数据结构严蔚敏----二叉树基本操作20个(用二叉链表结构)
看之前请注意!博主小菜鸡一个,所以有许多瑕疵,请做好心理准备!
编程语言:C
编译环境:Dev-C++
编程实现书P121 ADT BinaryTree 基本操作20个,用二叉链表结构实现
基本概念:
二叉树是一种应用广泛的树型结构,它的特点是每个结点至多只有两棵子树
并且二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒
1.Status InitBiTree(BiTree *T) 构造空二叉树
2.Status DestroyBiTree(BiTree *T) 销毁二叉树,前提T存在
3.Status CreateBiTree(BiTree *T) 用先序遍历创建二叉树
4.Status ClearBiTree(BiTree *T) 清空二叉树,前提T存在
5.Status BiTreeEmpty(BiTree T) 探空,前提T存在,很抱歉只有这个我不会
6.int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T) 返回二叉树的深度,前提T存在,这个我写的不太好,有缺点
7.BiTree Root(BiTree T) 返回二叉树的根,前提T存在
8.ElemType Value(BiTree T,BiTree e) 若e是T中某个结点,返回e的值,前提T存在
9.Status Assign(BiTree T,BiTree *e,ElemType value) 若e是T中某个结点,结点e赋值为value,前提T存在
10.BiTree Parent(BiTree T,BiTree e) 若e是T中某个非根结点,则返回它的双亲,否则返回NULL,前提T存在
11.BiTree LeftChild(BiTree T,BiTree e) 若e是T中某个结点,返回e的左孩子。若e无左孩子,则返回NULL,前提T存在
12.BiTree RightChild(BiTree T,BiTree e) 若e是T中某个结点,返回e的右孩子。若e无右孩子,则返回NULL,前提T存在
13.BiTree LeftSibling(BiTree T,BiTree e) e是T中某个结点,返回e的左兄弟。若e是其双亲的左孩子或无左兄弟,则返回NULL,前提T存在
14.BiTree RightSibling(BiTree T,BiTree e) e是T中某个结点,返回e的右兄弟。若e是其双亲的右孩子或无右兄弟,则返回NULL,前提T存在
15.Status InsertChild(BiTree T,BiTree p,int LR,BiTree c)
初始条件:T存在,p指向T中某个结点,LR为0或1,非空二叉树c与T不相交且右子树为空。
操作结果:根据LR为0或1,插入c为T中p所指结点的左或右子树。p所指结点的原有左或右子树则成为c的右子树。
16.Status DeleteChild(BiTree T,BiTree p,int LR)
初始条件:T存在,p指向T中某个结点,LR为0或1
操作结果:根据LR为0或1,删除T中p所指结点的左或右子树
17.Status PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T) 先序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
18.Status InOrderTraverse(BiTree T) 中序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
19.Status PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T) 后序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
20.Status LevelOrderTraverse(BiTree T) 层序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
源代码:
#include
#include
#include
//函数结果状态代码
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OVERFLOW -1
typedef char ElemType;
typedef int Status;
//二叉树的二叉链表存储表示
typedef struct BiTNode{
ElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild,*rchild;//左右孩子指针
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
//数据元素类型为BiTree的队列,用于层序遍历
typedef struct QNode{
BiTree Qdata;
struct QNode *next;
}QNode,*QueuePtr;
typedef struct{
QueuePtr front;
QueuePtr rear;
}LinkQueue;
//构造一个空队列Q
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
(*Q).front=(QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!(*Q).front) exit(OVERFLOW);
(*Q).front->next=NULL;
(*Q).rear=(*Q).front;
return OK;
}
//探空,前提Q存在
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
//插入元素e作为新的队尾元素,前提Q存在
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q,BiTree e)
{
QueuePtr p=(QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));//开辟新结点
if(!p) exit(OVERFLOW);
p->Qdata=e;
p->next=NULL;
(*Q).rear->next=p;
(*Q).rear=p;
return OK;
}
//若队列不空,删除队头元素,用e返回其值,前提Q存在
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q,BiTree *e)
{
if((*Q).front==(*Q).rear)
return ERROR;
QueuePtr p=(*Q).front->next;
*e=p->Qdata;
(*Q).front->next=p->next;
if((*Q).rear==p)
(*Q).rear=(*Q).front;
free(p);
return OK;
}
//1.构造空二叉树
Status InitBiTree(BiTree *T)
{
(*T)=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if(!(*T)) exit(OVERFLOW);
(*T)->lchild=NULL;
(*T)->rchild=NULL;
return OK;
}
//2.销毁二叉树,前提T存在
Status DestroyBiTree(BiTree *T)
{
if(!(*T))
return OK;
DestroyBiTree(&((*T)->lchild));
DestroyBiTree(&((*T)->rchild));
free(*T);
return OK;
}
//3.用先序遍历创建二叉树
Status CreateBiTree(BiTree *T)
{
char ch=getchar();//读入一个字符
if(ch=='.') //个人认为用.表示空树比较好(这样输入多个空树的时候方便检验有没有输入错误,但是如果用空格的话,嗯......实在是无法检验)
*T=NULL;
else
{
*T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if(!(*T)) exit(OVERFLOW);
(*T)->data=ch;
CreateBiTree(&((*T)->lchild));
CreateBiTree(&((*T)->rchild));
}
return OK;
}
//4.清空二叉树,前提T存在(二叉链表的根结点和单链表的头结点是不同的,所以二叉树的清空不太一样)
Status ClearBiTree(BiTree *T)//清空之后,根结点是改变了的
{
if(!(*T))
return ERROR;
DestroyBiTree(&((*T)->lchild));
DestroyBiTree(&((*T)->rchild));//这里的确是销毁,你没看错
free(*T);
(*T)=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));//重新分配空间
if(!(*T)) exit(OVERFLOW);
(*T)->lchild=NULL;
(*T)->rchild=NULL;
return OK;
}
//5.探空,前提T存在
//哎呀,这个真不会写
//空树的特点是只有一个根结点,数据域没有赋数据,左右指针指向空
//所以怎么判断根结点的数据域有没有赋数据啊
//6.返回二叉树的深度,前提T存在
int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T)
{
if(!T)
return 0;
else
return max(BiTreeDepth(T->lchild),BiTreeDepth(T->rchild))+1;//这有个缺点,空树会返回深度1
}
//辅助函数
int max(int a,int b)
{
return (a>=b)?a:b;
}
//7.返回二叉树的根,前提T存在
BiTree Root(BiTree T)
{
return T;
}
//8.若e是T中某个结点,返回e的值,前提T存在
ElemType Value(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(Search(T,e)==TRUE)
return e->data;
else
return '.';
}
//辅助函数
Status Search(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(!T)
return FALSE;
if(T==e||Search(T->lchild,e)==TRUE||Search(T->rchild,e)==TRUE)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
//9.若e是T中某个结点,结点e赋值为value,前提T存在
Status Assign(BiTree T,BiTree *e,ElemType value)
{
if(Search(T,*e)==TRUE)
{
(*e)->data=value;
return OK;
}
return ERROR;
}
//10.若e是T中某个非根结点,则返回它的双亲,否则返回NULL,前提T存在
BiTree Parent(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(T==e)
return NULL;
if(T->lchild==e||T->rchild==e)
return T;
else if(Search(T->lchild,e)==TRUE)
return Parent(T->lchild,e);
else if(Search(T->rchild,e)==TRUE)
return Parent(T->rchild,e);
else
return NULL;
}
//11.若e是T中某个结点,返回e的左孩子。若e无左孩子,则返回NULL,前提T存在
BiTree LeftChild(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(Search(T,e)==TRUE)
return e->lchild;
else
return NULL;
}
//12.若e是T中某个结点,返回e的右孩子。若e无右孩子,则返回NULL,前提T存在
BiTree RightChild(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(Search(T,e)==TRUE)
return e->rchild;
else
return NULL;
}
//13.e是T中某个结点,返回e的左兄弟。若e是其双亲的左孩子或无左兄弟,则返回NULL,前提T存在
BiTree LeftSibling(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(Search(T,e)==TRUE&&Parent(T,e)->lchild!=e)
return Parent(T,e)->lchild;
else
return NULL;
}
//14.e是T中某个结点,返回e的右兄弟。若e是其双亲的右孩子或无右兄弟,则返回NULL,前提T存在
BiTree RightSibling(BiTree T,BiTree e)
{
if(Search(T,e)==TRUE&&Parent(T,e)->rchild!=e)
return Parent(T,e)->rchild;
else
return NULL;
}
//15.初始条件:T存在,p指向T中某个结点,LR为0或1,非空二叉树c与T不相交且右子树为空。
// 操作结果:根据LR为0或1,插入c为T中p所指结点的左或右子树。p所指结点的原有左或右子树则成为c的右子树。
Status InsertChild(BiTree T,BiTree p,int LR,BiTree c)
{
if(!T||Search(T,p)==FALSE)
return ERROR;
BiTree q;
if(LR==0)
{
q=p->lchild;
p->lchild=c;
c->rchild=q;
}
else if(LR==1)
{
q=p->rchild;
p->rchild=c;
c->rchild=q;
}
else
return ERROR;
return OK;
}
//16.初始条件:T存在,p指向T中某个结点,LR为0或1
// 操作结果:根据LR为0或1,删除T中p所指结点的左或右子树
Status DeleteChild(BiTree T,BiTree p,int LR)
{
if(T&&Search(T,p)==FALSE)
return ERROR;
if(LR==0)
{
DestroyBiTree(&p->lchild);
p->lchild=NULL;
}
else if(LR==1)
{
DestroyBiTree(&p->rchild);
p->rchild=NULL;
}
else
return ERROR;
return OK;
}
//17.先序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
Status PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if(!T)
return ERROR;
printf("%c ",T->data);
PreOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
PreOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
return OK;
}
//18.中序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
Status InOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if(!T)
return ERROR;
InOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
printf("%c ",T->data);
InOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
return OK;
}
//19.后序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
Status PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if(!T)
return ERROR;
PostOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
PostOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
printf("%c ",T->data);
return OK;
}
//20.层序遍历二叉树,前提T存在
Status LevelOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if(!T)
return ERROR;
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(&Q);
BiTree p;
EnQueue(&Q,T);
while(QueueEmpty(Q)==FALSE)
{
DeQueue(&Q,&p);
printf("%c ",p->data);
if(p->lchild)
EnQueue(&Q,p->lchild);
if(p->rchild)
EnQueue(&Q,p->rchild);
}
return OK;
}
int main()
{
BiTree T,c;
char ch;
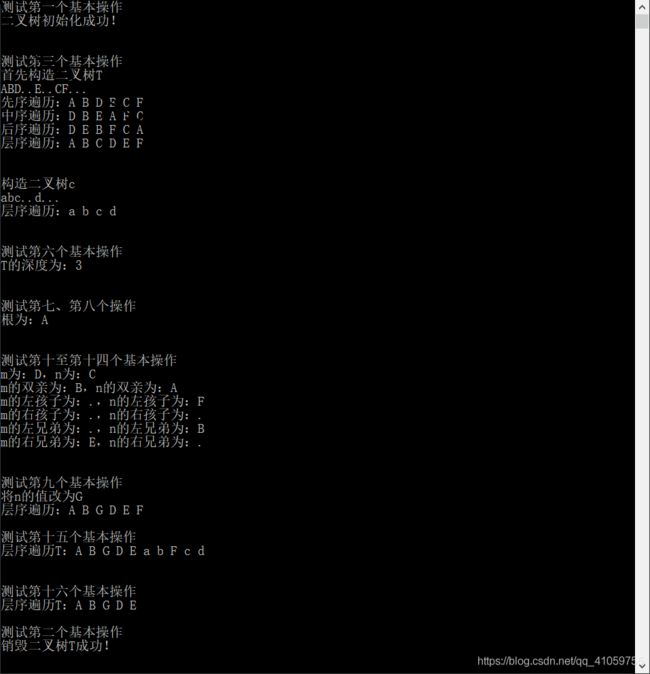
printf("测试第一个基本操作\n");
if(InitBiTree(&T)==OK&&InitBiTree(&c)==OK)
printf("二叉树初始化成功!\n");
printf("\n\n测试第三个基本操作\n");
printf("首先构造二叉树T\n");
CreateBiTree(&T);
ch=getchar();//吸收换行符
printf("先序遍历:");
PreOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n中序遍历:");
InOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n后序遍历:");
PostOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n层序遍历:");
LevelOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n\n\n构造二叉树c\n");
CreateBiTree(&c);
printf("层序遍历:");
LevelOrderTraverse(c);
printf("\n\n\n测试第六个基本操作\n");
printf("T的深度为:%d\n",BiTreeDepth(T));
printf("\n\n测试第七、第八个操作\n");
printf("根为:%c\n",Value(T,Root(T)));
printf("\n\n测试第十至第十四个基本操作\n");
BiTree m=T->lchild->lchild,n=T->rchild;//这里我是在知道二叉树结构的情况下进行赋值的
printf("m为:%c,n为:%c\n",Value(T,m),Value(T,n));
printf("m的双亲为:%c,n的双亲为:%c\n",Value(T,Parent(T,m)),Value(T,Parent(T,n)));
printf("m的左孩子为:%c,n的左孩子为:%c\n",Value(T,LeftChild(T,m)),Value(T,LeftChild(T,n)));
printf("m的右孩子为:%c,n的右孩子为:%c\n",Value(T,RightChild(T,m)),Value(T,RightChild(T,n)));
printf("m的左兄弟为:%c,n的左兄弟为:%c\n",Value(T,LeftSibling(T,m)),Value(T,LeftSibling(T,n)));
printf("m的右兄弟为:%c,n的右兄弟为:%c\n",Value(T,RightSibling(T,m)),Value(T,RightSibling(T,n)));
printf("\n\n测试第九个基本操作\n");
printf("将n的值改为G\n");
Assign(T,&n,'G');
printf("层序遍历:");
LevelOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n\n测试第十五个基本操作\n");
InsertChild(T,n,0,c);
printf("层序遍历T:");
LevelOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n\n\n测试第十六个基本操作\n");
DeleteChild(T,n,0);
printf("层序遍历T:");
LevelOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n\n测试第二个基本操作\n");
if(DestroyBiTree(&T)==OK)
printf("销毁二叉树T成功!\n");
return 0;
}