【机器学习】实战系列四——聚类实验
系列文章目录
学习笔记:
【机器学习】第一章——机器学习分类和性能度量
【机器学习】第二章——EM(期望最大化)算法
【机器学习】第六章——概率无向图模型
实战系列:
【机器学习】实战系列一——波士顿房价预测(一文学会)
【机器学习】实战系列二——梯度下降(一文学会)
【机器学习】实战系列三——支持向量机(一文学会)
【机器学习】实战系列四——聚类实验(一文学会)
【机器学习】实战系列五——天文数据挖掘实验(天池比赛)
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 开源
- 一、实验简介
- 二、相关理论及知识点
- 二、实验流程
-
- 1.导入库
- 2.载入数据集
- 3. 数据可视化
- 4. 画出散点图
- 5. 划分数据集
- 6. K-means聚类
- 7. 计算K-means准确率
- 8. EM聚类
- 9. 计算分类准确率
- 10. 谱聚类
- 11. 计算谱聚类准确率
- 12. 实验结果
- 参考资料
【注】本文实验环境为Jupyter Notebook
开源
完整代码已开源至github
https://github.com/TommyGong08/BIT-CS-Code/tree/master/Machine_Learning
如果对你有帮助的话,欢迎star和follow~
一、实验简介
本实验采用三种聚类方法,对iris数据集进行聚类,其目的是提升学生应用聚类方法解决实际问题的能力。
二、相关理论及知识点
(1)聚类的原理
(2)聚类方法的应用
(3)聚类方法评价指标
二、实验流程
1.导入库
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
2.载入数据集
代码如下:
%matplotlib inline
sns.set(style="white")
pd.set_option("display.max_rows", 1000)
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
Y = iris.target
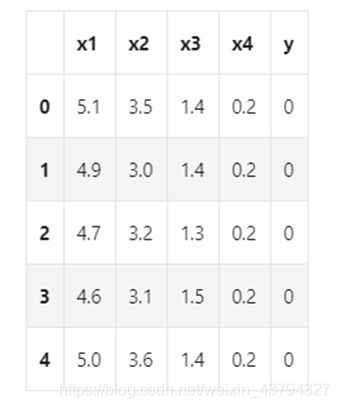
3. 数据可视化
代码如下:
Y = Y.reshape(-1,1)
print(Y.shape)
data = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate((X, Y), axis=1),\
columns=["x1", "x2", "x3", "x4", "y"])
data["y"] = data["y"].astype("int64")
data.head()
如图所示,数据能够直观地表现出来
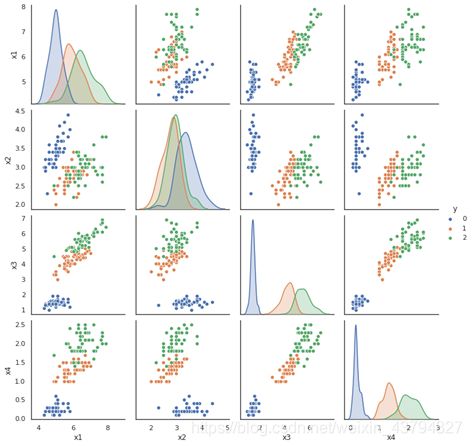
4. 画出散点图
通过四个变量两两之间的散点图,我们能够较为直观地自变量之间的关系对因变量的影响。
5. 划分数据集
num = X.shape[0] # 样本总数
ratio = 7/3 # 划分比例,训练集数目:测试集数目
num_test = int(num/(1+ratio)) # 测试集样本数目
num_train = num - num_test # 训练集样本数目
index = np.arange(num) # 产生样本标号
np.random.shuffle(index) # 洗牌
x_test = X[index[:num_test],:] # 取出洗牌后前 num_test 作为测试集
y_test = Y[index[:num_test]]
x_train = X[index[num_test:],:] # 剩余作为训练集
y_train = Y[index[num_test:]]
6. K-means聚类
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=3)
kmeans.fit(x_train)
y_test_pre_kmeans = kmeans.predict(x_test)
print("y_test_pre:")
print(y_test_pre_kmeans)
print("y_test:")
print(y_test)
7. 计算K-means准确率
# 计算分类准确率
acc = calc_acc(y_test_pre_kmeans, y_test)
acc = sum(y_test_pre_kmeans==y_test)/y_test.shape[0]
print('the accuracy is', acc) # 显示预测准确率
8. EM聚类
# 采用EM聚类
from sklearn import mixture
clf=mixture.GaussianMixture(n_components=3, covariance_type='full')
clf.fit(x_train)
y_test_pre_EM = clf.predict(x_test)
print("y_test_pre:")
print(y_test_pre_EM)
print("y_test:")
print(y_test)
9. 计算分类准确率
# 计算分类准确率
acc = calc_acc(y_test_pre_EM, y_test)
acc = sum(y_test_pre_EM==y_test)/y_test.shape[0]
print('the accuracy is', acc) # 显示预测准确率
10. 谱聚类
选择支持向量机的kernel为‘linear’,分别令C=1,10,100对iris数据集进行预测。代码如下:
# 谱聚类
from sklearn.cluster import SpectralClustering
clustering = SpectralClustering(n_clusters=3,assign_labels="discretize",random_state=0).fit(x_train)
y_test_pre_sp = clustering.fit_predict(x_test)
print("y_test_pre:")
print(y_test_pre_sp)
print("y_test:")
print(y_test)
11. 计算谱聚类准确率
选择支持向量机的kernel为‘rbf’,分别令C=1,10,100对iris数据集进行预测。代码如下:
acc = calc_acc(y_test_pre_sp, y_test)
acc = sum(y_test_pre_sp==y_test)/y_test.shape[0]
print('the accuracy is', acc) # 显示预测准确率
12. 实验结果
准确率由于数据集被打乱了,每次实验的结果都不一样,这里就不展示了。
参考资料
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/clustering.html#clustering
你的点赞将是对我最大的支持,如果本次这篇博客对你有所帮助,欢迎点赞收藏~