1 建立基本SpringMVC工程
1.1 建立SpringMVC Maven工程
web.xml
spring
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
Servlet Context
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring-config/applicationContext.xml
1
spring
/
1.2 创建一个TestController
package com.study.swagger.control;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value="/hello", method=RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String sayHello(String name){
return "hello " + name;
}
}
1.3 配置spring bean
applicatonContext.xml
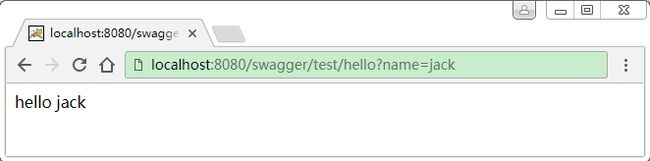
确保该Controller能够正常访问:
2 引入Swagger2
2.1 引入Swagger2依赖
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.7.0
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
2.8.7
2.2 新增Swagger配置类
package com.study.swagger.config;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket swaggerSpringMvcPlugin() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.build()
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Impler Apis")
.description("Impler Apis details")
.license("copyright©impler.cn")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
2.3 配置swagger bean
2.4 添加@ApiOperation注解
在Controller Bean中的@RequestMapping标识的方法上添加@ApiOperation注解。
package com.study.swagger.control;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@ApiOperation(value = "sayHello")
@RequestMapping(value="/hello", method=RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String sayHello(String name){
return "hello " + name;
}
}
2.5 部署启动
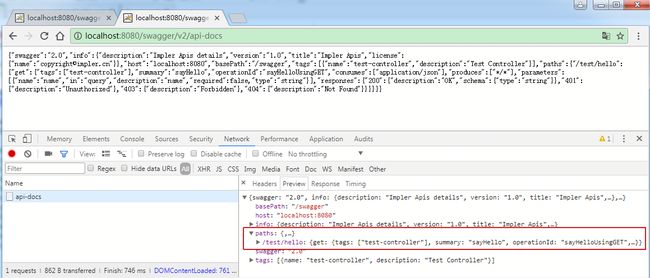
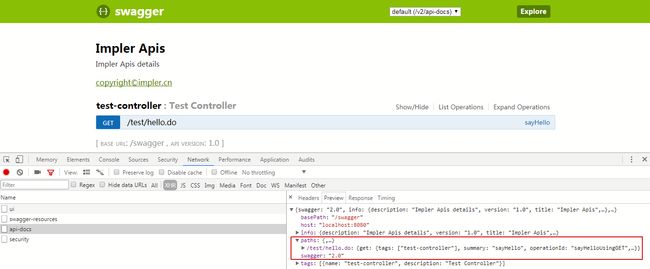
访问http://localhost:8080/swagger/v2/api-docs:
返回的JSON信息中,paths对应Controller中RequestMapping配置的路径
3 引入Swagger UI
上面的配置保证了Swagger后台运作正常。Swagger UI实际就是一套完整的操作页面。可以到https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui将这些静态文件下载下来,然后放到webapp根目录。但是这样显然会增加项目结构复杂度。这里采用另外一种方式,即以依赖jar包的方式引入这些静态文件。
3.1 引入Swagger UI依赖
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.7.0
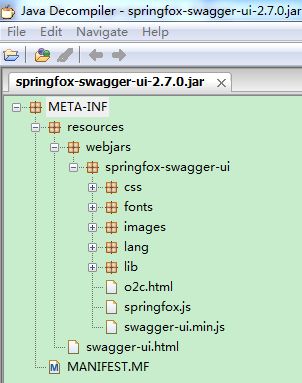
该jar包的结构如下:
这种方式的好处就是不会对现有项目结构造成污染,配置方便。
3.2 部署启动
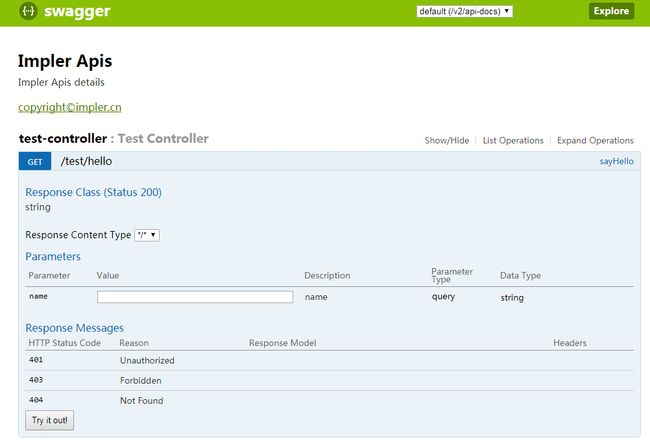
直接访问Swagger UI的首页:http://localhost:8080/swagger/swagger-ui.html。
点开某个接口连接,输入入参信息,点击Try it Out!按钮即可。
完整示例:https://github.com/Impler/SwaggerIntegration/tree/master/swagger-suffix
4 包含后缀的URL配置
上述配置的Spring DispatcherServlet拦截所有请求,包括静态资源,即url-pattern为/。但是现实中有很多将DispatcherServlet专门用来处理.do、.action等后缀结尾的请求,即。url-pattern为.do、.action。对静态资源的请求则交由default servlet来处理。
web.xml
spring
*.do
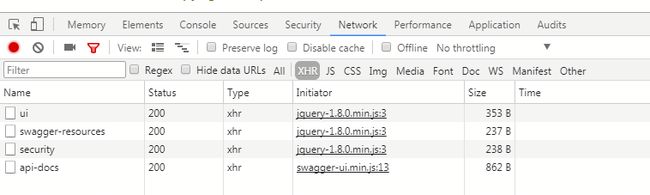
经过观察网络请求发现,Swagger UI在页面加载时会发送如下4个请求:
- /swagger-resources/configuration/ui:swagger配置信息
- /swagger-resources:swagger资源路径,默认default
- /swagger-resources/configuration/security:swagger安全性信息
- /v2/api-docs:项目内的接口信息(重要)
这些请求url均在swagger-ui的jar包内的静态文件中定义,我们一般不去修改。但是swagger的这些请求又需要DispatcherServlet来分发处理,所以需要为这些url配置额外的url-pattern。
spring
*.do
/v2/api-docs
/swagger-resources
/swagger-resources/configuration/security
/swagger-resources/configuration/ui
/v2/api-docs请求响应返回的json串的path属性中包含项目内接口的所有url信息,其实现是在springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers.ServiceModelToSwagger2MapperImpl Bean中,通过扫描所有Controller类中@RequestMapping注解来获取的。所以这里借助Spring强大的AOP功能,在swagger返回后台接口信息前拦截,然后在所有的接口url中拼接指定的请求后缀。
package com.study.swagger.config;
/**
* 将接口url中追加模式后缀.do
* @author impler
* @date 2017年9月30日
*/
@Aspect
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Component
public class SwaggerApiSuffixAspect {
@AfterReturning(pointcut="execution(public io.swagger.models.Swagger springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers.ServiceModelToSwagger2MapperImpl.mapDocumentation(..))",
returning="swagger")
public void doBeforeBussinessCheck(Swagger swagger){
Map paths = swagger.getPaths();
if(null != paths){
Map newPaths = new HashMap(paths);
paths.clear();
Iterator it = newPaths.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String oldKey = it.next();
// 添加模式后缀 .do
String newKey = oldKey + ".do";
paths.put(newKey, newPaths.get(oldKey));
}
newPaths = null;
}
}
}
完整示例:https://github.com/Impler/SwaggerIntegration/tree/master/swagger-suffix