1. tectonics : the branch of geology studying the folding and faulting of the earth's crust.
E.g. Geologists describe the motion of the plates and the consequences of such motion as plate tectonics. 地质学家把板块运动及这种运动所造成的后果看作是板块构造运动.
Wiki: Tectonics,from the Late Latin tectonicus from the Ancient Greek τεκτονικός, "pertaining to building", is the process that controls the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. In particular, it describes the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other.
2. crust : the outer layer of the Earth . E.g : Earth quakes can result from stresses in the earth's crust.地壳内的应力可能引起地震.
Wiki : In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle. The crusts of Earth, the Moon,Mercury,Venus,Mars,Io, and other planetary bodies have been generated largely byigneousprocesses, and these crusts are richer in incompatible elements than their respective mantles. The Earth's crust is composed of distinctly different continental crust and oceanic crust, which have different chemical compositions and physical properties, and which were formed by different geological processes.
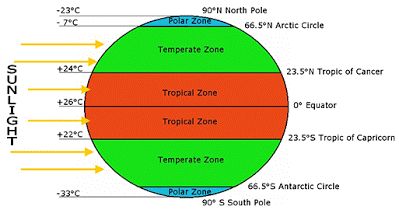
3. climate zones:
4. altitude: elevation especially above sea level or above the earth's surface
E.g. What is the altitude of the top of the mountain?
Wiki: Altitude or height(sometimes known as depth) is defined based on the context in which it is used (aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, and many more). As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context. Although the term altitude is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage.
5.flora and fauna : Wild fauna and flora are important integrants of ecosystem野生动植物是生态系统的重要组成部分.
Wiki: Fauna is all of the animal life of any particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora. Flora, fauna and other forms of life such as fungi are collectively referred to as biota. Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna".Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils.
6. fold mountains : 褶皱山脉;
Fold mountains aremountains that form mainly by the effects of folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust. Before either plate tectonic theory developed, or the internal architecture of thrust belts became well understood, the term was used for most mountain belts, such as the Himalayas.
7. The Appalachian Mountains(/ˌæpəˈlæʃᵻn, -ˈleɪtʃᵻn/ ,French:les Appalaches), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. It once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before naturally occurring erosion.The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east-west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most roads running east or west.
8.Rocky Mountains : The Rocky Mountains, commonly known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the South western United States. Within the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are somewhat distinct from the Pacific Coast Ranges and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada which all lie further to the west.
10. block mountains : also called fault-block mountains, 断块山 Mountains or ranges that result from the upthrow of large fault blocks and that are separated from others by basins or troughs, producing an upland unit bounded by normal or reversed faults.断层山
wiki: Fault-block mountains often result from rifting, another indicator of tensional tectonic forces. These can be small or form extensive rift valley systems, such as the East African Rift zone.Death Valley in California is a smaller example. There are two types of block mountains; lifted and sloped.
11. magma: very hot liquid rock found below the earth's surface 岩浆;熔岩
wiki : is a mixture of molten or semi-molten rock,volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals, dissolved gas and sometimes gas bubbles. Magma often collects in magma chambers that may feed a volcano or solidify underground to form an intrusion. Magma is capable of intruding into adjacent rocks (forming igneousdikes and sills), extrusion onto the surface as lava, and explosive ejection astephra to form pyroclastic rock.