点语法
- set方法和get方法的调用
OC中的set方法和get方法都是对成员变量的修改和操作。在方法调用上set方法和get方法都使用中括号来调用,如果仅仅是修改成员变量的值可以直接使用OC的点语法的功能来简化set方法和get方法的调用进而简化重复代码书写。
Person.h
@interface Person : NSObject
{
int _age;
NSString *_name;
}
- (void)setAge:(int)age;
- (int)age;
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name;
- (NSString *)name;
@end
Person.m
@implementation Person
- (void)setAge:(int)age
{
_age = age;
}
- (int)age
{
return _age;
}
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name;
{
_name = name;
}
- (NSString *)name
{
return _name;
}
@end
main.m
int main()
{
Person *p = [Person new];
p.age = 10;
NSLog("age = %d",p.age);
p.name = @"seed";
NSLog("name = %@",p.name);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2017-11-26 22:52:28.021589+0800 04-点语法[29003:2221261] age =10
2017-11-26 22:52:28.021930+0800 04-点语法[29003:2221261] name = seed
Program ended with exit code: 0
成员变量的作用域
@public : 在任何地方都能直接访问对象的成员变量
@private : 只能在当前类的对象方法中直接访问(@implementation中默认是@private)
@protected: 可以在当前类及其子类的对象方法中直接访问(@interface中默认就是@protected)
@package : 只要处在同一个框架中,就能直接访问对象的成员变量
@interface和@implementation中不能声明同名的成员变量。
#import
@interface Person : NSObject
{
int _no;
@public // 在任何地方都能直接访问对象的成员变量
int _age;
@private // 只能在当前类的对象方法中直接访问
int _height;
@protected // 能在当前类和子类的对象方法中直接访问
int _weight;
int _money;
}
- (void)setHeight:(int)height;
- (int)height;
- (void)test;
@end
property声明简化
@property:自动声明操作成员变量的set方法和get方法。property同时也自动生成方法的实现,使得set方法和get方法的书写量大为减少。
> 用在@interface中
> 用来自动生成setter和getter的声明
> @property int age; 可以替代下面的两行
- (void)setAge:(int)age;
- (int)age;
Student.h
@interface Student : NSObject
@property int age;
@property int score;
- (void)test;
@end
Student.m
@implementation Student
- (void)test
{
_age = 20;
_score = 90;
}
@end
main.m
int main()
{
Student *s = [Student new];
s.age = 10;
NSLog(@"age = %d",s.age);
s.score = 100;
NSLog(@"score = %d",s.score);
[s test];
NSLog(@"age = %d",s.age);
NSLog(@"score = %d",s.score);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2014-06-04 22:36:09.619 ff[571:303] age = 10
2014-06-04 22:36:09.622 ff[571:303] score = 100
2014-06-04 22:36:09.623 ff[571:303] age = 20
2014-06-04 22:36:09.624 ff[571:303] score = 90
Program ended with exit code: 0
自动生成的成员变量是私有的,不能直接被外部访问只能在类的内部访问。
property新特性
> 自从xcode4.4后,@property独揽@synthesize的功能,即@property也可以自动生成方法的实现
> 默认情况下,setter和getter方法中的实现,会去访问下划线_开头的成员变量
> 若已有setter或getter方法的实现,不会自动生成setter或getter
synthesize的实现
synthesize与property相对,property自动声明方法,synthesize自动完成方法的对应实现。一般synthesize可以省略不写,也可以写明成员变量的赋值保护成员变量不被非法访问。
> 用在@implementation中
> 用来自动生成setter和getter的实现
> @synthesize age = _age;
* setter和getter实现中会访问成员变量_age
* 如果成员变量_age不存在,就会自动生成一个@private的成员变量_age
> @synthesize age;
* setter和getter实现中会访问成员变量age
* 如果成员变量age不存在,就会自动生成一个@private的成员变量age
> 手动实现
* 若手动实现了setter方法,编译器就只会自动生成getter方法
* 若手动实现了getter方法,编译器就只会自动生成setter方法
* 若同时手动实现了setter和getter方法,编译器就不会自动生成不存在的成员变量
Good.h
@interface Good : NSObject
{
int _count;
NSString *_na;
}
@property int count;
@property NSString *name;
@end
Good.m
@implementation Good
@synthesize count = _cou;
@synthesize name = _na;
@end
main.m
int main()
{
Good *g = [Good new];
g.count = 10;
NSLog(@"count = %d",g.count);
g.name = @"buster";
NSLog(@"name = %@",g.name);
return 0;
}
synthesize可以指定成员变量间的赋值,这样可以保护成员变量被非法访问。
id
1.简介
- 万能指针,能指向任何OC对象,相当于NSObject*
- id类型的定义
typedef struct objc_object{
Class isa;
}*id;
2.使用
//注意:id后面不要加上*
id p = [Person new];
3.局限性
调用一个不存在的方法,编译器会马上报错
构造方法
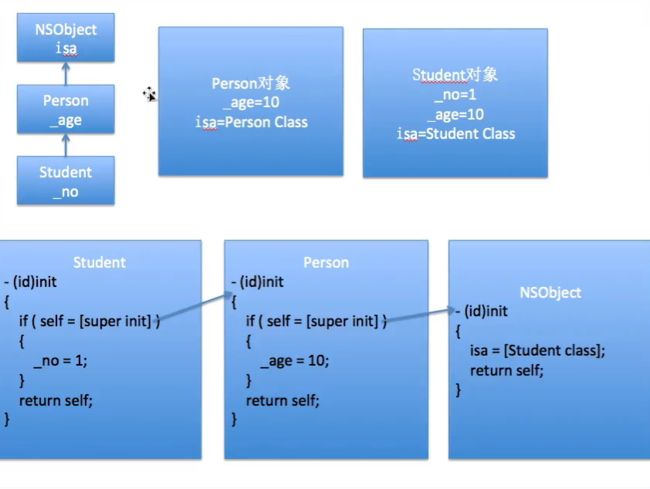
1.对象创建原理
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
2.init方法的重写
- 想在对象创建完毕后,成员变量马上就有一些默认的值
- init方法的重写过程
- (id)init
{
if (self = [super init])
{
//初始化成功
_age = 10 ;
}
//返回一个已经初始化完毕的对象
return self;
}
3.自定义构造方法
- 自定义构造方法的规范
- 一定是对象方法,一定以- 开头
- 返回值一般是id类型
- 方法名一般以init开头
// Person.h
// 自定义构造方法
//
#import
@interface Person : NSObject
@property NSString *name;
@property int age;
- (id)initWithName:(NSString *)name;
- (id)initWithAge:(int)age;
- (id)initWithName:(NSString *)name andAge:(int)age;
@end
参考:黑马程序员_OC的特有语法
iOS笔记之_OC特有语法