编程之乐
转载请注明原创出处,谢谢!
根据上篇文章- Launcher源码浅析,我们知道点击Launcher某个图标后,会调用Launcher的startActivitySafely方法。
如下:
public boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, ItemInfo item) {
boolean useLaunchAnimation = (v != null) &&
!intent.hasExtra(INTENT_EXTRA_IGNORE_LAUNCH_ANIMATION);
Bundle optsBundle = useLaunchAnimation ? getActivityLaunchOptions(v) : null;
// Prepare intent
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
if (v != null) {
intent.setSourceBounds(getViewBounds(v));
}
try {
// ================== begin ======================
startActivity(intent, optsBundle);
return true;
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException|SecurityException e) {
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.activity_not_found, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to launch. tag=" + item + " intent=" + intent, e);
}
return false;
}
Launcher最终调用了父类 Activity 的startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options)方法,startActivity又调用了startActivityForResult。
在startActivityForResult方法内,会调用Instrumentation的execStartActivity方法。
注: 这里的mInstrumentation是Launcher里面的。
public void startActivityForResult(
String who, Intent intent, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options) {
Uri referrer = onProvideReferrer();
if (referrer != null) {
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REFERRER, referrer);
}
options = transferSpringboardActivityOptions(options);
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, who,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, who, requestCode,
ar.getResultCode(), ar.getResultData());
}
cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);
}
startActivityForResult里面调用了mInstrumentation.execStartActivity方法
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, String target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) { ... }
其中有个参数是mMainThread.getApplicationThread(),mMainThread是Activity类的成员变量(ActivityThread类型),mMainThread.getApplicationThread()获取的是ApplicationThread类型,ApplicationThread则是ActivityThread的内部类,可以看出ApplicationThread是一个Binder对象。
为了后面研究的方便,有必要提前说明下即将出现的这几个类的关系,它们分别是
- IApplicationThread
- ApplicationThread
- ApplicationThreadNative
- ApplicationThreadProxy
如果你查看过AIDL生成的文件,那么这几个类就比较容易理解了,IApplicationThread相当于AIDL接口
class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
// 因为ApplicationThreadNative继承 Binder,且ApplicationThreadNative是抽象类,所以ApplicationThread才是真正的Binder实现。
}
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder implements IApplicationThread {
// Activity中常用到的那个获取接口的方法如:ServiceConnection中 IMedia iMedia = IMedia.Stub.asInterface(binder);
static public IApplicationThread asInterface(IBinder obj) {
// 内部代理类
return new ApplicationThreadProxy(obj);
}
看下这个AIDL接口的部分定义,其中后面要用到。
public interface IApplicationThread extends IInterface {
void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving,
int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean showWindow,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleWindowVisibility(IBinder token, boolean showWindow) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSleeping(IBinder token, boolean sleeping) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleResumeActivity(IBinder token, int procState, boolean isForward, Bundle resumeArgs)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSendResult(IBinder token, List results) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state,
PersistableBundle persistentState, List pendingResults,
List pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleRelaunchActivity(IBinder token, List pendingResults,
List pendingNewIntents, int configChanges,
boolean notResumed, Configuration config) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleNewIntent(List intent, IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleReceiver(Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean sync,
int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void bindApplication(String packageName, ApplicationInfo info, List providers,
ComponentName testName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle testArguments,
IInstrumentationWatcher testWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection uiAutomationConnection,
int debugMode, boolean openGlTrace, boolean restrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent,
Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services,
Bundle coreSettings) throws RemoteException;
注意
mMainThread在Launcher中,且mMainThread变量也是在Activity.attach()中绑定的。
目前我们使用到的某些变量如(mMainThread,mInstrumentation)都是Launcher中已经初始化好的,但我们现在分析的是Launcher启动第三方Activity而不是Launcher本身,后面我们会再次遇到这些变量,这些变量的初始化和绑定过程会出现在新Activity的创建中,目前先不要对这些变量的由来疑惑!
Instrumentation 仪表盘
这个也是非常重要的一个类,大致对这个类有些了解,否则后面很难理解。
mInstrumentation是Activity的一个成员变量,且mInstrumentation是在Activity的 attach(xxx)方法里面赋值的,这个方法非常重要,里面还有mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
等操作。后面会分析到此方法。
Instrumentation 仪表盘,命名就好像管理生命周期一样,事实也差不多如此。
看下Instrumentation 的主要方法:
execStartActivity
callApplicationOnCreate
newActivity
callActivityOnCreate
callActivityOnDestroy
callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState
callActivityOnPostCreate
callActivityOnNewIntent
callActivityOnStart
callActivityOnRestart
callActivityOnResume
callActivityOnStop
callActivityOnSaveInstanceState
callActivityOnPause
callActivityOnUserLeaving
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity内部调用了ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startActivity()方法。
如下:
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
// ...
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
try {
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()是个什么东西,这就是前面为什么要提一下ApplicationThread的原因了,形式几乎一样。
同样看下面几个类:
- IActivityManager
- ActivityManagerService(AMS)
- ActivityManagerNative
- ActivityManagerProxy
和前面完全对应,AMS闪亮登场。
很明显,AMS是真正Binder的实现类。
为了体现AMS的重要性和更好理解Binder,这里的主要部分的代码多贴一些,我们发现和ApplicationThread形式几乎一模一样,而且IActivityManager就是AIDL的接口,而ActivityManagerNative 继承自Binder 且是抽象的,真正的实现是AMS,那么AMS类在哪里呢?
ActivityManagerNative 有一个静态的getDefault方法,根据类加载机制 ,类在调用static方法时候才会初始化,此时返回gDefault.get(); Singleton是Android的一个单例封装类工具类,第一次调用get方法时候会通过create方法初始化AMS对象。
这个单例写法很有意思,又GET一个技能。
public abstract class Singleton {
private T mInstance;
protected abstract T create();
public final T get() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = create();
}
return mInstance;
}
}
}
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
这个Binder对象就是ActivityManagerService。
在线 ActivityManagerService.java
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager
{
/**
* Cast a Binder object into an activity manager interface, generating
* a proxy if needed.
*/
static public IActivityManager asInterface(IBinder obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
IActivityManager in =
(IActivityManager)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor);
if (in != null) {
return in;
}
return new ActivityManagerProxy(obj);
}
/**
* Retrieve the system's default/global activity manager.
*/
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();
}
public IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
private static final Singleton gDefault = new Singleton() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service binder = " + b);
}
IActivityManager am = asInterface(b);
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service = " + am);
}
return am;
}
};
}
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager {
public ActivityManagerProxy(IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(startFlags);
if (profilerInfo != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
profilerInfo.writeToParcel(data, Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
if (options != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
options.writeToParcel(data, 0);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
}
// ..............
// ..............
//
}
简单看下 IActivityManager 接口的部分声明:
public interface IActivityManager extends IInterface {
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int flags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) throws RemoteException;
public int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int flags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, int userId) throws RemoteException;
public int startActivityAsCaller(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int flags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity,
int userId) throws RemoteException;
public WaitResult startActivityAndWait(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho,
int requestCode, int flags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options,
int userId) throws RemoteException;
public int startActivityWithConfig(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho,
int requestCode, int startFlags, Configuration newConfig,
Bundle options, int userId) throws RemoteException;
public int startActivityIntentSender(IApplicationThread caller,
IntentSender intent, Intent fillInIntent, String resolvedType,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int flagsMask, int flagsValues, Bundle options) throws RemoteException;
public int startVoiceActivity(String callingPackage, int callingPid, int callingUid,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IVoiceInteractionSession session,
IVoiceInteractor interactor, int flags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options,
int userId) throws RemoteException;
public boolean startNextMatchingActivity(IBinder callingActivity,
Intent intent, Bundle options) throws RemoteException;
public int startActivityFromRecents(int taskId, Bundle options)
throws RemoteException;
public boolean finishActivity(IBinder token, int code, Intent data, int finishTask)
throws RemoteException;
public void finishSubActivity(IBinder token, String resultWho, int requestCode) throws RemoteException;
public boolean finishActivityAffinity(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
public void finishVoiceTask(IVoiceInteractionSession session) throws RemoteException;
public boolean releaseActivityInstance(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
public void releaseSomeActivities(IApplicationThread app) throws RemoteException;
public boolean willActivityBeVisible(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
public Intent registerReceiver(IApplicationThread caller, String callerPackage,
IIntentReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter,
String requiredPermission, int userId) throws RemoteException;
public void unregisterReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver) throws RemoteException;
public int broadcastIntent(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IIntentReceiver resultTo, int resultCode,
String resultData, Bundle map, String[] requiredPermissions,
int appOp, Bundle options, boolean serialized, boolean sticky, int userId) throws RemoteException;
public void unbroadcastIntent(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, int userId) throws RemoteException;
public void finishReceiver(IBinder who, int resultCode, String resultData, Bundle map,
boolean abortBroadcast, int flags) throws RemoteException;
public void attachApplication(IApplicationThread app) throws RemoteException;
public void activityResumed(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
我们接着上一步ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startActivity()即
AMS(ActivityManagerService).startActivity();
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
AMS的startActivity方法调用了startActivityAsUser。
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),
userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, null);
}
下面是一系列的调用关系
1. AMS.startActivityAsUser-> ActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait
2. ActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait -> ActivityStarter.startActivityLocked
3. ActivityStarter.startActivityLocked -> ActivityStarter.doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked
4. ActivityStarter.doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked -> ActivityStarter.startActivityUnchecked
5. ActivityStarter.startActivityUnchecked -> mSupervisor(ActivityStackSupervisor).resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
6. ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked->.targetStack(ActivityStack).resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked
7. ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked -> ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked
8. ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked -> mStackSupervisor(ActivityStackSupervisor).startSpecificActivityLocked
9. ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked -> ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked
这段调用过程真是非常复杂,几乎每个类或方法都是千百行,绕的我快晕了。
这些流程,会挑选着代码讲解,如果每个流程一下子把代码贴出来,几乎都会被搞疯。
先看下最后一步:ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
// mService是AMS
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
tips:
在 AMS中,每一个 Activity 组件都有一个用户 ID 和一个进程名称,其中,用户 ID 是在安装该 Activity 组件时由 PackageManagerService 分配的,而进程名称则是由该 Activity 组件的 android:process属性来决定的。
ActivityManagerService 在启动一个 Activity 组件时,首先会以它的用户 ID 和进程名称来检查系统中是否存在一个对应的应用程序进程。如果存在,就会直接通知这个应用程序进程将 Activity 组件启动起来;否则,就会先以这个用户 ID 和进程名称来创建一个应用程序进程,然后在通知这个应用程序进程将该 Activity 组件启动起来。
根据上面if语句的判断:
(1). if (app != null && app.thread != null) { }
如果app已经启动,则通过realStartActivityLocked()启动Activity。
(2). 如果app还未启动,则通过AMS创建应用进程。
上述代码第一次启动必定先运行(2)
查看ActivityManagerService类的 startProcessLocked()方法,注意startProcessLocked方法有多个重载
下面的方法调用app = newProcessRecordLocked,
最后又调用了另一个重载方法startProcessLocked。
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,
boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,
String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) { // 传入的 isolated 参数为 false ,if 成立,并不是隔离的进程
// 根据进程名称和用户 ID 得到应用程序进程,由于不存在,则为 null 。
app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid, keepIfLarge);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: after getProcessRecord");
// 省略部分代码
} else {
// If this is an isolated process, it can't re-use an existing process.
app = null;
}
// 当进程已经被分配的 PID 时,
if (app != null && app.pid > 0) {
}
// 应用程序进程不存在,创建新的进程
if (app == null) {
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: creating new process record");
// 创建应用程序进程
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid);
if (app == null) {
}
app.crashHandler = crashHandler;
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done creating new process record");
} else {
// If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.versionCode, mProcessStats);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: added package to existing proc");
}
// 创建应用程序进程后,最终调用 startProcessLocked 方法
startProcessLocked(
app, hostingType, hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
}
上面的startProcessLocked方法最后调用了下面这个startProcessLocked。
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
// ................ 省略
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: starting to update cpu stats");
updateCpuStats();
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done updating cpu stats");
try {
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
app.processName);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!");
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done updating pids map");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
}
}
可以看到上面调用了Process.start方法启动一个进程。其中有这么一小段代码,如下:
if (entryPoint == null) {
entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
}
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,app.processName,....);
Process.start()方法的第一个参数是 entryPoint 指明入口类是ActivityThread(虽然名字是XXThread,但其实是个普通类),而Java的入口一般都是main方法,那么ActivityThread 的 main 方法将在这里启动。
ActivityThread.main方法并不复杂,来看下它大致干些什么。
public final class ActivityThread {
final Looper mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
final H mH = new H();
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
private static volatile ActivityThread sCurrentActivityThread;
Instrumentation mInstrumentation;
static volatile Handler sMainThreadHandler;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化主线程的消息队列
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
// 开启消息循环
Looper.loop();
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) { // 是否为系统进程
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
} else {
// 省略系统进程代码
}
// 省略 ViewRootImpl 相关代码
}
}
// AMS的 attachApplication方法
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
- Looper.prepareMainLooper();准备循环主线程。
- 创建一个 ActivityThread 对象并attach();
最终sCurrentActivityThread = this; // 当前静态sCurrentActivityThread
AMS.attachApplication(mAppThread);// mAppThread是ApplicationThread - 调用Looper.loop();使主线程中消息循环
AMS.attachApplication(mAppThread);中又调用了AMS的attachApplicationLocked,查看该方法:
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread, int pid) {
ProcessRecord app;
// 移除超时消息,应用程序在规定时间内完成了启动。
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
try{
// 序号1. ************************** IPC 调用 ActivityThread,绑定并创建Application **************************
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode, enableOpenGlTrace,
enableTrackAllocation, isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
}catch(Exception e){
//
}
boolean badApp = false;
boolean didSomething = false;
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
// 序号2. ************************** 调度 Activity **************************
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
badApp = true;
}
}
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
// 序号3 ************************** 调度 Service **************************
if (!badApp) {
try {
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
} catch (Exception e) {
badApp = true;
}
}
// Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process...
// 序号4 ************************** 调度 Broadcast **************************
if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) {
try {
didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
// If the app died trying to launch the receiver we declare it 'bad'
badApp = true;
}
}
}
这个地方代码很多,需要特别注意:
下面把这几个步骤分为几个序号:
- thread.bindApplication启动Application
- 启动Activity
- 启动Service
- 启动Broadcast
每个序号里面都执行跳转多次,一个序号一个序号来说,否则容易犯迷糊。
AMS.attachApplication(mAppThread) 序号一
先看 thread.bindApplication,这是一个IPC通信,thread是IApplicationThread 接口,最终调用的方法是服务端真正的Binder对象即 ApplicationThread.bindApplication()
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings) {
// delete the fucking code ...................
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
可以看到该方法发送一条H.BIND_APPLICATION消息交给handler处理。
我们看下这个Handler,在ActivityThread的内部。
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY");
} break;
case BIND_APPLICATION:
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
break;
case RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
handleRelaunchActivity(r);
} break;
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
handlePauseActivity((IBinder) args.arg1, false,
(args.argi1 & USER_LEAVING) != 0, args.argi2,
(args.argi1 & DONT_REPORT) != 0, args.argi3);
maybeSnapshot();
} break;
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
handlePauseActivity((IBinder) args.arg1, true, (args.argi1 & USER_LEAVING) != 0,
args.argi2, (args.argi1 & DONT_REPORT) != 0, args.argi3);
} break;
// .................. delete
}
根据消息case BIND_APPLICATION:
将执行ActivityThread.handleBindApplication(data);方法。
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// 设置进程名
Process.setArgV0(data.processName);
// 创建 Android 运行环境 ContextImpl .
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
// 初始化 Intrumentation 对象
if (data.instrumentationName != null) {
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext,
new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name), data.instrumentationWatcher,
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
} else {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
}
try {
// If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment with the base application class.
// 创建 Application 对象
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
List providers = data.providers;
if (providers != null) {
installContentProviders(app, providers);
// For process that contains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT is enabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
}
}
// Do this after providers, since instrumentation tests generally start their
// test thread at this point, and we don't want that racing.
try {
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
}
catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
// 执行 Application 的 onCreate 方法
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
} finally {
}
}
AMS.attachApplication(mAppThread) 序号二
序号二调用了mStackSupervisor(ActivityStackSupervisor).attachApplicationLocked(app)方法:
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
final String processName = app.processName;
boolean didSomething = false;
for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
ArrayList stacks = mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks;
for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() - 1; stackNdx >= 0; --stackNdx) {
final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get(stackNdx);
if (!isFocusedStack(stack)) {
continue;
}
ActivityRecord hr = stack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (hr != null) {
if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
&& processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
try {
if (realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
}
if (!didSomething) {
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
return didSomething;
}
该方法遍历 ActivityStack 和 TaskRecord,找到位于 Activity 堆栈顶端的一个 ActivityRecord 对象 hr,接着检查这个 Activity 组件的用户 ID 和 进程名是否与 ProcessRecord 对象 app 所描述的应用程序的用户 ID 和进程名一致,如果一致,则调用 StackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked方法来请求该应用程序进程启动一个 Activity 组件。
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
// .... 删 删 删 删 删 删 删 删 fuck
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
new Configuration(task.mOverrideConfig), r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage,
task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle, r.persistentState, results,
newIntents, !andResume, mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
}
StackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked方法内部调用了app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity()方法,其中thread是ApplicationThread类型,binder对象。
ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity方法如下:
@Override
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List pendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
updateProcessState(procState, false);
ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
// .......... delete code
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
scheduleLaunchActivity里面同样是发送了一条handler消息。
根据上面handleMessage处理的消息类型,将执行
ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity()方法。
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// Initialize before creating the activity
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity
// manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null, false);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
分别调用:
- performLaunchActivity将 Activity 组件启动起来
- handleResumeActivity方法将 Activity 组件的状态设置为 Resumed。
下面只讲Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);就可以了,handleResumeActivity设置Resumed就没有什么必要说了。
ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity是个重重重要的方法 ,我们最前面提到某些 重要角色对象 的设置都是在这个方法里面初始化的。
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// 获取ActivityInfo信息
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
// 获取要启动的Activity的组件信息
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
// 根据相关信息构建组件对象
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
// 通过反射 新建一个 Activity 对象
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
// 这个地方我稍有疑惑,因为根据前面的逻辑 BIND_APPLICATION消息[app == null情况下]->handleApplication()中
// 已经使用LoadedApk.makeApplication()生成一个Application对象了,这里在case LAUNCHER_ACTIVITY又调用一遍。
// 不过LoadedApk.makeApplication有判断null处理,所以只会返回一个Application对象啦!
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (activity != null) {
// 创建 Activity的 ContextImpl ,作为 Activity 的运行上下文环境
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
// 构造Configuration对象
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
// ============= Window对象
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
// ******** 重要 : activity.attach(),我最前面提到的这个方法,把上面这些重要对象都设置为activity的成员变量。********
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
// 设置主题
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
// 根据是否需要持久化调用此方法通知Activity已被创建和启动
// 回调 Activity 的 onCreate 函数
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
// 回调 Activity 的 onStart 函数
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
// Activity 的 onRestoreInstanceState 函数
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
// 返回创建并初始化过的activity对象
return activity;
}
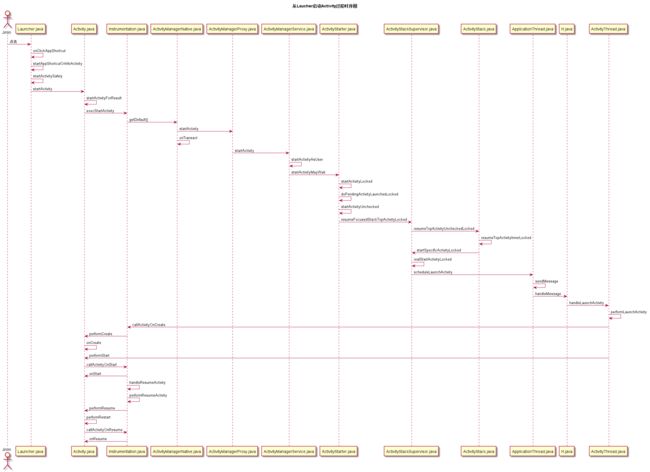
终于讲完了序号1和序号2,这里的序号1和序号2指的是下图这几个步骤的前2个:
讲了这么多,AMS.attachApplication这个方法还没执行完,我了个去,累死了!写的最累的一篇博客了。
时序图实在懒得画了,画这个图估计也够呛,这篇文章篇幅虽然和其他分析AMS的文章比起来算是短些了,因为很多文章几乎把源码全部都贴上了,我看着都晕,单单
AMS.startActivityAsUser->ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked 那9步就够你贴上十几页了,那一部分确实跳来跳去搞得人眼花缭乱,而且每段代码都是千百行,但是最重要的确是最后那两步,所以我把该省略的跳转代码都省掉了,如果具体研究某个步骤就比较容易了,有兴趣的可以查找9步中的某一段代码进行具体分析。花了整整3天时间,如果你喜欢,请点一个赞!nnd......Fuck the code!!!
小结
从上面的执行流程:我们发现Application会创建一个appContext,一个Activity会创建一个Context,(一个Service也会创建一个Context),那么一个应用中 Context的总数 = Activity对象数 + Service对象数 + 1个Application对象。四大组件中的BroadcastReciver和ContentProvider的Context都是直接或间接来自于 Application,Activity,Service。
最后找来自己参考过的一种博主画的图,和我的流程差不多,盗图一张!
相关补充说明
ActivityStack :Android 中的 Activity 组件堆栈信息,也就是 Task。
ActivityStackSupervisor:管理ActivityStack的类。
参考
Android开发艺术探索
Android源码设计模式
Android 7.0 源码
Activity启动过程分析(从Launcher启动)
Android 6.0 Launcher 启动 Activity 过程源码分析(二)