080 乘法口诀数列 (20 分)
这道题说实话当时只拿了17分,有点失望····不知道哪个点卡了(主要切慢了···)
2 3 10
输出样例:
2 3 6 1 8 6 8 4 8 4
思想
这道题怎么说呢,说恶心其实还好吧,主要是题意要看清,之前题意没搞懂直接莽就很浪费时间····题意就是先给你两个初始数a1,a2,之后的数据通过这两个初始数计算而来,也就是a3为a1*a2,但是如果a3是多位数就得把每一位按权值高到低依次存放入a数组。具体例子看看Sample就懂了。
所以我们用双指针标记,一个是当前已经算好的新数存进stack倒一下(LIFO的原则,具体可以查看我的二进制水题那有写---->传送门)然后存入a数组,另一个指针标记当前是把哪两个数相乘,便于接下来向后移动。
Half-AC代码(两个点没过)
#includeAC代码
#include见鬼了,改了几个无关紧要的点,反而能过····无语,毒瘤测试点一生黑
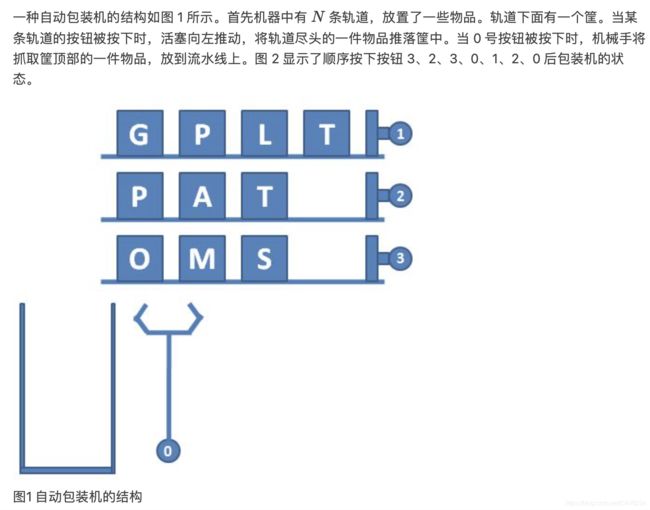
L2-037 包装机 (25 分)
输入样例:
3 4 4
GPLT
PATA
OMSA
3 2 3 0 1 2 0 2 2 0 -1
输出样例:
MATA
思想
这道题就硬模拟呗~~~用STL吧
借用朋友的代码了~~~
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52480906/article/details/116116174
AC代码
#include