C#语言入门详解---委托(刘铁猛)
委托:函数指针的升级版,可以类比C语言中的函数指针进行理解
变量的本质就是以变量名所对应的内存地址为起点的一段内存,这段内存中存储的就是变量的数据,这段内存的大小由变量的数据类型决定。
函数代表算法,函数的本质是以函数名所对应的内存地址为起点的一段内存中,这段内存中存储的不是某个值,而是一组机器语言的指令,CPU就是按照这组指令一条一条执行完成这段函数中所包含的算法。
无论是数据还是算法都是保存在内存中的,变量是用来寻找数据的地址,函数是用来寻找算法的地址。
C#通过委托这种数据类型保留了与C/C++语言中函数指针对应的功能。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Caculator caculator = new Caculator();
Action action = new Action(caculator.Report);
Func func1 = new Func(caculator.Add);
Func func2 = new Func(caculator.Sub);
caculator.Report(); //直接调用
action.Invoke(); //间接调用1
action(); //间接调用2
int a = 200;
int b = 300;
int c = 0;
//直接调用
c = caculator.Add(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = caculator.Sub(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
//间接调用1
c = func1.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = func2.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
//间接调用2
c = func1(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = func2(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
class Caculator
{
public void Report()
{
Console.WriteLine("I have 3 methods");
}
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
public int Sub(int a, int b)
{
int result = a - b;
return result;
}
}
}
自定义委托时一定要注意:
1)委托与封装的方法必须类型兼容,返回值和参数的数据类型和参数数目需一致
2)委托是一种类,因此将其声明在名称空间里面时其和其它类处于同一级。C#中允许嵌套类,即在一个类中可以嵌套另一个类,因此若将委托放到某一个类中,则委托就变成了该类中的嵌套类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y); //定义委托
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Add);
Calc calc2 = new Calc(calculator.Sub);
Calc calc3 = new Calc(calculator.Mul);
Calc calc4 = new Calc(calculator.Div);
double a = 100;
double b = 200;
double c = 0;
c = calc1.Invoke(a, b);//等价于c = calc1(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc2.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc3.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = calc4.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------");
Calc[] calcArray = new Calc[4];
calcArray[0] = calculator.Add;
calcArray[1] = calculator.Sub;
calcArray[2] = calculator.Mul;
calcArray[3] = calculator.Div;
foreach (var item in calcArray)
{
c = item.Invoke(a, b);//等价于c = item(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
}
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double x, double y)
{
return x + y;
}
public double Sub(double x, double y)
{
return x - y;
}
public double Mul(double x, double y)
{
return x * y;
}
public double Div(double x, double y)
{
return x / y;
}
}
}
模板方法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y); //定义委托
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func func1 = new Func(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func func2 = new Func(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
///
/// 模板方法,委托的调用getProduct是可以修改的地方,传入不同的getProduct可以实现
/// 不同的产出产品,不同的产品不用再修改WrapProduct中的方法
///
///
/// getProduct)
{
Box box = new Box(); //准备一个Box
Product product = getProduct.Invoke(); //获取一个产品
box.Product = product; //把产品装到Box里面
return box; //返回Box
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
}
参照如上代码,体会使用模板方法的好处是:Product类、Box类、WrapFactory类都不用修改,只需要扩展ProductFactory类中的产品就可以生产不同的产品。不管是生产哪种产品的方法,只要将该方法封装到委托类型的对象里传给模板方法,调用模板方法时就可以将产品包装成箱子再交还回来,这样可以最大限度的实现代码的重复使用。代码的复用不但可以提高工作效率,还可以减少程序Bug的引入,良好的复用结构是所有优秀软件所追求的共同目标之一。
回调方法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y); //定义委托
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func func1 = new Func(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func func2 = new Func(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action log = new Action(logger.Log);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1, log);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2, log);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Logger
{
public void Log(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine("Product {0} created at {1}. Price is {2}",
product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
///
/// 模板方法,委托的调用getProduct是可以修改的地方,传入不同的getProduct可以实现
/// 不同的产出产品,不同的产品不用再修改WrapProduct中的方法
///
///
/// getProduct, Action logCallback)
{
Box box = new Box(); //准备一个Box
Product product = getProduct.Invoke(); //获取一个产品
if (product.Price >= 50) //产品价格大于等于50则打印log信息
{
logCallback(product);
}
box.Product = product; //把产品装到Box里面
return box; //返回Box
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
product.Price = 12;
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
product.Price = 100;
return product;
}
}
}
回调关系是对于某个方法可以调用或者不调用,用的着的时候调用它,用不着得时候不调用它。回调方法还给了我们一个机会,可以动态的选择后续将被调用的方法(有多个备选方法)。当以回调方法的形式使用委托时,需将委托类型的参数传进主调方法里面,被传入抓主调方法中的委托的参数它内部会封装一个被回调的方法。主调函数会根据自己的逻辑来决定是否要调用回调方法。一般情况下,主调方法会在主要逻辑执行完之后,决定是否需要调用回调方法。
无论是模板方法还是回调方法,其本质都是用委托类型的参数封装一个外部的方法,然后将这个委托传入方法的内部来进行间接调用。委托的功能非常强大,但使用不当会造成严重的后果。
单播委托:一个委托封装一个方法
多播委托:使用一个委托封装多个方法,在调用时执行的顺序按照封装的顺序
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.White };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//单播委托
action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();
//多播委托
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1.Invoke();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000); //谁调用DoHomewrok方法谁就休眠1000mS
}
}
}
}
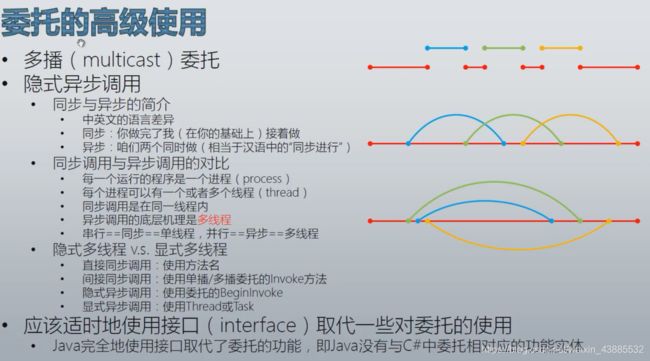
委托还有另外一种高级使用方式,叫做隐式异步调用。
什么叫做隐式异步调用?我们可以将隐式异步调用分为2部分,即隐式、异步调用,接下来我们针对每一部分进行理解。
【隐式和显式】
- 隐式指的是自动多线程,程序会自动创建分支线程辅助任务的执行。
- 显式指的是用户使用Thread或Task手动创建分支线程进行任务的执行。
【同步和异步】
异步调用与同步调用是相对的,同步和异步这两个词在中文和英文中的意思有些差别。
同步指的是两个人做事情,你先做等你做完了我在你做的基础之上接着做,我做完了你再在我做的基础上接着做。
异步指的是两个人做事情,你做你的,我做我的,我们各不相干同时在做。
每一个程序运行起来之后都是内存当中的一个进程(Process),每一个进程都可能包含一个或者多个线程(Thread)。当程序启动的时候会生成一个进程,这个进程里面一定会有第一个运行起来的线程。这个第一个运行起来的线程就是这个进程或者说这个程序的主线程。进程中除主线程之外还可以有其它线程,主线程之外的线程叫做分支线程。
【同步调用和异步调用】
我们再来看一下方法的调用。当我们在同一个线程内去调用方法的时候,方法的执行是按照方法的调用先后顺序执行的,即前一个执行完了后一个才能得到执行。这种在同一个线程内依次执行的方法调用,叫做同步调用。
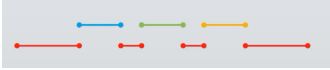
上图是典型的同步调用,图中红色部分表示主线程,其它颜色的表示在主线程中调用的不同方法。我们在主线程里调用了3个方法,主线程最先开始执行,然后调用第1个蓝色表示的方法。当第1个方法执行的时候,CPU的执行指针就进入到第1个方法里,而主线程就暂停在这个地方。直到第1个方法执行完成,执行指针返回到的主线程,主线程才可以继续执行。如此循环调用第2个、第3个方法,直到第3个方法执行完,执行指针再次返回到主线程,主线程执行完成后程序结束。
上图是典型的异步调用,图中红色部分表示主线程,其它颜色的表示在主线程中调用的不同方法。异步调用指的就是在不同的线程当中去调用方法,每个线程和另外的线程互不相干。一个线程的开始和结束不会影响到另外一个线程的开始和结束,而且不同的开始与结束时机又构成不同的运行组合。这就是我们对方法的异步调用,也叫做多线程调用。换句话来说,异步调用它的底层机理就是多线程。
【同步调用的三种方法】
同步调用指的就是在单线程里进行串行的调用,同步调用有三种形式:
- 第一种是直接同步调用。直接同步调用就是用方法的名字来调用这个方法。
- 第二种是单播委托间接同步调用。使用单播委托按顺序对方法进行间接的调用,使用Invoke的调用是同步调用,尽管是间接调用,但程序运行起来也是同步的。千万不要把直接、间接与同步、异步搞混了,这两组概念是相互独立的。
- 第三种是多播委托间接同步调用。使用多播委托是将多个方法按顺序绑定到同一个委托上,使用Invoke的调用是同步调用,通过对这一个委托的调用实现对委托上绑定的方法按照其绑定的先后顺序顺序由前向后依次执行。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.White};
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
//第一种:直接同步调用
//stu1.DoHomework();
//stu2.DoHomework();
//stu3.DoHomework();
//实例化委托
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//第二种:单播委托间接同步调用
//action1.Invoke();
//action2.Invoke();
//action3.Invoke();
//第三种:多播委托间接同步调用
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1.Invoke();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main Thread {0}", i);
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(500); //谁调用DoHomewrok方法谁就休眠500mS
}
}
}
}
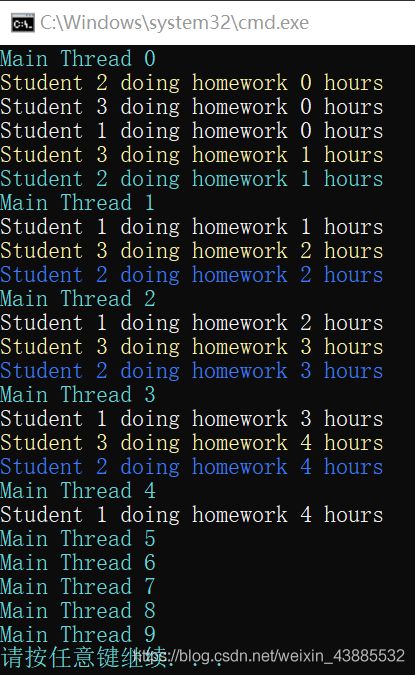
上面代码的执行结果如下:
【异步调用的三种方法】
异步调用的指的就是使用多线程进行并行的调用,异步调用有三种形式:
- 第一种是使用委托进行隐式异步调用。这是委托的另一种高级用法,使用委托的BeginInvoke方法的调用是异步调用。使用BeginInvoke时会自动生成一个分支线程,在这个分支线程里面调用委托中封装的方法。使用BeginInvoke调用委托中的方法,会发现主线程以及三个分支线程在调用后就开始并行的执行,谁都不会等着谁执行完再执行,这就是典型的异步调用。三个线程同时访问控制台的前景色属性,多个线程在访问同一个资源的时候就可能在争抢这个资源的时候发生冲突,现在我们看到的就是发生冲突的场景。为了避免这个冲突,有的时候我们会为线程加锁避免多线程程序当中的资源冲突。
- 第二种是使用Thread的显式异步调用。使用比较古老的Thread手动声明多线程。
- 第三种是使用Task的显式异步调用。使用更高级的Task手动声明多线程。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.White };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
//第一种:使用委托进行隐式异步调用
//Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
//Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
//Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//action1.BeginInvoke(null, null);
//action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);
//action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);
//第二种:使用Thread的显式异步调用
//Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomework));
//Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomework));
//Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomework));
//thread1.Start();
//thread2.Start();
//thread3.Start();
//第三种:使用Task的显式异步调用
Task task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomework));
Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomework));
Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomework));
task1.Start();
task2.Start();
task3.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main Thread {0}", i);
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(500); //谁调用DoHomewrok方法谁就休眠500mS
}
}
}
}
使用接口取代委托:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托_刘铁猛
{
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y); //定义委托
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();
ToyCarFactory toyFactory = new ToyCarFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toyFactory);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
interface IProductFactory
{
Product Make();
}
class PizzaFactory:IProductFactory
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
}
class ToyCarFactory:IProductFactory
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory)
{
Box box = new Box(); //准备一个Box
Product product = productFactory.Make(); //获取一个产品
box.Product = product; //把产品装到Box里面
return box; //返回Box
}
}
}