【C++学习笔记】----模拟实现vector容器(详解常见方法实现)
1.简介
概念:vector是一种可变大小的容器,物理上是一段连续的空间,和数组相比,它可以实现按需增长,十分好用,和list相比,vector可以直接访问任意位置的元素,不足的是,除尾插尾删之外的插入和删除,效率比较差。
结构:
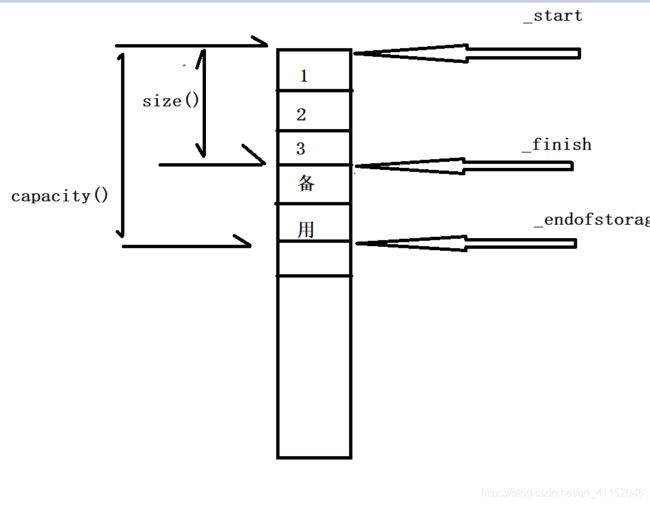
2.代码展示
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include v1(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> v2(v);
vector<int> v3(6,6);
//v.clear();
//cout << v.front() <<" "<
//v.swap(v3);
//cout << v[0]<< endl;
//v3 = v2;
v.insert(v.begin() + 5, 6);
v.insert(v.begin() + 6, 7);
v.insert(v.begin() + 7, 8);
v.insert(v.begin() + 8, 9);
//v.erase(v.begin()+2);
cout << v.size() << " " << v.capacity() << endl;
//string s("hello");
//vector v4(s.begin(), s.end());
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
void test_vector_string()
{
vector<string> str;
str.push_back("1111");
str.push_back("2222");
str.push_back("3333");
str.push_back("4444");
vector<string> str2(str);
//str.pop_back();
//cout << str.front() <<" "<< str.back() << endl;
//str.reserve(10);
//str.resize(1);
//str.clear();
//str.erase(str.begin()+1);
//str.insert(str.begin()+str.size(), "a");
//vector str1(str.begin(), str.begin() + 2);
//str.swap(str1);
//cout << str.empty();
cout << str.size() << " " << str.capacity() << endl;
//str2 = str1;
for (auto s : str)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
}
}
#include
//cout << v.size() <<" "<< v.capacity() << endl;
//v.clear();
//v.erase(v.begin(),v.begin()+2);
//v.insert(v.end(),2);
//v.swap(v1);
//v.pop_back();
//auto pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
//v.erase(v.begin());
vector<char> v3(s.begin(), s.end());
for (auto e : v3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
//test_vector();
xff::test_vector_int();
//xff::test_vector_string();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.总结
vector的一些方法实现和string很类似。
但是,实现过程中我发现几个需要注意的点。
1.vector 不一定存储int类型的数据,所以我们要解决类型的问题。
2.由于类型的问题,我们在扩容的时候不能直接用拷贝函数,memcpy(dst,src,n),按字节拷贝,浅拷贝。自定义类型可能会出现错误,如果是string类型的话,值拷贝析构就出现问题了。
3.迭代器实际上就是原生指针,在构造函数那里,我们不限定是哪个容器的迭代器,如果直接用vector的话,就只能构造vector的对象中的一部分。
4.迭代器失效,由于插入删除都有可能导致迭代器失效,插入可能导致扩容,底层的指针改变了,所以会失效,删除的话,按理说不会失效,但是编译器在程序运行的过程中,检查到有空间的变化时就会失效,所以我在实现insert和erase的时候,只给了初始位置,当可能会失效时,重新将头指针指向心的空间。
通过自己实现vector容器,我对vector的使用更加熟练,同时也掌握了底层原理,对我的代码能力也是一种提升,初学难免会有错误,您发现错误,欢迎留言。