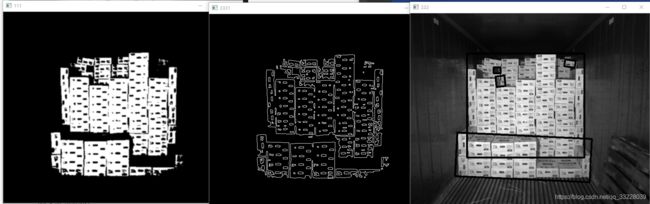
opencv 箱子分割案例分析
1.https://www.jb51.net/article/164348.htm
import cv2
import numpy as np
img= cv2.imread('15_13_57_06.jpg')
grey=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
retVal,greyimg=cv2.threshold(grey,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
greyimg=cv2.GaussianBlur(greyimg,(5,5),0)
canny1 = cv2.Canny(greyimg, 100, 150)
contours, hierarchy=cv2.findContours(greyimg,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c)>200:
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
# 计算最小区域的坐标
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
# 坐标规范化为整数
box = np.int0(box)
cv2.drawContours(grey, [box], 0, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# cv2.drawContours(grey,contours,-1,(0,0,255),3)
cv2.imshow('111',greyimg)
cv2.imshow('222',grey)
cv2.imshow('3331',canny1)
# cv2.imshow('333',dict)
cv2.waitKey(0)1.1 cv2.threshold 图像二值化
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinliang-liang/p/9293310.html
# 1.简单阈值
retVal,th1=cv2.threshold(gray,100,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
#Otsu 滤波
ret2,th2= cv2.threshold(gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 2.自适应阈值
th3 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,\
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,3,2) #换行符号 \
th4 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,\
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,3,2) #换行符号 \
cv2.imshow('111',gray)
cv2.imshow('221',th1)
cv2.imshow('222',th2)
cv2.imshow('223',th3)
cv2.imshow('224',th4)2.cv2.GaussianBlur
高斯模糊,就是使用权重满足正则化的原则。越是中心的数据权重越大,使用正则化的权重去模糊数据。具体就是拿正则化的比例去卷积数据。卷积核的大小和均方差的大小。如果均方差大,说明中心的数据的权重就小一点。
import numpy
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
from math import floor
import cv2
gaussian_kernel_size = 3 # 3 * 3 #
gaussian_kernel_sigma = 2
gaussian = norm(loc = 0.0, scale = gaussian_kernel_sigma)
pdf = gaussian.pdf(
numpy.arange(
-floor(gaussian_kernel_size * 0.5),
floor(gaussian_kernel_size * 0.5) + 1,
dtype = numpy.float64
)
)
pdf /= numpy.sum(pdf) + numpy.finfo(numpy.float64).eps # 别忘了这一步要归一化 #
data = numpy.array(
[
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
],
dtype = numpy.float64
)
a=[]
for i,d in enumerate(numpy.pad(data, 1)):
for j in range(5):
a.append(np.dot(pdf, d[j:j + 3]))
ary=np.array(a).reshape(7,5).T
b=[]
for i,d in enumerate(ary):
for j in range(5):
b.append(np.dot(pdf, d[j:j + 3]))
ary1=np.array(b).reshape(5,5)
print(ary1)
cv2.GaussianBlur(data, (gaussian_kernel_size, gaussian_kernel_size), gaussian_kernel_sigma)3.cv2.Sobel 先高斯然后使用X,Y两个卷积核卷积
4.cv2.Canny
import cv2
import numpy as np
img= cv2.imread('16_09_10_40.jpg')
gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray=cv2.bilateralFilter(gray,d=0,sigmaColor=100,sigmaSpace=15)
# gray=cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
rows,cols=gray.shape
gradientX=np.zeros((rows,cols),np.uint8)
gradientY=np.zeros((rows,cols),np.uint8)
gradientXY=np.zeros((rows,cols),np.uint8)
pointDirection=np.zeros((rows,cols),np.uint8)
threshold=np.zeros((rows,cols),np.uint8)
highThreshold=100
lowThreshold=20
sobelx=[[-1,0,1],
[-1,0,1],
[-1,0,1]]
sobely=[[1,2,1],
[0,0,0],
[-1,-2,-1]]
sobelx=np.array(sobelx)
sobely=np.array(sobely)
sobel_x_h,sobel_x_w=sobelx.shape
sobel_y_h,sobel_y_w=sobely.shape
pad_x_img=np.pad(gray,((sobel_x_h//2,sobel_x_h//2),(sobel_x_w//2,sobel_x_w//2)))
pad_y_img=np.pad(gray,((sobel_y_h//2,sobel_y_h//2),(sobel_y_w//2,sobel_y_w//2)))
gradientX=cv2.filter2D(pad_x_img,-1,sobelx)
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
cur_output_x = pad_x_img[i:i+sobel_x_h,j:j+sobel_x_w] * sobelx
cur_output_y = pad_y_img[i:i + sobel_y_h, j:j + sobel_y_w] * sobely
conv_sum_x = np.sum(cur_output_x)
conv_sum_y = np.sum(cur_output_y)
gradientY[i, j] = conv_sum_y
gradientX[i, j] = conv_sum_x
gradientXY[i,j]=np.sqrt(conv_sum_y**2+conv_sum_x**2)
pointDirection[i,j]=np.arctan(conv_sum_y/conv_sum_x)
outputImage=gradientXY.copy()
for i in range(1,rows-1):
for j in range(1,cols-1):
NE=gradientXY[i-1,j+1]
NW=gradientXY[i-1,j-1]
N=gradientXY[i-1,j]
W=gradientXY[i,j-1]
E=gradientXY[i,j+1]
SW=gradientXY[i+1,j-1]
S=gradientXY[i+1,j]
SE=gradientXY[i+1,j+1]
theta=pointDirection[i,j]
if theta<=np.pi/4 and theta>=0 :
gp1=(1-np.tan(theta))*E+np.tan(theta)*NE
gp2=(1-np.tan(theta))*W+np.tan(theta)*SW
elif theta>np.pi/4:
gp1=(1-1/np.tan(theta))*N+1/np.tan(theta)*NE
gp2=(1-1/np.tan(theta))*S+1/np.tan(theta)*SW
elif theta<0 and theta>=-np.pi/4:
gp1 = (1 - np.tan(-theta)) * E + np.tan(-theta) * SE
gp2 = (1 - np.tan(-theta)) * W + np.tan(-theta) * NW
else:
gp1 = (1 - 1/np.tan(-theta)) * S + 1/np.tan(-theta) * SE
gp2 = (1 - 1/np.tan(-theta)) * N + 1/np.tan(-theta) * NW
if gradientXY[i,j]=highThreshold:
outputImage[i,j]=255
highPoints.append([i,j])
elif outputImage[i,j]= rows - 1 or j >= cols - 1:
return
if image[i - 1, j - 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j - 1] < 255:
image[i - 1, j - 1]=255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j - 1)
if (image[i - 1, j] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j] < 255):
image[i - 1, j]= 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j)
if (image[i - 1, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j + 1] < 255):
image[i - 1, j + 1]=255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j + 1)
if (image[i, j - 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i, j - 1] < 255):
image[i, j - 1]= 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i, j - 1)
if (image[i, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i, j + 1] < 255):
image[i, j + 1]= 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i, j + 1)
if (image[i + 1, j - 1]>= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j - 1] < 255):
image[i + 1, j - 1]= 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j - 1)
if (image[i + 1, j] >= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j] < 255):
image[i + 1, j]=255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j)
if (image[i + 1, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j + 1] < 255):
image[i + 1, j + 1]=255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j + 1)
for poinst in highPoints:
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(outputImage,lowThreshold,poinst[0],poinst[1])
for i in range(1,rows-1):
for j in range(1,cols-1):
if outputImage[i,j]<255:
outputImage[i,j]=0
# canny_car=cv2.Canny(gray,200,256)
higth=10
width=3
kernel1_temp = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(width, higth))
kernel2_temp = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(higth, width))
test_ONE_1 = cv2.morphologyEx(outputImage,cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel1_temp)
test_ONE_2 = cv2.morphologyEx(test_ONE_1,cv2.MORPH_OPEN,kernel1_temp)
test_TWO_1 = cv2.morphologyEx(outputImage,cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel2_temp)
test_TWO_2 = cv2.morphologyEx(test_TWO_1,cv2.MORPH_OPEN,kernel2_temp)
test_combine = test_ONE_2 + test_TWO_2
cv2.imshow('gradientX',gradientX)
cv2.imshow('gradientY',gradientY)
cv2.imshow('gradientXY',gradientXY)
cv2.imshow('outputImage',outputImage)
cv2.imshow('canny_car',canny_car)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.imshow('test_combine',test_combine)
cv2.waitKey(0)
5.cv2.bilateralFilter 双线滤波
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
# 高斯核生成函数
def gaussian_kernel(gaussian_kernel_size, sigma=1, k=1):
if sigma == 0:
sigma = ((gaussian_kernel_size - 1) * 0.5 - 1) * 0.3 + 0.8
X = np.linspace(-k, k, gaussian_kernel_size)
Y = np.linspace(-k, k, gaussian_kernel_size)
x, y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
gauss = np.exp(-(x ** 2 + y ** 2) / (2 * sigma ** 2))
return gauss * (1 / np.sum(gauss))
def pixel_kernel(pix, box, pg):
box1 = np.zeros(box.shape)
for i in range(len(box)):
t = int(math.fabs(int(pix) - int(box[i])))
box1[i] = pg[t]
return box1
def pixel_gaussion(sigma=30):
box = np.zeros(256)
for i in range(0, 255):
box[i] = np.exp(-(i ** 2) / (2 * sigma ** 2))
return box
def spilt(a):
if a / 2 == 0:
x1 = x2 = a / 2
else:
x1 = math.floor(a / 2)
x2 = a - x1
return -x1, x2
def get_pixel(i, j, gaussian_kernel_size, gray):
temp = np.zeros(gaussian_kernel_size * gaussian_kernel_size)
count = 0
x1, x2 = spilt(gaussian_kernel_size)
for m in range(x1, x2):
for n in range(x1, x2):
if i + m < 0 or i + m > gray.shape[0] - 1 or j + n < 0 or j + n > gray.shape[1] - 1:
temp[count] = gray[i, j]
else:
temp[count] = gray[i + m, j + n]
count += 1
return temp
def main():
# 高斯kernel_size=5
gaussian_kernel_size = 5
# 空间高斯sigma
s_sigma = 10
# 灰度高斯sigma
g_sigma = 30
gk = gaussian_kernel(gaussian_kernel_size, s_sigma) # 空间高斯核
img = cv2.imread('16_09_11_55.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rows, cols = gray.shape
mybilateralFilter = np.zeros(gray.shape,np.uint8)
pg = pixel_gaussion(g_sigma)
print(np.sum(pg)) # list
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
box = get_pixel(i, j, gaussian_kernel_size, gray) # 获取相邻像素
pk = pixel_kernel(gray[i, j], box, pg)
box = np.array(box).reshape(gaussian_kernel_size, gaussian_kernel_size)
pk = np.array(pk).reshape(gaussian_kernel_size, gaussian_kernel_size)
evalue = np.multiply(gk, pk)
mybilateralFilter[i, j] = int(np.sum(box * evalue))
blur = cv2.bilateralFilter(gray,9,10,30)
cv2.imshow('myblur', mybilateralFilter)
cv2.imshow('blur',blur)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
6.cv2.kmeans 聚类
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import os
srcImage=cv2.imread("15_13_57_06.jpg")
# 均值聚类提取前景:二维转一维
def kmean_img(srcImage):
imgVec = np.float32(srcImage.reshape((-1,3)))
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,10,1.0)
flags = cv2.KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS
ret,label,clusCenter = cv2.kmeans(imgVec,2,None,criteria,10,flags)
clusCenter = np.uint8(clusCenter)
clusResult = clusCenter[label.flatten()]
imgres = clusResult.reshape((srcImage.shape))
imgres = cv2.cvtColor(imgres,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
max=int(np.max(imgres))
min=int(np.min(imgres))
bwThresh = (max+min)/2
_,thresh = cv2.threshold(imgres,bwThresh,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
thresh1=np.zeros(thresh.shape,np.uint8)
thresh1[thresh==0]=255
kernel=cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(9,9))
test_ONE_2 = cv2.dilate(thresh1, kernel)
# threshRotate = cv2.merge([thresh,thresh,thresh])
# cv2.imshow("thresh",thresh)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# 确定前景外接矩形
# find contours
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(test_ONE_2, cv2.RETR_TREE , cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE )
maxconArea = 0
maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxconArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxconArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
objCont = contours[maxAreaPos]
print(maxconArea)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(objCont)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
srcImage=cv2.drawContours(srcImage,[box],-1,(255,255,0),3)
# for c in contours:
# # if cv2.contourArea(c) > 2000:
# rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
# # 计算最小区域的坐标
# box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
# # 坐标规范化为整数
# box = np.int0(box)
# cv2.drawContours(srcImage, [box], 0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("srcImage",srcImage)
# cv2.imshow("thresh1",thresh1)
cv2.imshow("imgres",imgres)
# cv2.imshow("test_ONE_2",test_ONE_2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def panelAbstract(srcImage):
# read pic shape
imgHeight,imgWidth = srcImage.shape[:2]
imgHeight = int(imgHeight);imgWidth = int(imgWidth)
# 均值聚类提取前景:二维转一维
imgVec = np.float32(srcImage.reshape((-1,3)))
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,10,1.0)
flags = cv2.KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS
ret,label,clusCenter = cv2.kmeans(imgVec,2,None,criteria,10,flags)
clusCenter = np.uint8(clusCenter)
clusResult = clusCenter[label.flatten()]
imgres = clusResult.reshape((srcImage.shape))
imgres = cv2.cvtColor(imgres,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
bwThresh = int((int(np.max(imgres))+int(np.min(imgres)))/2)
_,thresh = cv2.threshold(imgres,bwThresh,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
threshRotate = cv2.merge([thresh,thresh,thresh])
# 确定前景外接矩形
#find contours
kernel=cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(9,9))
thresh1=np.zeros(thresh.shape,np.uint8)
thresh1[thresh==0]=255
test_ONE_2 = cv2.dilate(thresh1, kernel)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(test_ONE_2,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
minvalx = np.max([imgHeight,imgWidth]);maxvalx = 0
minvaly = np.max([imgHeight,imgWidth]);maxvaly = 0
maxconArea = 0;maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxconArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxconArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
objCont = contours[maxAreaPos]
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(objCont)
# box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
# box = np.int0(box)
# srcImage=cv2.drawContours(srcImage,[box],-1,(255,255,0),3)
# # for c in contours:
# # # if cv2.contourArea(c) > 2000:
# # rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
# # # 计算最小区域的坐标
# # box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
# # # 坐标规范化为整数
# # box = np.int0(box)
# # cv2.drawContours(srcImage, [box], 0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
# cv2.imshow("srcImage",srcImage)
# # cv2.imshow("thresh1",thresh1)
# cv2.imshow("imgres",imgres)
# # cv2.imshow("test_ONE_2",test_ONE_2)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# # 旋转校正前景
# rect = cv2.minAreaRect(objCont)
for j in range(len(objCont)):
minvaly = np.min([minvaly,objCont[j][0][0]])
maxvaly = np.max([maxvaly,objCont[j][0][0]])
minvalx = np.min([minvalx,objCont[j][0][1]])
maxvalx = np.max([maxvalx,objCont[j][0][1]])
if rect[2] <=-45:
rotAgl = 90 +rect[2]
else:
rotAgl = rect[2]
if rotAgl == 0:
panelImg = srcImage[minvalx:maxvalx,minvaly:maxvaly,:]
else:
rotCtr = rect[0]
rotCtr = (int(rotCtr[0]),int(rotCtr[1]))
rotMdl = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(rotCtr,rotAgl,1)
imgHeight,imgWidth = srcImage.shape[:2]
#图像的旋转
dstHeight = math.sqrt(imgWidth *imgWidth + imgHeight*imgHeight)
dstRotimg = cv2.warpAffine(threshRotate,rotMdl,(int(dstHeight),int(dstHeight)))
dstImage = cv2.warpAffine(srcImage,rotMdl,(int(dstHeight),int(dstHeight)))
dstRotimg = cv2.cvtColor(dstRotimg,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('dstRotimg',dstRotimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
_,dstRotBW = cv2.threshold(dstRotimg,127,255,0)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dstRotBW,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
maxcntArea = 0;maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxcntArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxcntArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[maxAreaPos])
#提取前景:panel
panelImg = dstImage[int(y):int(y+h),int(x):int(x+w),:]
return panelImg
# 使用grabCut算法
def grabcut_img(img):
mask = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], np.uint8)
# 背景模型
bgdModel = np.zeros((1, 65), np.float64)
# 前景模型
fgdModel = np.zeros((1, 65), np.float64)
rect = (0, 0, 512, 640)
# 使用grabCut算法
cv2.grabCut(img, mask, rect, bgdModel, fgdModel, 5, cv2.GC_INIT_WITH_RECT)
mask2 = np.where((mask == 2) | (mask == 0), 0, 1).astype('uint8')
img = img * mask2[:, :, np.newaxis]
cv2.imshow("thresh",img)
cv2.imshow("mask2",mask2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
path=r"C:\Users\39314\Desktop\qingdao"
for file in os.listdir(path):
if file.endswith('jpg'):
file_path=os.path.join(path,file)
srcImage=cv2.imread(file_path)
kmean_img(srcImage)
# kmean_img(srcImage)
# a = panelAbstract(srcImage)
# cv2.imshow('figa', a)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
7.方法柔和
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import os
#首先背景分割,切出需要检测的范围
#然后使用双线滤波的canny边缘检测算子
def kmean_img(srcImage):
dstimg=np.zeros(srcImage.shape,np.uint8)
imgVec = np.float32(srcImage.reshape((-1,3)))
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,10,1.0)
flags = cv2.KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS
ret,label,clusCenter = cv2.kmeans(imgVec,2,None,criteria,10,flags)
clusCenter = np.uint8(clusCenter)
clusResult = clusCenter[label.flatten()]
imgres = clusResult.reshape((srcImage.shape))
imgres = cv2.cvtColor(imgres,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
max=int(np.max(imgres))
min=int(np.min(imgres))
bwThresh = (max+min)/2
_,thresh = cv2.threshold(imgres,bwThresh,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
thresh1=np.zeros(thresh.shape,np.uint8)
thresh1[thresh==0]=255
kernel=cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(9,9))
test_ONE_2 = cv2.dilate(thresh1, kernel)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(test_ONE_2, cv2.RETR_TREE , cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE )
maxconArea = 0
maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxconArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxconArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
objCont = contours[maxAreaPos]
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(objCont)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
minx=np.min(box[:,1])
miny=np.min(box[:,0])
maxx=np.max(box[:,1])
maxy=np.max(box[:,0])
dstimg[minx:maxx,miny:maxy]=srcImage[minx:maxx,miny:maxy]
return dstimg
# # srcImage=cv2.drawContours(srcImage,[box],-1,(255,255,0),3)
# srcImage = cv2.drawContours(srcImage, [box], -1, (255, 255, 0), 3)
# cv2.imshow("srcImage", srcImage)
# cv2.imshow("dstimg",dstimg)
# # cv2.imshow("thresh1",thresh1)
# cv2.imshow("imgres",imgres)
# # cv2.imshow("test_ONE_2",test_ONE_2)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
def canny(img):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur=cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
canny_car = cv2.Canny(blur, 200, 256)
return canny_car
def bilateralFilter_canny(img):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.bilateralFilter(gray, 9, 10, 30)
canny_car=my_canny(blur)
higth = 11
width = 3
kernel1_temp = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (width, higth))
kernel2_temp = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (higth, width))
test_ONE_1 = cv2.morphologyEx(canny_car, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel1_temp)
test_ONE_2 = cv2.morphologyEx(test_ONE_1, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel1_temp)
test_TWO_1 = cv2.morphologyEx(canny_car, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel2_temp)
test_TWO_2 = cv2.morphologyEx(test_TWO_1, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel2_temp)
test_combine = cv2.bitwise_and(test_ONE_2 ,test_TWO_2)
# canny_car = cv2.Canny(blur, 200, 256)
return test_combine
def my_canny(gray):
rows, cols = gray.shape
gradientY = np.zeros((rows, cols), np.uint8)
gradientXY = np.zeros((rows, cols), np.uint8)
pointDirection = np.zeros((rows, cols), np.uint8)
highThreshold = 100
lowThreshold = 20
sobelx = [[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1]]
sobely = [[1, 2, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[-1, -2, -1]]
sobelx = np.array(sobelx)
sobely = np.array(sobely)
sobel_x_h, sobel_x_w = sobelx.shape
sobel_y_h, sobel_y_w = sobely.shape
pad_x_img = np.pad(gray, ((sobel_x_h // 2, sobel_x_h // 2), (sobel_x_w // 2, sobel_x_w // 2)))
pad_y_img = np.pad(gray, ((sobel_y_h // 2, sobel_y_h // 2), (sobel_y_w // 2, sobel_y_w // 2)))
gradientX = cv2.filter2D(pad_x_img, -1, sobelx)
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
cur_output_x = pad_x_img[i:i + sobel_x_h, j:j + sobel_x_w] * sobelx
cur_output_y = pad_y_img[i:i + sobel_y_h, j:j + sobel_y_w] * sobely
conv_sum_x = np.sum(cur_output_x)
conv_sum_y = np.sum(cur_output_y)
gradientY[i, j] = conv_sum_y
gradientX[i, j] = conv_sum_x
gradientXY[i, j] = np.sqrt(conv_sum_y ** 2 + conv_sum_x ** 2)
pointDirection[i, j] = np.arctan(conv_sum_y / conv_sum_x)
outputImage = gradientXY.copy()
for i in range(1, rows - 1):
for j in range(1, cols - 1):
NE = gradientXY[i - 1, j + 1]
NW = gradientXY[i - 1, j - 1]
N = gradientXY[i - 1, j]
W = gradientXY[i, j - 1]
E = gradientXY[i, j + 1]
SW = gradientXY[i + 1, j - 1]
S = gradientXY[i + 1, j]
SE = gradientXY[i + 1, j + 1]
theta = pointDirection[i, j]
if theta <= np.pi / 4 and theta >= 0:
gp1 = (1 - np.tan(theta)) * E + np.tan(theta) * NE
gp2 = (1 - np.tan(theta)) * W + np.tan(theta) * SW
elif theta > np.pi / 4:
gp1 = (1 - 1 / np.tan(theta)) * N + 1 / np.tan(theta) * NE
gp2 = (1 - 1 / np.tan(theta)) * S + 1 / np.tan(theta) * SW
elif theta < 0 and theta >= -np.pi / 4:
gp1 = (1 - np.tan(-theta)) * E + np.tan(-theta) * SE
gp2 = (1 - np.tan(-theta)) * W + np.tan(-theta) * NW
else:
gp1 = (1 - 1 / np.tan(-theta)) * S + 1 / np.tan(-theta) * SE
gp2 = (1 - 1 / np.tan(-theta)) * N + 1 / np.tan(-theta) * NW
if gradientXY[i, j] < gp1 or gradientXY[i, j] < gp2:
outputImage[i, j] = 0
highPoints = []
for i in range(1, rows - 1):
for j in range(1, cols - 1):
if outputImage[i, j] >= highThreshold:
outputImage[i, j] = 255
highPoints.append([i, j])
elif outputImage[i, j] < lowThreshold:
outputImage[i, j] = 0
def DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i, j):
if i <= 0 or j <= 0 or i >= rows - 1 or j >= cols - 1:
return
if image[i - 1, j - 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j - 1] < 255:
image[i - 1, j - 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j - 1)
if (image[i - 1, j] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j] < 255):
image[i - 1, j] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j)
if (image[i - 1, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i - 1, j + 1] < 255):
image[i - 1, j + 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i - 1, j + 1)
if (image[i, j - 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i, j - 1] < 255):
image[i, j - 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i, j - 1)
if (image[i, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i, j + 1] < 255):
image[i, j + 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i, j + 1)
if (image[i + 1, j - 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j - 1] < 255):
image[i + 1, j - 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j - 1)
if (image[i + 1, j] >= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j] < 255):
image[i + 1, j] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j)
if (image[i + 1, j + 1] >= lowThreshold and image[i + 1, j + 1] < 255):
image[i + 1, j + 1] = 255
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(image, lowThreshold, i + 1, j + 1)
for poinst in highPoints:
DoubleThresholdLinkRecurrent(outputImage, lowThreshold, poinst[0], poinst[1])
for i in range(1, rows - 1):
for j in range(1, cols - 1):
if outputImage[i, j] < 255:
outputImage[i, j] = 0
return outputImage
srcImage=cv2.imread("15_13_57_06.jpg")
dstimg=kmean_img(srcImage)
canny_car=bilateralFilter_canny(dstimg)
cv2.imshow("canny_car",canny_car)
cv2.waitKey(0)