【图像处理】基于matlab GUI算子+滤波器+数米粒【含Matlab源码 007期】
一、简介
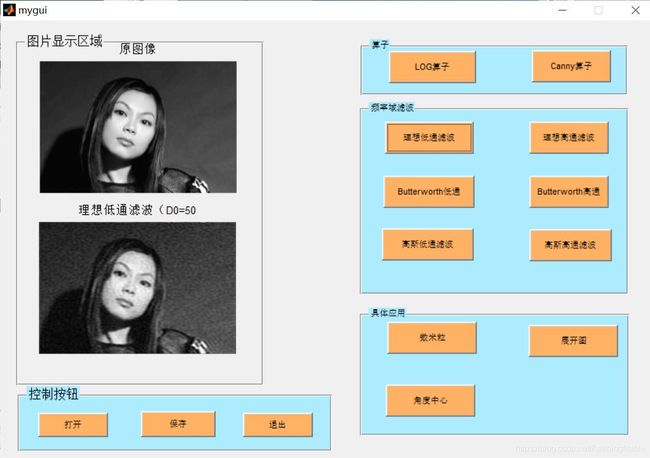
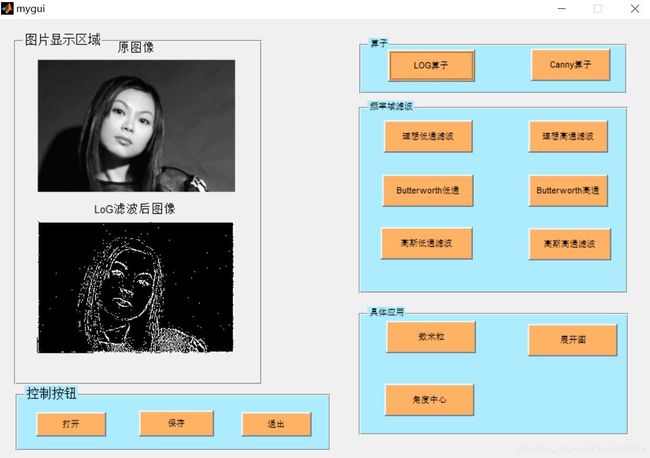
基于matlab GUI算子+滤波器+数米粒
二、源代码
function varargout = mygui(varargin)
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
global im;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @mygui_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @mygui_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{
1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{
1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{
1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before mygui is made visible.
function mygui_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to mygui (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for mygui
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes mygui wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = mygui_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{
1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in open_pushbutton.
function open_pushbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to open_pushbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global im;
[filename,pathname]=...
uigetfile({
'*.*';'*.bmp';'*.tif';'*.png';'*.gif';'*.jpg'},'select picture'); %选择图片路径
str = [pathname filename]; %合成路径+文件名
im = imread(str); %读取图片
axes(handles.axes1); %使用第一个axes
imshow(im); %显示图片
title('原图像');
% --- Executes on button press in blpf_pushbutton.
function blpf_pushbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to blpf_pushbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global im;
button_state = get(hObject,'Value');
if button_state == get(hObject,'Max')
I0 = im;
% I0 = imread('beauty.jpg');
% subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I0);title('原图');
str={
'半径D0大小:','阶数n:'}; %输入相关参数:高斯模板大小、方差、二值化阈值
sData=InputDlg(str,'输入参数',1);
if ~isempty(sData)
d0=str2double(sData(1));%模板大小
n=str2double(sData(2));%次数
end
I1 = imnoise(I0,'gaussian'); %对原图像加噪声
% subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);title('加入噪声后图像')
%将灰度图像的二维不连续Fourier 变换的零频率成分移到频谱的中心
s=fftshift(fft2(I1));
[M,N]=size(s); %分别返回s的行数到M中,列数到N中
n1=floor(M/2); %对M/2进行取整
n2=floor(N/2); %对N/2进行取整
%IHPF滤波
% d0=200; %初始化d0
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
d=sqrt((i-n1)^2+(j-n2)^2); %点(i,j)到傅立叶变换中心的距离
h(i,j)=1/((1+(d/d0))^(2*n)); %butterrworth lowpass滤波函数,取n=4
s(i,j)=h(i,j)*s(i,j); %butterworth低通滤波后的频域表示
end
end
s=ifftshift(s); %对s进行反FFT移动
%对s进行二维反离散的Fourier变换后,取复数的实部转化为无符号8位整数
s=uint8(real(ifft2(s)));
% subplot(2,2,3),imshow(h);title('传递函数'); %butterworth低通滤波的传递函数
% subplot(2,2,3),imshow(s); title('butterworth低通滤波(D0=200,n=4)'); %显示butterworth高通滤波后的图像
axes(handles.axes2); %使用第一个axes
imshow(s);
title('butterworth低通滤波');
end
% --- Executes on button press in canny_pushbutton.
function canny_pushbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to canny_pushbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global im;
button_state = get(hObject,'Value');
if button_state == get(hObject,'Max')
I = im;
I1=edge(I,'canny');
% subplot(2,3,2),imshow(I1),title('canny算子');
axes(handles.axes2); %使用第一个axes
imshow(I1);
title('canny算子演示');
end
%
% I=imread('diaohua.jpg');
% %第一步,用3x3高斯滤波器进行滤波,消除噪声;
% k1=filter2(fspecial('gaussian',3),I);
% % k=rgb2gray(I);
% %第二步,针对每一个像素,计算横向与纵向两方向的微分近似,以得到像素的梯度大小和方向;
% [m,n]=size(k1);
% for i=2:m-1
% for j=2:n-1
% zz1=k1(m,n-1)+k1(m+1,n-1);
% zz2=k1(m,n)+k1(m+1,n);
% zz3=k1(m,n-1)+k1(m,n);
% zz4=k1(m+1,n-1)+k1(m+1,n);
% kp(m,n)=0.5*(zz2-zz1);
% kq(m,n)=0.5*(zz3-zz4);
% kfu(m,n)=sqrt((kp(m,n)^2)+(kq(m,n)^2));%梯度大小
% angle(m,n)=atan(kq(m,n)/(kp(m,n)+0.001));%梯度方向
% end
% end
% %第三步,对梯度进行"非极大抑制"
% for i=2:m-1
% for j=2:n-1
% if angle(i,j)>=3/8*pi
% angle(m,n)=2;
% else if angle(i,j)>=1/8*pi
% angle(m,n)=1;
% else if angle(i,j)>=-1/8*pi
% angle(i,j)=0;
% else if angle(m,n)>=-3/8*pi
% angle(i,j)=3;
% else
% angle(i,j)=2;
% end
% end
% end
% end
% end
% end
% %判断该点是否是8邻域的局部最大值(梯度方向),比如,梯度方向为左右方向的点,
% %判断其是否比左右两点的值来的大,如果不是,使该点的值为0.
% %按照各个方向分别判断
% k2=k1;
% for i=2:m-1
% for j=2:n-1
% if angle(i,j)==0
% if k1(i,j)>k1(i,j-1)&&k1(ij)>k1(i,j+1);
% else k2(i,j)=0;
% end
% end
% if angle(i,j)==1
% if k1(i,j)>k1(i+1,j-1)&&k1(i,j)>k1(i-1,j+1);
% else k2(i,j)=0;
% end
% end
% if angle(i,j)==2
% if k1(i,j)>k1(i-1,j)&&k1(i,j)>k1(i+1,j);
% else k2(m,n)=0;
% end
% end
% if angle(i,j)==3
% if k1(i,j)>k1(i-1,j-1)&&k1(i,j)>k1(i+1,j+1);
% else k2(i,j)=0;
% end
% end
% end
% end
%
% %第四步,对两次梯度取阈值,t2=2*t1,若f<t1,则f=0
% %两次阈值分割
% k3=k2;%以t1为阈值分割后的矩阵
% k4=k2;%以t2为阈值分割后的矩阵
% t1=50;
% t2=2*t1;
% for i=2:m-1
% for j=2:n-1
% if kfu(i,j)<t1
% k3(i,j)=0;
% end
% if kfu(i,j)<t2
% k4(i,j)=0;
% end
% end
% end
三、运行结果
四、备注
版本:2014a
完整代码或代写添加QQ 1564658423