2021-04-29:栈,队列,优先队列(堆),字典,232,225,20,703,239
栈,队列, 优先队列:
1. stack栈: 先入后出 用python自带的List结构,
push, pop, peek, empty ,就不过多介绍了
2.queue队列: 先入后出
一、队列(Queue)
import queue as q
self.q1 = q.Queue()
构造一个q1的队列
Python的Queue模块中提供了同步的、线程安全的队列类,包括FIFO(先入先出)队列Queue,LIFO(后入先出)队列LifoQueue,和优先级队列PriorityQueue。这些队列都实现了锁原语,能够在多线程中直接使用。可以使用队列来实现线程间的同步。
class Queue.Queue(maxsize = 0 )
FIFO队列的构造函数。 maxsize是一个整数,用于设置可以放入队列的项目数的上限。达到此大小后,插入将阻止,直到消耗队列项。如果 maxsize小于或等于零,则队列大小为无限大。
常用方法:
Queue.qsize() 返回队列的大小
Queue.empty() 如果队列为空,返回True,反之False
Queue.full() 如果队列满了,返回True,反之False,Queue.full 与 maxsize 大小对应
Queue.get([block[, timeout]])获取队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.get_nowait() 相当于Queue.get(False),非阻塞方法
Queue.put(item) 写入队列,timeout等待时间
Queue.task_done() 在完成一项工作之后,Queue.task_done()函数向任务已经完成的队列发送一个信号。每个get()调用得到一个任务,接下来task_done()调用告诉队列该任务已经处理完毕。
Queue.join() 实际上意味着等到队列为空,再执行别的操作
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Survivior_Y」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43533825/article/details/89155648
双端队列Deque ,两端都可以插入删除的
(2条消息) Python deque的用法介绍_Python碎片的博客-CSDN博客
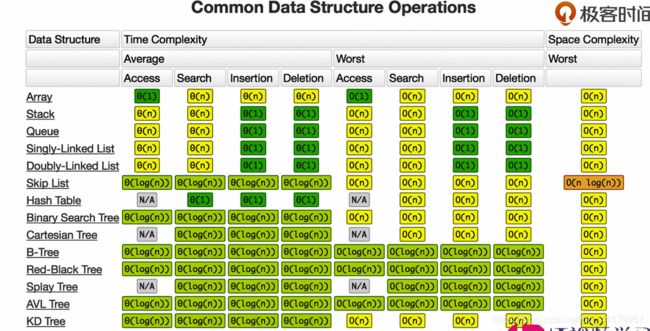
常用数据结构时间复杂度:
232.
class MyQueue:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.stack1 = []
self.stack2 = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
Push element x to the back of queue.
"""
self.stack1.append(x)
return
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.
"""
if self.stack2:
return self.stack2.pop()
else:
while self.stack1:
self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop())
return self.stack2.pop()
def peek(self) -> int:
"""
Get the front element.
"""
if self.stack2:
return self.stack2[-1]
else:
while self.stack1:
self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop())
return self.stack2[-1]
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
Returns whether the queue is empty.
"""
if not self.stack1 and not self.stack2:
return True
else:
return False
# Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyQueue()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.peek()
# param_4 = obj.empty()225
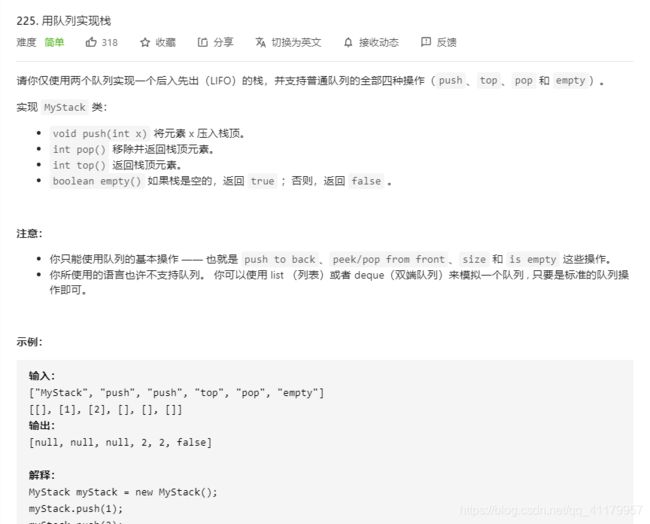
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
import queue as q
self.q1 = q.Queue()
self.q2 = q.Queue()
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
Push element x onto stack.
"""
self.q1.put(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
"""
while self.q1.qsize()>1:
self.q2.put(self.q1.get())
ans = self.q1.get()
self.q1, self.q2 = self.q2, self.q1
return ans
def top(self) -> int:
"""
Get the top element.
"""
while self.q1.qsize()>1:
self.q2.put(self.q1.get())
ans = self.q1.get()
self.q2.put(ans)
self.q1, self.q2 = self.q2, self.q1
return ans
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
"""
return self.q1.empty()
# Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyStack()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.top()
# param_4 = obj.empty()
栈的应用题目 20:
字典,键值对:
1. 只对键的遍历
一个简单的for语句就能循环字典的所有键,就像处理序列一样:
d = {'name1' : 'pythontab', 'name2' : '.', 'name3' : 'com'}
for key in d:
print (key, ' value : ', d[key])
name1 value : pythontab
name2 value : .
name3 value : com
2. 对键和值都进行遍历
如果只需要值,可以使用d.values,如果想获取所有的键则可以使用d.keys。
如果想获取键和值d.items方法会将键-值对作为元组返回,for循环的一大好处就是可以循环中使用序列解包。
代码实例:
for key, value in d.items():
print (key, ' value : ', value)
name1 value : pythontab
name2 value : .
name3 value : com
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = []
dict = {")":"(","]":"[","}":"{"}
for c in s:
if stack and c in dict:
if dict[c] == stack.pop():
continue
else:
return False
stack.append(c)
return not stack
3.优先队列 Priority Queue,正常进,按照所设置的优先级出
实现机制:Heap, Binary Search Tree
大部分python, java里面的二叉堆都是斐波拉契堆,或者别的来实现的
703题:
只要用优先队列去维护一个包含K个数据的最小堆就行
Python 的 heapq 的文档
1、heapq.heapify 可以原地把一个 list 调整成堆
2、heapq.heappop 可以弹出堆顶,并重新调整
3、heapq.heappush 可以新增元素到堆中
4、heapq.heapreplace 可以替换堆顶元素,并调整下
5、为了维持为 K 的大小,初始化的时候可能需要删减,后面需要做处理就是如果不满 K 个就新增,否则做替换;
6、heapq 其实是对一个 list 做原地的处理,第一个元素就是最小的,直接返回就是最小的值
作者:shuai-shuai-31
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-a-stream/solution/pythonde-heapqben-shen-jiu-shi-xiao-ding-dui-by-sh/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
def heappush(heap, item):
"""Push item onto heap, maintaining the heap invariant."""def heappop(heap):
"""Pop the smallest item off the heap, maintaining the heap invariant."""
def heapreplace(heap, item):
"""Pop and return the current smallest value, and add the new item.
def heappushpop(heap, item):
"""Fast version of a heappush followed by a heappop."""
def heapify(x):
"""Transform list into a heap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time."""
def _heappop_max(heap):
"""Maxheap version of a heappop."""def _heapreplace_max(heap, item):
"""Maxheap version of a heappop followed by a heappush."""
def _heapify_max(x):
"""Transform list into a maxheap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time."""
import heapq
class KthLargest:
k = 0
heap = []
def __init__(self, k: int, nums: List[int]):
self.k = k
self.heap = nums
heapq.heapify(self.heap)
while len(self.heap) > k:
heapq.heappop(self.heap)
def add(self, val: int) -> int:
if len(self.heap) < self.k:
heapq.heappush(self.heap,val)
else:
if self.heap[0] < val:
heapq.heappop(self.heap)
heapq.heappush(self.heap,val)
return self.heap[0]
# Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = KthLargest(k, nums)
# param_1 = obj.add(val)enumerate就是枚举的意思,把元素一个个列举出来,第一个是什么,第二个是什么,所以他返回的是元素以及对应的索引。
>>> line = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> for i,j in enumerate(line):
... print(i,j)
...
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5Python的列表[ ] 就是一个队列
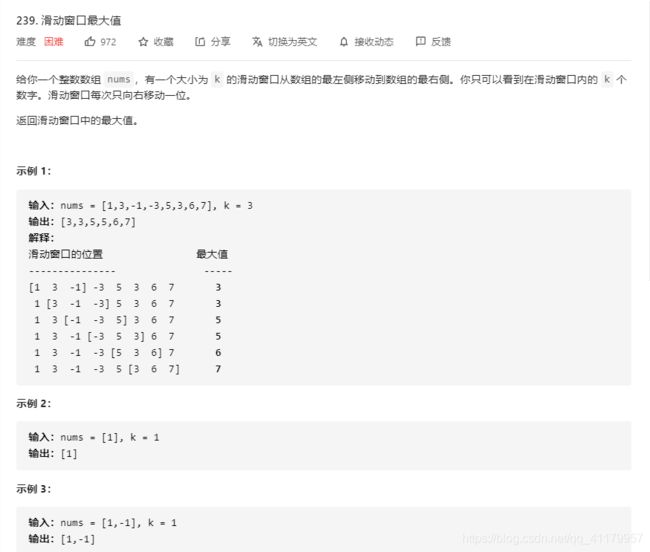
思路1:维护一个最大堆。答案就是堆顶。这种方式浪费内存,且插入新的顺序维护起来速度也慢。
思路2:一个列表用来记录滑动窗口内的东西,一个列表用来记录答案
在滑动列表中,当最前面的下标小于等于i - k, pop出去。 或者新的比前面大,可以把前面都kill掉,从而减少内存
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
if not nums:
return []
windows = []
res = []
for i, x in enumerate (nums):
if i>=k and windows[0] <= i-k:
windows.pop(0)
while windows and nums[windows[-1]] <= x:
windows.pop(0)
windows.append(i)
if i>=k-1 and windows:
res.append(nums[windows[0]])
return res