一 : 文件
凡是与输入输出相关的类,接口等定义在java.io包下
File类->java.io.File.
File可以有构造器创建其对象,此对象对应着一个文件或文件目录.
File类对象是与平台无关的,File中的方法,仅涉及到如何创建,删除,重命名一个文件是要涉及文件内容的,File是无能为力的,必须由IO来完成.
File类的对象常作为IO流的具体类的构造器的形参
-
文件常用方法
public void test() {
绝对路径 : 包括盘符在内的完整的文件路径
File file1 = new File("d:/io/hewllow.txt");
File file3 = new File("d:\\io\\io1");
File file4 = new File("c:\\");
相对路线 : 在当前文件下的文件的路径
File file2 = new File("dfdf.txt");
获取文件名
System.out.println(file1.getName());
获取文件路径
System.out.println(file1.getPath());
获取绝对文件名
System.out.println(file1.getAbsoluteFile());
获取文件绝对路径
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());
获取文件的父目录
System.out.println(file1.getParent());
System.out.println();
//renameTo(File newName):重命名
//file1.renameTo(file2):file1重命名为file2 要求file1文件一定存在,file2一定不存在
boolean bool = file1.renameTo(file2);
System.out.println(bool);
boolean b1 = file4.renameTo(file3);
System.out.println(b1);
}
public void test2() {
File file1 = new File("d:/io/hewllow.txt");
File file2 = new File("dfdf");
//判断文件是否存在
System.out.println(file1.exists());
//判断文件是否可写
System.out.println(file1.canWrite());
//判读是否是一个文件
System.out.println(file1.isFile());
//是检查一个对象是否是文件夹。返回值是boolean类型的。如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());
//最后修改时间
System.out.println(file1.lastModified());
//文件长度
System.out.println(file1.length());
}
public void test3() throws IOException{
File file1 = new File("d:/io/hewllow.txt");
System.out.println(file1.delete());
if (!file1.exists()) {
//创建文件
boolean bool = file1.createNewFile();
System.out.println(bool);
}
File file2 = new File("d:\\io\\io1");
if (!file2.exists()) {
//mkdir();创建一个文件目录,只有在上层文件目录存在的情况下才能返回true
//mkdirs(); 创建一个文件目录,若此文件不存在,一并创建
boolean b = file2.mkdir();
boolean b = file2.mkdirs();
System.out.println(b);
}
//遍历文件名字,打印是个字符串
File file3 = new File("d:\\teach");
String[]str = file3.list();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i])
}
//遍历文件名字,打印是文件对象,可以进行对其进行文件操作
File[] files = file3.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
System.out.println(files[i].getName());
}
}
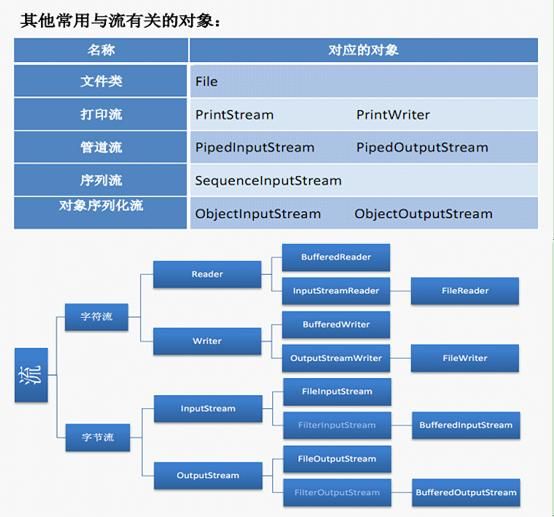
二 : 主要的流
-
流的分类
①按照流向的不同 : 输入流,输出流
输入:input 读取外部数据到程序中
输出:output将程序数据输出外部数据中
②按照处理数据的单位不同 : 字节流,字符流(处理的文本文件)
③按照处理数据角色的不同 : 节点流(直接作用于文件的),处理流.
-
IO体系
抽象基类 : InputStream,OutputStream,Reader,Writer.
节点流(文件流) : FileInputStream,FileOutputStream,FileReader,FileWriter
缓冲流(处理流的一种,可以提高文件的效率) : BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream(flush()),BufferedReader (readLine()),BufferedWriter(flush())
-
FileInputStream
//从硬盘存在的一个文件中,读取其内容到程序中
//要读取的文件一定要存在,否则跑FileNotFoundException
@Test
public void testFileInputStream1() throws Exception{
//1.创建一个File类的对象
File file = new File("dfdf.txt");
//2.创建一个FileInputStream类的对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.调用FileInputStream方法,实现file的读取
/*
* read():读取文件的一个字节 当执行到文件结尾时,返回 -1
* */
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)b);
}
//4.关闭相应的流
fis.close();
}
-
使用try-catch的方式处理如下异常更合理:保证流的关闭操作一定能够执行
public void testFileInputStream2() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.创建一个File类的对象
File file = new File("dfdf.txt");
//2.创建一个FileInputStream类的对象
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.调用FileInputStream方法,实现file的读取
/*
* read():读取文件的一个字节 当执行到文件结尾时,返回 -1 abcdefgf
* */
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)b);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.关闭相应的流
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
byte[]方式读取
public void testFileInputStream3() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.创建一个File类的对象
File file = new File("dfdf.txt");
//2.创建一个FileInputStream类的对象
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.调用FileInputStream方法,实现file的读取
byte[] b = new byte[5];//读取到的数据要写入数组
int len;//每次读入到byte中的字节的长度
while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
String str = new String(b, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.关闭相应的流
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
FileOutputStream
public void testFileOutputStream() {
//1.创建一个File对象,表明要写入的文件位置
//输出的物理文件可以不存在,当执行过程中,若不存在,会自动创建
//若存在会将原有的文件覆盖
File file = new File("tt.txt");
//2.创建一个FileOutputStream的对象,将file的对象作为形参
//传递给FileOutputStream的构造器中
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//3写入操作
fos.write(new String("xue fu zhen shuang").getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭操作
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
复制
从硬盘读取文件,并写入到另一个位置,相当于文件的复制
public void testFileInputOutputStream() {
//1.提供读入,写出的文件
File file1 = new File("/Users/admin/Desktop/1.jpg");
File file2 = new File("/Users/admin/Desktop/2.jpg");
//2.提供相应的流
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
//实现文件的复制
byte[] b = new byte[20];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
//错误的写法 fos.write(b); fos.write(b, 0, b.length);
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("11111"+e.getMessage());
}finally {
if(fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
FileReader FileWriter
使用FileReader FileWriter可以实现文本文件的复制
对于非文本文件(视频文件,音频文件,图片),只能使用字节流
FileReader
public void TestFileReader() {
File file = new File("tt.txt");
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] c = new char[24];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(c)) != -1) {
String str = new String(c, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileWriter 进行复制操作
public void TestFileWriter() {
//1.输入流对应的文件src一定要存在,否则抛异常
//输出流对应的文件dest可以不存在,执行过程中会自动创建
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//2.
File src = new File("tt.txt");
File dest = new File("zz.txt");
fr = new FileReader(src);
fw = new FileWriter(dest);
//3.
char[] c = new char[24];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(c)) != -1) {
fw.write(c, 0, len);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}finally {
if(fw != null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutPutStream
使用BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutPutStream实现非文本文件的复制
public void TestBufferedInputOutputStream(){
//3.将创建的节点流的对象作为形参传递给缓冲流的构造器中
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.提供读入,写出的文件
File file1 = new File("/Users/admin/Desktop/1.jpg");
File file2 = new File("/Users/admin/Desktop/2.jpg");
//2.创建响应的节点流FileInputStream,FileOutputStream
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//4.具体的实现文件复制的操作
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.println("111");
bos.write(b, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(bos != null) {
//关闭相应的流
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
BufferedReader,BufferedReader
使用BufferedReader 和 BufferedReader实现文本文件的复制
public void testBufferedReader() {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
File file = new File("tt.txt");
File file1 = new File("baibai.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file1);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
// char[] c = new char[5];
// int len;
// while((len = br.read(c)) != -1) {
// String str = new String(c, 0, len);
// System.out.print(str);
// }
String str;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
// System.out.println(str);
bw.write(str + "\n");
// bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
三 : 其他流介绍
-
转换流
InutStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter
解码 : 字符串 - > 字节数组
编码 : 字节数组 - > 字符串
(针对文本是字符类型)
demo例子 :
@Test
public void test1() {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//解码
File file = new File("dfdf.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
//编码
File file1 = new File("dfdf4.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");
String str;
bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(bw != null) {
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(br !=null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
标准输入输出流
标准的输出流 System.out
标准的输入流 System.in
demo 例子:
将输入字符变成大写,如果遇到e 或者 exit 字符 则退出程序
@Test
public void test2() {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
InputStream is = System.in;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
System.out.println("请输入字符串");
String str;
while(true) {
str = br.readLine();
if(str.equalsIgnoreCase("e")||str.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
break;
}
String str1 = str.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(str1);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(br!=null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
打印流
字节流 : printeStream
字符流 : printWriter
demo例子 :
@Test
public void printStreamWriter() {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("tt.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//创建打印输出流.设置自动刷新模式(写入换行符或字节 '\n' 时都会刷新输出缓冲区)
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos,true);
if (ps != null) {
System.setOut(ps);//把标准输出流(控制台输出)改成文件
}
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++) {//输出ASCLL字符
System.out.print((char)i);
if (i % 50 == 0) {//每50个数据换行
System.out.print(i);
}
}
ps.close();
}
-
数据流
用来处理基本数据类型,String ,字节数组的数据
DataInputstream
DataOutstream
输出demo :
@Test
public void testData() {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data.txt");
dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
dos.writeUTF("啦啦啦啦");
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeLong(1432444495);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (dos != null) {
try {
dos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
读入demo
public void testData1() {
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(str);
boolean b = dis.readBoolean();
System.out.println(b);
long l = dis.readLong();
System.out.println(l);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (dis != null) {
try {
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
对象流
对象的序列化过程,将内存中的对象通过ObjectOutputStream转换为二进制流,存储在硬盘文件中
被序列化的类
① : 要求此类是可序列化的,实现接口 Serializable
② : 属性也要实现 Serializable 接口
③ : 使用static 或 transien 修饰的属性,不可实现序列化.
④ : 提供一个版本号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
class Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
String name;
Integer age;
public Person(String name,Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
序列化输出 :
//对象的序列化过程,将内存中的对象通过ObjectOutputStream转换为二进制流,存储在硬盘文件中
@Test
public void testObjectOutPutStream() {
Person P1 = new Person("雪芙", 19);
Person p2 = new Person("星仪", 22);
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("person.txt"));
oos.writeObject(P1);
oos.flush();
oos.writeObject(p2);
oos.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (oos != null) {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
读入demo :
//对象的反序列化,将硬盘中文件通过ObjectInputStream转换为相应的对象
@Test
public void test2() {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("person.txt"));
Person p1 = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p1);
Person p2 = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p2);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (ois != null) {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
随机访问流
RandomAccessFile :支持随机访问
1.既可以充当一个输入流,又可以充当一个输出流
2.支持从文件的开头读取,写入.
3.支持从任意位置的读取,写入(插入)
写入输出demo :
//进行文件的读写
@Test
public void test1() {
RandomAccessFile raf1 = null;
RandomAccessFile raf2 = null ;
try {
raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("tz.txt"),"r");
raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("tz22.txt"),"rw");
byte[] b = new byte[20];
int len;
while((len = raf1.read(b)) != -1) {
raf2.write(b, 0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (raf2 != null) {
try {
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (raf1 != null) {
try {
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
覆盖的效果demo :
@Test
public void test2() {
//实现的实际上是覆盖的效果
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("tz22.txt"),"rw");
raf.seek(5);
raf.write("baihua".getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (raf != null) {
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
插入效果demo :
@Test
public void test4() {
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("tz22.txt"),"rw");
raf.seek(5);
byte[]b = new byte[10];
int len;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while((len = raf.read(b)) != -1) {
sb.append(new String(b,0,len));
}
raf.seek(5);
raf.write(" i fuck you ".getBytes());
raf.write(sb.toString().getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (raf != null) {
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}