目标检测中的4种IoU Loss
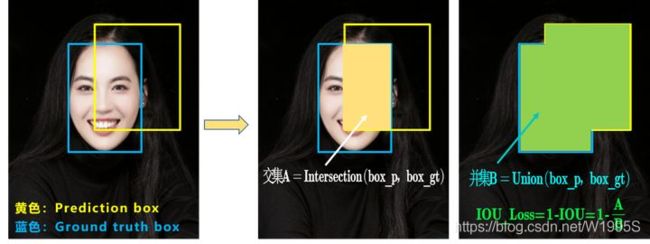
IoU(Intersection of Union)
目标检测任务的损失函数一般由**Classificition Loss(分类损失函数)和Bounding Box Regeression Loss**(回归损失函数)两部分构成。
Bounding Box Regeression Loss Function
近些年的发展过程是:
Smooth L1 Loss-> IoU Loss(2016)-> GIoU Loss(2019)-> DIoU Loss(2020)->CIoU Loss(2020)
IoU是指预测检测框A和真实检测框B的交并比,是目标检测中最常用的指标,在anchor-based的方法中,他的作用不仅用来确定正样本和负样本,还可以用来作为输出框(predict box)和ground-truth的距离的评价指标和训练Loss。
import numpy as np
def Iou(box1, box2, wh=False):
if wh == False:
xmin1, ymin1, xmax1, ymax1 = box1
xmin2, ymin2, xmax2, ymax2 = box2
else:
xmin1, ymin1 = int(box1[0]-box1[2]/2.0), int(box1[1]-box1[3]/2.0)
xmax1, ymax1 = int(box1[0]+box1[2]/2.0), int(box1[1]+box1[3]/2.0)
xmin2, ymin2 = int(box2[0]-box2[2]/2.0), int(box2[1]-box2[3]/2.0)
xmax2, ymax2 = int(box2[0]+box2[2]/2.0), int(box2[1]+box2[3]/2.0)
# 获取矩形框交集对应的左上角和右下角的坐标(intersection)
xx1 = np.max([xmin1, xmin2])
yy1 = np.max([ymin1, ymin2])
xx2 = np.min([xmax1, xmax2])
yy2 = np.min([ymax1, ymax2])
# 计算两个矩形框面积
area1 = (xmax1-xmin1) * (ymax1-ymin1)
area2 = (xmax2-xmin2) * (ymax2-ymin2)
inter_area = (np.max([0, xx2-xx1])) * (np.max([0, yy2-yy1])) #计算交集面积
iou = inter_area / (area1+area2-inter_area+1e-6) #计算交并比
return iou
IoU的两个缺点
- 即状态1的情况,当预测框和目标框不相交时,IOU=0,无法反应两个框距离的大小(重合度),此时loss=0,损失函数不可导,没有梯度回传,无法进行学习训练,IOU_Loss无法优化两个框不相交的情况。
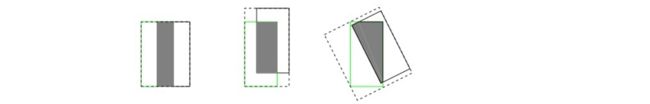
- 即状态2和状态3的情况,当两个预测框大小相同,两个IOU也相同,IOU_Loss无法区分两者相交情况的不同。更直观的说,下面三个框,三种情况IoU都相等,但看得出来他们的重合度是不一样的,左边的图回归的效果最好,右边的最差。

GIoU(Generalized Intersection over Union)
由于IoU是比值的概念,对目标物体的scale是不敏感的。然而检测任务中的BBox的回归损失(MSE loss, l1-smooth loss等)优化和IoU优化不是完全等价的,而且 Ln 范数对物体的scale也比较敏感,IoU无法直接优化没有重叠的部分。
《Generalized Intersection over Union》论文提出可以直接把IoU设为回归的loss。
![]()
上面公式的意思是:先计算两个框的最小闭包区域面积 Ac (通俗理解:同时包含了预测框和真实框的最小框的面积),再计算出IoU,再计算闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重,最后用IoU减去这个比重得到GIoU。

def Giou(rec1,rec2):
#分别是第一个矩形左右上下的坐标
x1,x2,y1,y2 = rec1
x3,x4,y3,y4 = rec2
iou = Iou(rec1,rec2)
area_C = (max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4))*(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))
area_1 = (x2-x1)*(y1-y2)
area_2 = (x4-x3)*(y3-y4)
sum_area = area_1 + area_2
w1 = x2 - x1 #第一个矩形的宽
w2 = x4 - x3 #第二个矩形的宽
h1 = y1 - y2
h2 = y3 - y4
W = min(x1,x2,x3,x4)+w1+w2-max(x1,x2,x3,x4) #交叉部分的宽
H = min(y1,y2,y3,y4)+h1+h2-max(y1,y2,y3,y4) #交叉部分的高
Area = W*H #交叉的面积
add_area = sum_area - Area #两矩形并集的面积
end_area = (area_C - add_area)/area_C #闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重
giou = iou - end_area
return giou
优点
- 与IoU相似,GIoU也是一种距离度量,作为损失函数的话,
GIOU_Loss=1—GIOU,满足损失函数的基本要求 - GIoU对scale不敏感
- GIoU是IoU的下界,在两个框无限重合的情况下,IoU=GIoU=1IoU取值[0,1],但GIoU有对称区间,取值范围[-1,1]。在两者重合的时候取最大值1,在两者无交集且无限远的时候取最小值-1,因此GIoU是一个非常好的距离度量指标。
- 与IoU只关注重叠区域不同,GIoU不仅关注重叠区域,还关注其他的非重合区域,能更好的反映两者的重合度。
缺点
状态1、2、3都是预测框在目标框内部且预测框大小一致的情况,这时预测框和目标框的差集都是相同的,因此这三种状态的GIOU值也都是相同的,这时GIOU退化成了IOU,无法区分相对位置关系。

DIoU(Distance-IoU)
DIoU要比GIou更加符合目标框回归的机制,将目标与anchor之间的距离,重叠率(面积)以及尺度都考虑进去,使得目标框回归变得更加稳定,不会像IoU和GIoU一样出现训练过程中发散等问题。当目标框包裹预测框的时候,直接度量2个框的距离,因此DIOU_Loss收敛的更快

其中,b , bgt 分别代表了预测框和真实框的中心点,且 ρ 代表的是计算两个中心点间的欧式距离。c 代表的是能够同时包含预测框和真实框的最小闭包区域的对角线距离。

def Diou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
dious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:#
return dious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
dious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
# #xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax->[:,0],[:,1],[:,2],[:,3]
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
dious = inter_area / union - (inter_diag) / outer_diag
dious = torch.clamp(dious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
dious = dious.T
return dious
优点
- 与GIoU loss类似,
DIoU loss( =1-DIOU )在与目标框不重叠时,仍然可以为边界框提供移动方向。 - DIoU loss可以直接最小化两个目标框的距离,因此比GIoU loss收敛快得多。
- 对于包含两个框在水平方向和垂直方向上这种情况,DIoU损失可以使回归非常快,而GIoU损失几乎退化为IoU损失
- DIoU还可以替换普通的IoU评价策略,应用于NMS中,使得NMS得到的结果更加合理和有效。
缺点
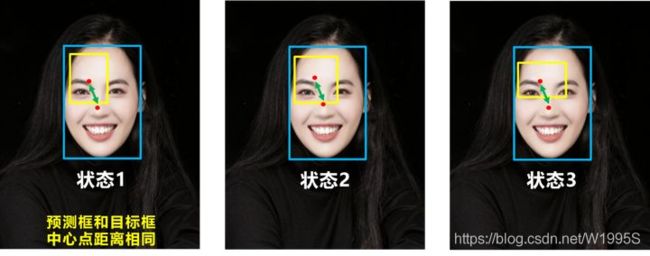
没有考虑到长宽比。下面三种请款预测框的中心点的位置都是一样的,因此按照DIOU_Loss的计算公式,三者的值都是相同的。
CIoU
CIoU(Complete-IoU)在DIoU的基础上增加了一个长宽比的影响因子。
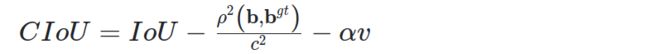
α 为权重,v 用来衡量长宽比的相似性,定义为

这样CIOU_Loss就将目标框回归函数应该考虑三个重要几何因素:重叠面积、中心点距离,长宽比全都考虑进去了.
完整的 CIoU 损失函数定义:
![]() 最后,CIoU loss的梯度类似于DIoU loss,但还要考虑 v 的梯度。在长宽在 [0, 1] 的情况下,
最后,CIoU loss的梯度类似于DIoU loss,但还要考虑 v 的梯度。在长宽在 [0, 1] 的情况下, ![]()
的值通常很小,会导致梯度爆炸,因此在 ![[公式]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c986af4c8d2146a4a38ddb93a5c3306d.jpg)
实现时将替换成1。
def Ciou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
cious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:
return cious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
cious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
u = (inter_diag) / outer_diag
iou = inter_area / union
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)), 2)
S = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (S + v)
w_temp = 2 * w1
ar = (8 / (math.pi ** 2)) * arctan * ((w1 - w_temp) * h1)
cious = iou - (u + alpha * ar)
cious = torch.clamp(cious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
cious = cious.T
return cious
总结
IOU_Loss:主要考虑检测框和目标框重叠面积。
GIOU_Loss:在IOU的基础上,解决边界框不重合时的问题。
DIOU_Loss:在IOU和GIOU的基础上,考虑边界框中心点距离的信息。
CIOU_Loss:在DIOU的基础上,考虑边界框宽高比的尺度信息。
Yolov4中采用了CIOU_Loss的回归方式,使得预测框回归的速度和精度更高一些。
参考(感谢)
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039339845?utm_source=sf-related
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94799295
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/143747206
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/104236411
https://www.jianshu.com/p/e3bf67cd4459