1.数据源模块需求
- 1)常见的数据源组件都实现了javax.sql.DataSource接口
- 2)MyBatis不但要能集成第三方数据源组件,自身也提供了数据源的实现
- 3)一般情况下,数据源的初始化过程参数较多,比较复杂
2.工厂模式
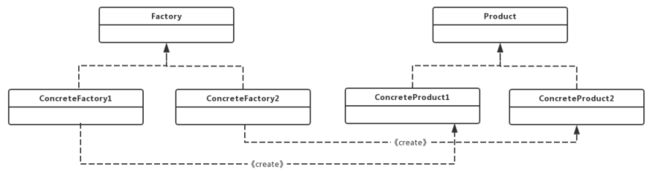
Factory Pattern属于创建型模式,提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。定义一个创建对象的接口,让其子类决定实例化哪一个工厂类,工厂模式使其创建过程延迟到子类进行。
- Factory工厂接口:是工厂方法模式的核心接口,调用者会直接和工厂接口交互用于获取具体的产品实现类
ConcreteFactory具体工程类:工厂接口的实现类,用于实例化产品对象,不同的具体工程类会根据需求实例化不同的产品实现类
Product产品接口:用于定义产品类的功能,具体工程类产生的所有产品都必须实现这个接口。调用者与产品接口直接交换,这是调用者最关心的接口。
ConcreteProduct具体产品类:产品接口的实现类,具体产品类中定义了具体的业务逻辑。
2.1 工厂模式的优点
创建对象有三种方式
1)使用new关键字直接创建对象
2)通过反射机制创建对象
3)通过工厂类创建对象前两种方式的缺点
1)对象创建和对象使用耦合在一起,违反单一职责原则
2)当业务扩展时,必须修改业务代码,违反了开闭原则工厂类创建对象的优点
1)把对象的创建和使用过程分开,对象创建和对象使用解耦
2)如果创建对象的过程很复杂,创建过程统一到工厂管理,既减少了重复代码,也方便以后对创建过程的修改维护
3)当业务扩展时,只需要增加工厂子类,符合开闭原则IOC容器就是将对象的创建和使用完全解耦
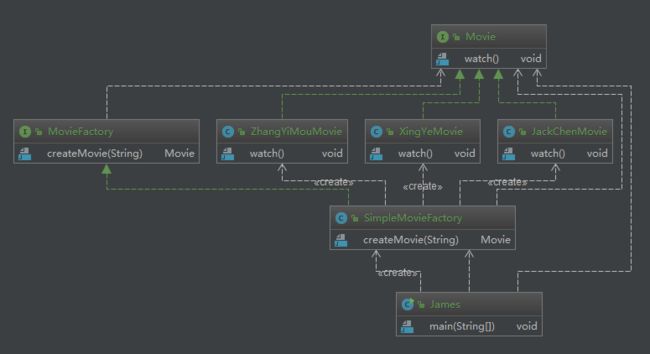
2.2 简单工厂模式
简单工厂实例
public class SimpleMovieFactory implements MovieFactory {
@Override
public Movie createMovie(String actorName) {
Movie movie = null;
if(actorName.equals("JackChen")){
movie = new JackChenMovie();
}else if(actorName.equals("ZhangYiMou")){
movie = new ZhangYiMouMovie();
}else if(actorName.equals("XingYe")){
movie = new XingYeMovie();
}
//拍摄电影的过程及其复杂,非专业人士请勿模仿
//…………
//此处省略一万字
return movie;
}
}
测试代码:
public class James {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//简单工厂使用
SimpleMovieFactory factory = new SimpleMovieFactory();
Movie movie = factory.createMovie("JackChen");
movie.watch();
}
}
- 简单工厂的优缺点及使用场景
优点:客户端免除了直接创建产品对象的责任,而仅仅负责调用,对象创建和对象使用使用的职责解耦
缺点:不符合设计原则之单一原则和开闭原则,对于需求的扩展需要修改代码;
使用场景:对象比较单一,需求不复杂的场景
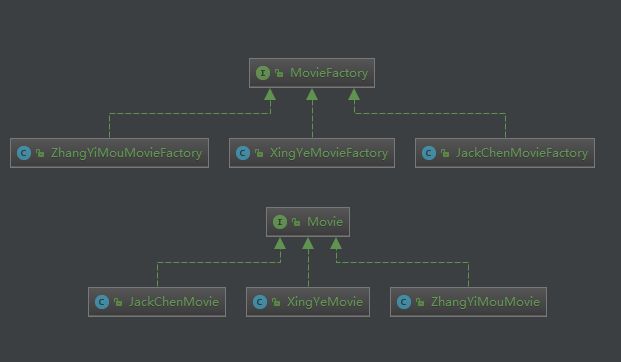
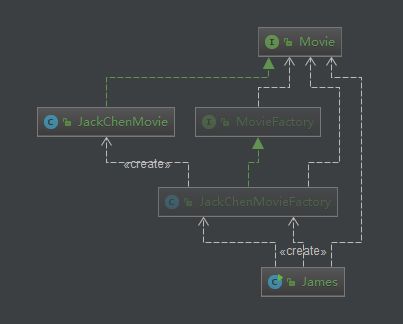
2.3 抽象工厂模式
工厂模式实例
public class JackChenMovieFactory implements MovieFactory{
@Override
public Movie createMovie() {
Movie movie = new JackChenMovie();
//拍摄电影的过程及其复杂,非专业人士请勿模仿
//…………
//此处省略一万字
return movie;
}
}
测试代码
public class James {
//工厂模式使用
JackChenMovieFactory factory = new JackChenMovieFactory();
Movie movie = factory.createMovie();
movie.watch();
}
}
- 工厂模式符合开闭原则,如果需要增加新类型的电影,只需要增加新的电影产品product和生产该product的工厂factory即可,这样即可不修改老代码实现新增。
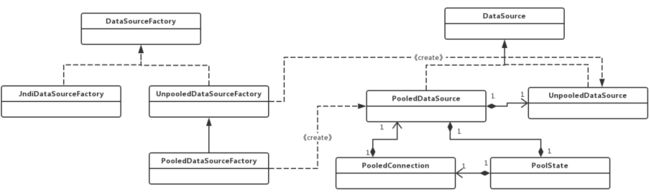
3.数据源类图
PooledConnection:使用动态代理封装了真正的数据库连接对象
PoolState:用于管理PooledConnection对象状态的组件,通过两个list分别管理空闲状态的连接资源和活跃状态的连接资源
PooledDataSource:一个简单、同步的、线程安全的数据库连接池解决需求3)初始化过程参数太多的情况
将初始化过程交给工厂来做!为什么Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")后,驱动就被注册到DriverManager?
UnpooledDataSource中的静态代码块:
//提问:为什么Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")后,驱动就被注册到DriverManager?
static {
Enumeration drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
注册时通过Driver的静态代码块来进行加载:classloader加载类时,会执行静态代码块
// STEP 2: 注册mysql的驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
4.DataSource获取和归还连接的过程
4.1 UnpooledDataSource
//从这个代码可以看出,unpooledDatasource获取连接的方式和手动获取连接的方式是一样的
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
initializeDriver();
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
//设置事务是否自动提交,事务的隔离级别
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
4.2 PooledDataSource
4.2.1 数据结构
- PooledConnection:使用动态代理封装了真正的数据库连接对象
PoolState:用于管理PooledConnection对象状态的组件,通过两个list分别管理空闲状态的连接资源和活跃状态的连接资源
PooledDataSource:一个简单、同步的、线程安全的数据库连接池
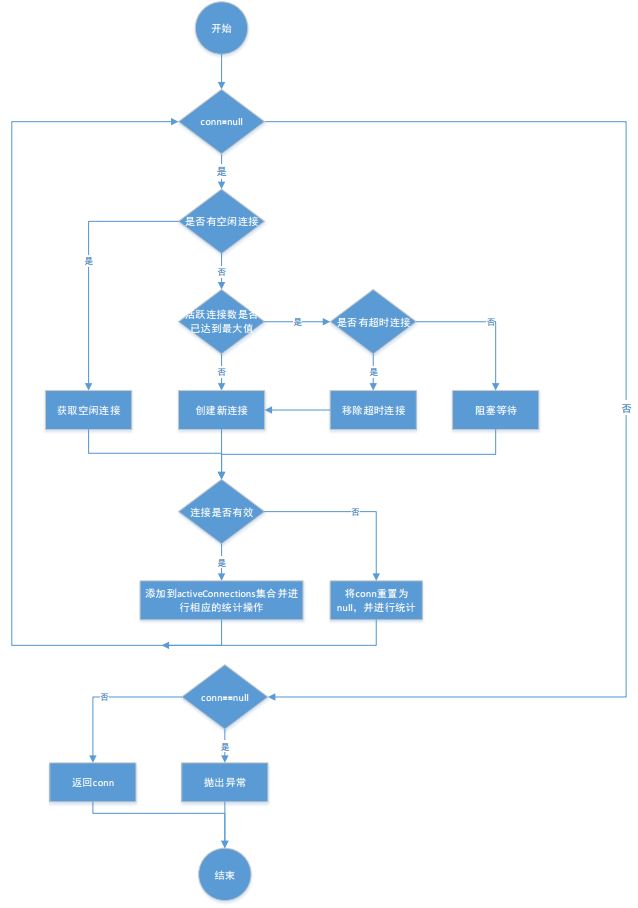
4.2.2 算法流程图
-
1)获取连接getConnection
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();//记录尝试获取连接的起始时间戳
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;//初始化获取到无效连接的次数
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {//获取连接必须是同步的
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {//检测是否有空闲连接
// Pool has available connection
//有空闲连接直接使用
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {// 没有空闲连接
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {//判断活跃连接池中的数量是否大于最大连接数
// 没有则可创建新的连接
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {// 如果已经等于最大连接数,则不能创建新连接
//获取最早创建的连接
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {//检测是否已经以及超过最长使用时间
// 如果超时,对超时连接的信息进行统计
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;//超时连接次数+1
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;//累计超时时间增加
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;//累计的使用连接的时间增加
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);//从活跃队列中删除
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {//如果超时连接未提交,则手动回滚
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {//发生异常仅仅记录日志
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happend.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not intterupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competion for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
//在连接池中创建新的连接,注意对于数据库来说,并没有创建新连接;
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
//让老连接失效
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 无空闲连接,最早创建的连接没有失效,无法创建新连接,只能阻塞
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;//连接池累计等待次数加1
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);//阻塞等待指定时间
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;//累计等待时间增加
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {//获取连接成功的,要测试连接是否有效,同时更新统计数据
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
if (conn.isValid()) {//检测连接是否有效
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();//如果遗留历史的事务,回滚
}
//连接池相关统计信息更新
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {//如果连接无效
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;//累计的获取无效连接次数+1
localBadConnectionCount++;//当前获取无效连接次数+1
conn = null;
//拿到无效连接,但如果没有超过重试的次数,允许再次尝试获取连接,否则抛出异常
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
-
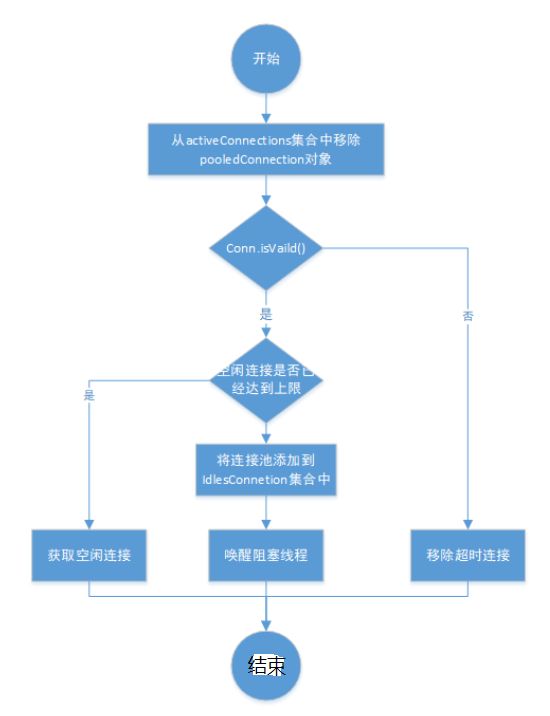
2)归还连接pushConnection
//回收连接资源
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {//回收连接必须是同步的
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);//从活跃连接池中删除此连接
if (conn.isValid()) {
//判断闲置连接池资源是否已经达到上限
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
//没有达到上限,进行回收
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();//如果还有事务没有提交,进行回滚操作
}
//基于该连接,创建一个新的连接资源,并刷新连接状态
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
//老连接失效
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
//唤醒其他被阻塞的线程
state.notifyAll();
} else {//如果闲置连接池已经达到上限了,将连接真实关闭
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
//关闭真的数据库连接
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
//将连接对象设置为无效
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
参考
- 1)享学课堂Lison老师笔记
- 2)抽象工厂模式和工厂模式的区别? caoglish答案