WCF开发之宿主(Hosting)
WCF想要对外提供服务,那么需要一个宿主来容纳这些服务。
宿主环境
• Self-hosting
– 控制台应用程序,Windows应用程序,Windows服务
– HTTP, TCP, named pipes, Microsoft® Message Queuing (MSMQ)
• IIS/Microsoft® ASP.NET
– HTTP
• Windows Activation Service (windows2008/IIS7的新东西)
– HTTP, TCP, named pipes, MSMQ
下面分别介绍这几种不同的宿主:
Self-Hosting
• ServiceHost实例必须进行初始化来为服务暴露出端点(endpoint)
• 每个ServiceHost与指定的服务类型(接口)相关联
• Self-hosting环境手动创建实例
• 核心方法:
– Open() – 打开信道监听器
– Close() – 关闭信道监听器
ServiceHost配置(1)
• 可以通过程序进行配置:
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(HelloIndigo.HelloIndigoService));
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(HelloIndigo.IHelloIndigoService), new NetTcpBinding(),"net.tcp://localhost:9000/HelloIndigo");
host.Open();
ServiceHost配置(2)
以通过置设置进行初始化
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(HelloIndigo.HelloIndigoService));
host.Open();
• 可配:
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="HelloIndigo.HelloIndigoService" >
<endpoint address="net.tcp://localhost:9000/HelloIndigoService" binding="netTcpBinding" contract="HelloIndigo.IHelloIndigoService" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
这2个Demo就不给大家作了,在前面的文章中作了无数遍,呵呵。节约时间,继续往下看。
多服务(1)
ServiceHost hostA = null;
ServiceHost hostB = null;
try
{
hostA = new ServiceHost(typeof(BusinessServices.ServiceA));
hostB = new ServiceHost(typeof(BusinessServices.ServiceB));
hostA.Open();
hostB.Open();
Console.ReadLine();
}
finally
{
hostA.Close();
hostB.Close();
}
多服务(2)
<services>
<service name="BusinessServices.ServiceA">
<endpoint address="http://localhost:8000/ServiceA" contract="BusinessServices.IServiceA" binding="basicHttpBinding" />
</service>
<service name="BusinessServices.ServiceB">
<endpoint address="http://localhost:8000/ServiceB" contract="BusinessServices.IServiceB" binding="basicHttpBinding" />
</service>
</services>
ServiceHost事件
• 可以钩住ServiceHost事件:
– Opening, Opened
– Closing, Closed
– Faulted, UnknownMessageReceived
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(ExceptionService.Service));
host.Faulted += new EventHandler(OnFaulted);
host.Open();
static void OnFaulted(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// TODO: report to administrator
}
服务行为(Service Behaviors)
• 可以通过程序与服务行为进行交互, 也可以通过配置的方式
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(ExceptionService.Service));
ServiceDebugBehavior debugBehavior = host.Description.Behaviors.Find<ServiceDebugBehavior>();
if (debugBehavior == null)
{
debugBehavior = new ServiceDebugBehavior();
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(debugBehavior);
}
debugBehavior.IncludeExceptionDetailInFaults = true;
host.Open();
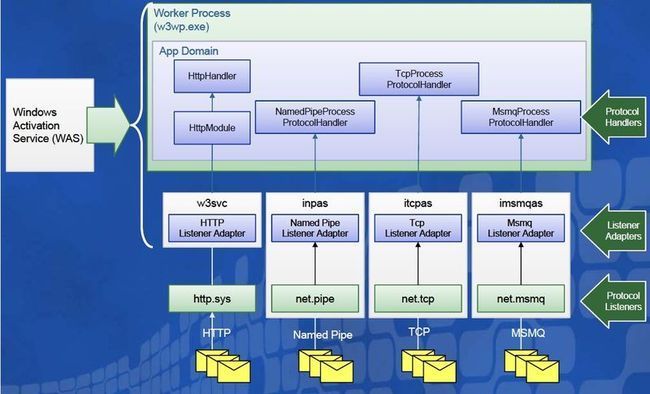
IIS/WAS宿主
请求根据.svc文件在IIS中的扩展映射到中WCFService中
<% @ServiceHost="HelloIndigo.HelloIndigoService" %>
• 服务类型与@ServiceHost的声明相关
• ServiceHost实例化为服务类型
Self-Hosting 与 IIS/WAS
• Self-hosted的端点(endpoint)可以直接进行配置
• IIS/WAS 端点与.svc文件相关联
对于传统的IIS来说,如果WCF用它来做宿主,那么只支持Http的binding。
对于传统的IIS作为宿主有一个好处,就是当客户端发起一个请求,每个不同的请求会在同一服务进程的不同Domain里处理,也就是说如果一个恶意的攻击成功了,他只会影响到某一个App Domain,其他的Domain不会受到影响仍然可以正常工作,服务本身的进程也不会受到影响、那些运行的dll也不会受到影响,这是IIS和.Net Framework的运行方式决定的,是特性。如果用命令行窗口程序的话,一旦恶意攻击成功,那么整个服务就用可能完全瘫痪。
WAS(Windows Process Activation Service):他扩展出了不同Binding的监听器和接口,所以它可以适应更多的通信方式。IIS7中才支持。
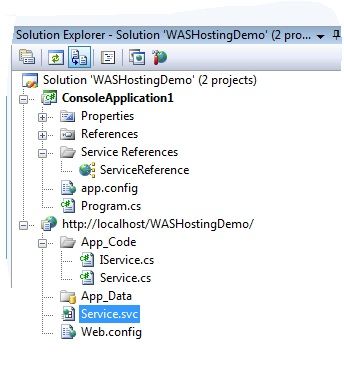
Demo:
对于WAS目前只支持在IIS7中支持,并且操作系统Server2008。可以在Server Manager添加IIS7这个Feature,然后把WAS也同时安装进去,并且启动WAS服务Windows Process Activation Service。同时可以检查下Services里的相关监听器服务是否已启用(e.g. Net.Tcp.ListenerAdapter服务)。这些都没有问题了就可以使用WAS了。个人建议把所有WebServer的Feature都装上。
VS2008可以创建一个Web方式的WCF工程,很方便,变成方式一样,配置方式也差不多。应为时IIS管理服务,如果在IE中看不到服务的话,可以尝试选中目标虚拟目录,双击Directory Browsing,然后启用即可,一般都可以搞定。
唯一不太一样的地方是Service.svc: <%@ ServiceHost Language="C#" Debug="true" Service="Service" CodeBehind="~/App_Code/Service.cs" %> 其他都差不多,配置是防盗Web.config里的。
<!--
Note: As an alternative to hand editing this file you can use the
web admin tool to configure settings for your application. Use
the Website->Asp.Net Configuration option in Visual Studio.
A full list of settings and comments can be found in
machine.config.comments usually located in
\Windows\Microsoft.Net\Framework\v2.x\Config
-->
< configuration >
< configSections >
< sectionGroup name ="system.web.extensions" type ="System.Web.Configuration.SystemWebExtensionsSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" >
< sectionGroup name ="scripting" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" >
< section name ="scriptResourceHandler" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingScriptResourceHandlerSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission ="false" allowDefinition ="MachineToApplication" />
< sectionGroup name ="webServices" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingWebServicesSectionGroup, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" >
< section name ="jsonSerialization" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingJsonSerializationSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission ="false" allowDefinition ="Everywhere" />
< section name ="profileService" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingProfileServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission ="false" allowDefinition ="MachineToApplication" />
< section name ="authenticationService" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingAuthenticationServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission ="false" allowDefinition ="MachineToApplication" />
< section name ="roleService" type ="System.Web.Configuration.ScriptingRoleServiceSection, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" requirePermission ="false" allowDefinition ="MachineToApplication" />
</ sectionGroup >
</ sectionGroup >
</ sectionGroup >
</ configSections >
< appSettings />
< connectionStrings />
< system.web >
<!--
Set compilation debug="true" to insert debugging
symbols into the compiled page. Because this
affects performance, set this value to true only
during development.
-->
< compilation debug ="false" >
< assemblies >
< add assembly ="System.Core, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089" />
< add assembly ="System.Xml.Linq, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089" />
< add assembly ="System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
< add assembly ="System.Data.DataSetExtensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089" />
</ assemblies >
</ compilation >
<!--
The <authentication> section enables configuration
of the security authentication mode used by
ASP.NET to identify an incoming user.
-->
< authentication mode ="Windows" />
<!--
The <customErrors> section enables configuration
of what to do if/when an unhandled error occurs
during the execution of a request. Specifically,
it enables developers to configure html error pages
to be displayed in place of a error stack trace.
<customErrors mode="RemoteOnly" defaultRedirect="GenericErrorPage.htm">
<error statusCode="403" redirect="NoAccess.htm" />
<error statusCode="404" redirect="FileNotFound.htm" />
</customErrors>
-->
< pages >
< controls >
< add tagPrefix ="asp" namespace ="System.Web.UI" assembly ="System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
</ controls >
</ pages >
< httpHandlers >
< remove verb ="*" path ="*.asmx" />
< add verb ="*" path ="*.asmx" validate ="false" type ="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
< add verb ="*" path ="*_AppService.axd" validate ="false" type ="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
< add verb ="GET,HEAD" path ="ScriptResource.axd" type ="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptResourceHandler, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" validate ="false" />
</ httpHandlers >
< httpModules >
< add name ="ScriptModule" type ="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
</ httpModules >
</ system.web >
< system.codedom >
< compilers >
< compiler language ="c#;cs;csharp" extension =".cs" warningLevel ="4" type ="Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider, System, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" >
< providerOption name ="CompilerVersion" value ="v3.5" />
< providerOption name ="WarnAsError" value ="false" />
</ compiler >
< compiler language ="vb;vbs;visualbasic;vbscript" extension =".vb" warningLevel ="4" type ="Microsoft.VisualBasic.VBCodeProvider, System, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" >
< providerOption name ="CompilerVersion" value ="v3.5" />
< providerOption name ="OptionInfer" value ="true" />
< providerOption name ="WarnAsError" value ="false" />
</ compiler >
</ compilers >
</ system.codedom >
< system.web.extensions >
< scripting >
< webServices >
<!--
Uncomment this section to enable the authentication service. Include
requireSSL="true" if appropriate.
<authenticationService enabled="true" requireSSL = "true|false"/>
-->
<!--
Uncomment these lines to enable the profile service, and to choose the
profile properties that can be retrieved and modified in ASP.NET AJAX
applications.
<profileService enabled="true"
readAccessProperties="propertyname1,propertyname2"
writeAccessProperties="propertyname1,propertyname2" />
-->
<!--
Uncomment this section to enable the role service.
<roleService enabled="true"/>
-->
</ webServices >
<!--
<scriptResourceHandler enableCompression="true" enableCaching="true" />
-->
</ scripting >
</ system.web.extensions >
<!--
The system.webServer section is required for running ASP.NET AJAX under Internet
Information Services 7.0. It is not necessary for previous version of IIS.
-->
< system.webServer >
< validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration ="false" />
< modules >
< add name ="ScriptModule" preCondition ="integratedMode" type ="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
</ modules >
< handlers >
< remove name ="WebServiceHandlerFactory-Integrated" />
< add name ="ScriptHandlerFactory" verb ="*" path ="*.asmx" preCondition ="integratedMode" type ="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
< add name ="ScriptHandlerFactoryAppServices" verb ="*" path ="*_AppService.axd" preCondition ="integratedMode" type ="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
< add name ="ScriptResource" preCondition ="integratedMode" verb ="GET,HEAD" path ="ScriptResource.axd" type ="System.Web.Handlers.ScriptResourceHandler, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35" />
</ handlers >
< directoryBrowse enabled ="true" />
</ system.webServer >
< system.serviceModel >
< services >
< service name ="Service" behaviorConfiguration ="ServiceBehavior" >
<!-- Service Endpoints -->
< endpoint address ="wsHttp" binding ="wsHttpBinding" contract ="IService" name ="wsHttpBinding_IService" >
<!--
Upon deployment, the following identity element should be removed or replaced to reflect the
identity under which the deployed service runs. If removed, WCF will infer an appropriate identity
automatically.
-->
< identity >
< dns value ="localhost" />
</ identity >
</ endpoint >
< endpoint address ="netTcp" contract ="IService" binding ="netTcpBinding" name ="netTcpBinding_IService" />
< endpoint address ="netPipe" contract ="IService" binding ="netNamedPipeBinding" name ="netNamedPipeBinding_IService" />
< endpoint address ="basicHttp" contract ="IService" binding ="basicHttpBinding" name ="basicHttpBinding_IService" />
< endpoint address ="mex" binding ="mexHttpBinding" contract ="IMetadataExchange" />
</ service >
</ services >
< behaviors >
< serviceBehaviors >
< behavior name ="ServiceBehavior" >
<!-- To avoid disclosing metadata information, set the value below to false and remove the metadata endpoint above before deployment -->
< serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled ="true" />
<!-- To receive exception details in faults for debugging purposes, set the value below to true. Set to false before deployment to avoid disclosing exception information -->
< serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults ="true" />
</ behavior >
</ serviceBehaviors >
</ behaviors >
</ system.serviceModel >
</ configuration >
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Text;
// NOTE: If you change the interface name "IService" here, you must also update the reference to "IService" in Web.config.
[ServiceContract]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
string GetData( int value);
}
public class Service : IService
{
public string GetData( int value)
{
return string .Format( " You entered: {0} " , value);
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string [] args)
{
ServiceReference.ServiceClient proxy = new ConsoleApplication1.ServiceReference.ServiceClient( " wsHttpBinding_IService " );
string s = proxy.GetData( 1 );
Console.WriteLine(s);
proxy = new ConsoleApplication1.ServiceReference.ServiceClient( " netTcpBinding_IService " );
s = proxy.GetData( 2 );
Console.WriteLine(s);
proxy = new ConsoleApplication1.ServiceReference.ServiceClient( " netNamedPipeBinding_IService " );
s = proxy.GetData( 3 );
Console.WriteLine(s);
proxy = new ConsoleApplication1.ServiceReference.ServiceClient( " basicHttpBinding_IService " );
s = proxy.GetData( 4 );
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
}
可以看出客户端是通过名字来区别使用哪个通信协议的。
在这里还要提一下WAS的配置方法,本人搞了半天才研究明白。
这些是默认站点的Binding配置,使自动建立的,我们需要知道Type的名称。然后,把这些Type到家到服务的虚拟目录的Advanced-Settings里,如下图:
只用作了上面的配置,WCF的服务才可以利用WAS来正常被客户端引用,否则会报出异常。
Windows应用程序: 通常用于在客户端安装,来控制WCF服务的开启和关闭。
Windows应用程序(1)
• Windows® Forms 或者WPF
• 从客户端主机暴露服务
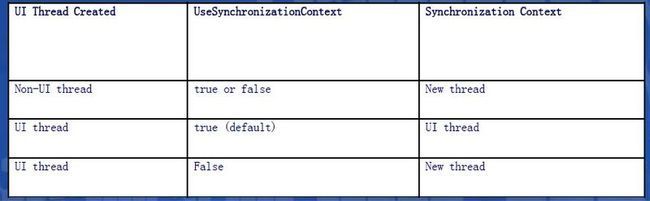
• 需要对上下文同步有所认识
– UI线程或者其他线程
• 值得注意:
– ServiceHost需要手动打开
–判断服务是否需要上下文同步
Windows应用程序(2)
• 如果ServiceHost在非UI线程上打开,服务操
作会在新线程上进行操作
• 如果在UI线程上调用,服务会自动加入到该线
程上,除非UseSynchronizationContext
设置为false
– 可配置的服务行为(service behavior)
有些东西要知道:
[ServiceBehavior(UseSynchronizationContext=true, ConcurrencyMode=ConcurrencyMode.Reentrant)]主要区别在于对线程的管理。
ConcurrencyMode.Single:对于一个服务对象的调用,同时只允许一个现成在处理。不可重入的调用模型。
ConcurrencyMode.Reentrant:可重入的调用模型,同时只允许一个现成在处理,当一个调用请求调用了服务的一个方法,在服务方法中有调用了自己本身。
ConcurrencyMode.Multiple:完全并发访问,同时只允许多个现成在处理,可重入,但要代码控制线程安全。
Callback的过程:
Client--Service Request-->Service (1)
Client<--Callback Request--Service (2)
Client--Callback Response-->Service (3)
Client<--Service Response--Service (4)
总体看来,Window应用程序作为宿主,要考虑很多线程方便的东西,尤其是在callback的方式下,其他的宿主可以自动控制,所以相比之下Windows应用程序在这方便相对麻烦一些。
Demo:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Messaging
{
[ServiceContract(Namespace = " http://www.cnblogs.com/charlesliu " , CallbackContract = typeof (IMessagingServiceCallback))]
public interface IMessagingService
{
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = false )]
void SendMessage( string message);
}
public interface IMessagingServiceCallback
{
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true )]
void MessageNotification( string message);
}
[ServiceBehavior(UseSynchronizationContext = true , ConcurrencyMode = ConcurrencyMode.Reentrant)]
public class MessagingService : IMessagingService
{
public void SendMessage( string message)
{
IMessagingServiceCallback callback = OperationContext.Current.GetCallbackChannel < IMessagingServiceCallback > ();
MessageBox.Show(String.Format( " Message '{0}' received on thread {1} : MessageLoop = {2} " , message, Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), Application.MessageLoop), " MessagingService.SendMessage() " );
callback.MessageNotification( string .Format( " MessagingService received message at {0} " , DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString()));
}
}
}
// Book: Learning WCF, O'Reilly
// Book Blog: www.thatindigogirl.com
// Michele's Blog: www.dasblonde.net
// IDesign: www.idesign.net
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Threading;
namespace WindowsHost
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
ServiceHost m_serviceHost;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this .button2.Enabled = false ;
m_serviceHost = new ServiceHost( typeof (Messaging.MessagingService));
}
private void button1_Click( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this .button1.Enabled = false ;
this .button2.Enabled = true ;
m_serviceHost.Open();
}
private void button2_Click( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this .button1.Enabled = true ;
this .button2.Enabled = false ;
m_serviceHost.Close();
}
private void Form1_FormClosing( object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
DialogResult result = MessageBox.Show( " Are you sure you want to close the service? " , " Service Controller " , MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Question, MessageBoxDefaultButton.Button2);
if (result == DialogResult.Yes)
{
if (m_serviceHost != null )
{
m_serviceHost.Close();
m_serviceHost = null ;
}
}
else
e.Cancel = true ;
}
private void Form1_Load( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this .Text += " : UI Thread " + Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode();
}
}
}
< configuration >
< system.web >
< compilation debug ="true" />
</ system.web >
<!-- When deploying the service library project, the content of the config file must be added to the host's
app.config file. System.Configuration does not support config files for libraries. -->
< system.serviceModel >
< services >
< service name ="Messaging.MessagingService" behaviorConfiguration ="Messaging.Service1Behavior" >
< host >
< baseAddresses >
< add baseAddress = "net.tcp://localhost:8731/Design_Time_Addresses/WcfServiceLibrary1/Service1/" />
< add baseAddress = "http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/WcfServiceLibrary1/Service1/" />
</ baseAddresses >
</ host >
<!-- Service Endpoints -->
<!-- Unless fully qualified, address is relative to base address supplied above -->
< endpoint address ="" binding ="netTcpBinding" contract ="Messaging.IMessagingService" >
<!--
Upon deployment, the following identity element should be removed or replaced to reflect the
identity under which the deployed service runs. If removed, WCF will infer an appropriate identity
automatically.
-->
< identity >
< dns value ="localhost" />
</ identity >
</ endpoint >
<!-- Metadata Endpoints -->
<!-- The Metadata Exchange endpoint is used by the service to describe itself to clients. -->
<!-- This endpoint does not use a secure binding and should be secured or removed before deployment -->
< endpoint address ="mex" binding ="mexHttpBinding" contract ="IMetadataExchange" />
</ service >
</ services >
< behaviors >
< serviceBehaviors >
< behavior name ="Messaging.Service1Behavior" >
<!-- To avoid disclosing metadata information,
set the value below to false and remove the metadata endpoint above before deployment -->
< serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled ="True" />
<!-- To receive exception details in faults for debugging purposes,
set the value below to true. Set to false before deployment
to avoid disclosing exception information -->
< serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults ="False" />
</ behavior >
</ serviceBehaviors >
</ behaviors >
</ system.serviceModel >
</ configuration >
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
using WindowsClient.ServiceReference1;
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace WindowsClient
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
ServiceReference1.MessagingServiceClient proxy;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this .Text += " : ThreadId " + Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode().ToString();
MessagingServiceCallback callbackType = new MessagingServiceCallback();
InstanceContext context = new InstanceContext(callbackType);
proxy = new MessagingServiceClient(context);
}
private void button1_Click( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
proxy.SendMessage( string .Format( " Hello from {0} " , this .Text));
}
}
[CallbackBehavior(UseSynchronizationContext = false )]
internal class MessagingServiceCallback : IMessagingServiceCallback
{
#region IMessagingServiceCallback Members
public void MessageNotification( string message)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format( " Message '{0}' received on thread {1} : MessageLoop = {2} " , message, Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), Application.MessageLoop), " IMessagingServiceCallback.MessageNotification() " );
}
#endregion
}
}
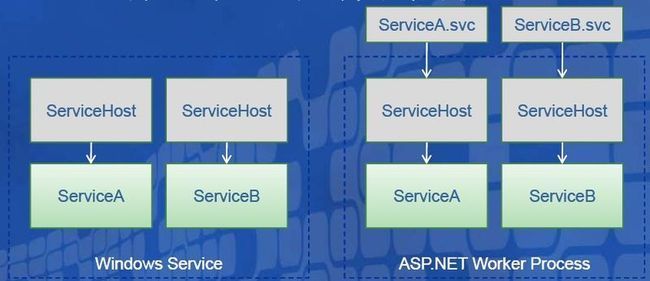
Windows服务宿主
• 用于无人值守的服务器主机
• 也可以部署在客户端主机
– 需要对Windows服务进行额外的配置
• 当主机启动时,宿主环境初始化,如果发生错误可以重新启动
• 打开与关闭Windows服务时,ServiceHost实例也会被打开与关闭
Demo:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Messaging
{
[ServiceContract(Namespace = " http://www.cnblogs.com/charlesliu " )]
public interface IMessagingService
{
[OperationContract]
string SendMessage( string message);
}
[ServiceBehavior(UseSynchronizationContext = false )]
public class MessagingService : IMessagingService
{
public string SendMessage( string message)
{
return String.Format( " Message '{0}' received on thread {1} " , message, Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode());
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.ServiceProcess;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel;
using Messaging;
namespace WindowsServiceHost
{
public partial class ServiceHost : ServiceBase
{
System.ServiceModel.ServiceHost host;
public ServiceHost()
{
InitializeComponent();
this .ServiceName = " MessageServiceHost_EventLog " ;
}
protected override void OnStart( string [] args)
{
host = new System.ServiceModel.ServiceHost( typeof (MessagingService));
host.Faulted += new EventHandler(host_Faulted);
host.Open();
string baseAddresses = "" ;
foreach (Uri address in host.BaseAddresses)
{
baseAddresses += " " + address.AbsoluteUri;
}
string s = String.Format( " {0} listening at {1} " , this .ServiceName, baseAddresses);
this .EventLog.WriteEntry(s, EventLogEntryType.Information);
}
void host_Faulted( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string s = String.Format( " {0} has faulted, notify administrators of this problem " , this .ServiceName);
this .EventLog.WriteEntry(s, EventLogEntryType.Error);
}
protected override void OnStop()
{
if (host != null )
{
host.Close();
string s = String.Format( " {0} stopped " , this .ServiceName);
this .EventLog.WriteEntry(s, EventLogEntryType.Information);
}
host = null ;
}
}
}
< configuration >
< system.web >
< compilation debug ="true" />
</ system.web >
<!-- When deploying the service library project, the content of the config file must be added to the host's
app.config file. System.Configuration does not support config files for libraries. -->
< system.serviceModel >
< services >
< service name ="Messaging.MessagingService" behaviorConfiguration ="Messaging.Service1Behavior" >
< host >
< baseAddresses >
< add baseAddress = "net.tcp://localhost:8731/Design_Time_Addresses/WcfServiceLibrary1/Service1/" />
< add baseAddress = "http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/WcfServiceLibrary1/Service1/" />
</ baseAddresses >
</ host >
<!-- Service Endpoints -->
<!-- Unless fully qualified, address is relative to base address supplied above -->
< endpoint address ="" binding ="netTcpBinding" contract ="Messaging.IMessagingService" >
<!--
Upon deployment, the following identity element should be removed or replaced to reflect the
identity under which the deployed service runs. If removed, WCF will infer an appropriate identity
automatically.
-->
< identity >
< dns value ="localhost" />
</ identity >
</ endpoint >
<!-- Metadata Endpoints -->
<!-- The Metadata Exchange endpoint is used by the service to describe itself to clients. -->
<!-- This endpoint does not use a secure binding and should be secured or removed before deployment -->
< endpoint address ="mex" binding ="mexHttpBinding" contract ="IMetadataExchange" />
</ service >
</ services >
< behaviors >
< serviceBehaviors >
< behavior name ="Messaging.Service1Behavior" >
<!-- To avoid disclosing metadata information,
set the value below to false and remove the metadata endpoint above before deployment -->
< serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled ="True" />
<!-- To receive exception details in faults for debugging purposes,
set the value below to true. Set to false before deployment
to avoid disclosing exception information -->
< serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults ="False" />
</ behavior >
</ serviceBehaviors >
</ behaviors >
</ system.serviceModel >
</ configuration >
对于Windows Service的开发这里不详细探讨,可以参考其他学习资料。其实很简单,上边的就是核心代码,写完后再设计窗口右键鼠标,选择Add Installer,会自动产生安装类。然后再VS2008.NET Command窗口,用installutil servicename.exe (/u)来安装和写在Windows Service, 然后就可以在管理工具/Service下找到这个Service了,开启服务后,Client就可以调用WCF服务了。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
using WindowsClient.ServiceReference1;
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace WindowsClient
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
ServiceReference1.MessagingServiceClient proxy;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this .Text += " : ThreadId " + Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode().ToString();
proxy = new MessagingServiceClient();
}
private void button1_Click( object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(proxy.SendMessage( string .Format( " Hello from {0} " , this .Text)));
}
}
}
宿主的应用场景
• 在每个平台上选择不同类型的宿主
• Windows Server® 2003
– 在IIS 6上应用HTTP协议
– 在Windows服务上应用non-HTTP
• Windows Server® 2008(Longhorn)
– 在IIS 7/WAS可以应用所有的协议
• Windows® XP Service Pack 2 与Windows Vista®
– 客户端主机运行Windows应用程序,或者Windows服务
(完)
转载地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/CharlesLiu/archive/2010/03/29/1689785.html