CTPN源码解析1-数据预处理split_label.py
文本检测算法一:CTPN
CTPN源码解析1-数据预处理split_label.py
CTPN源码解析2-代码整体结构和框架
CTPN源码解析3.1-model()函数解析
CTPN源码解析3.2-loss()函数解析
CTPN源码解析4-损失函数
CTPN源码解析5-文本线构造算法构造文本行
CTPN训练自己的数据集
由于解析的这个CTPN代码是被banjin-xjy和eragonruan大神重新封装过的,所以代码整体结构非常的清晰,简洁!不像上次解析FasterRCNN的代码那样跳来跳去,没跳几步脑子就被跳乱了[捂脸],向大神致敬!PS:里面肯定会有理解和注释错误的,欢迎批评指正!
解析源码地址:https://github.com/eragonruan/text-detection-ctpn
知乎:从代码实现的角度理解CTPN:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49588885
知乎:理解文本检测网络CTPN:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77883736
知乎:场景文字检测—CTPN原理与实现:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34757009
自己先标注的数据集格式如下:
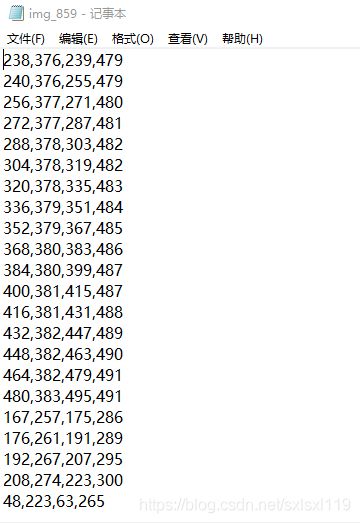
每一行表示一个文本标记框,顺序为(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4) ,分别是矩形框的左上点(x1,y1),右上点(x2,y2),右下点(x3,y3),左下点(x4,y4)。
split_label.py-》这玩意要干嘛呢?
- 就是将上面的每一个标记框都给拆分成宽为16的矩形框(两头的可以不为16)。
- 同时将图像缩放成指定大小,并保证宽和高都是16的整数倍。
拆分完后的矩形框变成这个样子:
将这些框画在图上是下面这个样子:
(可以看出,两边的框,宽度不必严格等于16)
108行代码如下,没啥好说的:
import os
import sys
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
from utils.prepare.utils import orderConvex, shrink_poly
DATA_FOLDER = "/CTPN/My_text-detection-ctpn-banjin-dev/MyGenData/imgtxt/"
OUTPUT = "/CTPN/My_text-detection-ctpn-banjin-dev/data/dataset/mlt/"
MAX_LEN = 1200
MIN_LEN = 600
im_fns = os.listdir(os.path.join(DATA_FOLDER, "image"))
im_fns.sort()
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "image")):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "image"))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "label")):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "label"))
for im_fn in tqdm(im_fns):
try:
_, fn = os.path.split(im_fn)
bfn, ext = os.path.splitext(fn)
if ext.lower() not in ['.jpg', '.png']:
continue
gt_path = os.path.join(DATA_FOLDER, "label", 'gt_' + bfn + '.txt')
img_path = os.path.join(DATA_FOLDER, "image", im_fn)
img = cv.imread(img_path) #读取图像
img_size = img.shape #获取图像的[h,w,c]
im_size_min = np.min(img_size[0:2]) #获取h,w中较小的
im_size_max = np.max(img_size[0:2]) #获取h,w中较大的
# 保持宽高比不变,且短边不大于600,长边不大于1200
im_scale = float(600) / float(im_size_min)
if np.round(im_scale * im_size_max) > 1200:
im_scale = float(1200) / float(im_size_max)
new_h = int(img_size[0] * im_scale)
new_w = int(img_size[1] * im_scale)
# 使得图像的w,h都是16的整数倍
new_h = new_h if new_h // 16 == 0 else (new_h // 16 + 1) * 16
new_w = new_w if new_w // 16 == 0 else (new_w // 16 + 1) * 16
re_im = cv.resize(img, (new_w, new_h), interpolation=cv.INTER_LINEAR)
re_size = re_im.shape
polys = []
with open(gt_path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
splitted_line = line.strip().lower().split(',')
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = map(float, splitted_line[:8])
poly = np.array([x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4]).reshape([4, 2])
poly[:, 0] = poly[:, 0] / img_size[1] * re_size[1]
poly[:, 1] = poly[:, 1] / img_size[0] * re_size[0]
poly = orderConvex(poly)
polys.append(poly)
# 可视化
# cv.polylines(re_im, [poly.astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2))], True,color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
res_polys = []
for poly in polys:
# delete polys with width less than 10 pixel
if np.linalg.norm(poly[0] - poly[1]) < 10 or np.linalg.norm(poly[3] - poly[0]) < 10:
continue
res = shrink_poly(poly)
# # 切分后的矩形框可视化
# for p in res:
# cv.polylines(re_im, [p.astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2))], True, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=1)
res = res.reshape([-1, 4, 2])
for r in res:
x_min = np.min(r[:, 0])
y_min = np.min(r[:, 1])
x_max = np.max(r[:, 0])
y_max = np.max(r[:, 1])
res_polys.append([x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max])
# # 可视化
# cv.imshow("demo",re_im)
# cv.waitKey(0)
if(len(res_polys)>0): #不为空的情况下再保存
cv.imwrite(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "image", fn), re_im)
with open(os.path.join(OUTPUT, "label", bfn) + ".txt", "w") as f:
for p in res_polys:
line = ",".join(str(p[i]) for i in range(4))
f.writelines(line + "\r\n")
# #可视化
# for p in res_polys:
# cv.rectangle(re_im,(p[0],p[1]),(p[2],p[3]),color=(0,0,255),thickness=1)
# cv.imshow("demo",re_im)
# cv.waitKey(0)
except:
print("Error processing {}".format(im_fn))
多说一句,94行的判断语句是我加上的,因为我的数据集在转化过程中,会出现保存的txt为空的情况,训练时会出错,所以加了一个判断。
if(len(res_polys)>0): #不为空的情况下再保存最终整理好的数据集: