Compose搭档 — ViewModel、LiveData
文章目录
- Compose如虎添翼 -- 搭配ViewModel、LiveData!!!
-
- 一、需求一览
- 二、架构、流程
- 三、Compose UI开发
-
- 3.1、搜索框
- 3.2、折线图
- 四、ViewModel 业务开发
- 五、Compose和ViewModel建立关系
- 六、总结
Compose如虎添翼 – 搭配ViewModel、LiveData!!!
Compose系列文章,请点原文阅读。原文:是时候学习Compose了!
单纯的使用Compose来进行UI的展示,相信我们已经运用自如了,接下来的文章我们一起搭配其他Jetpack组件,例如LiveData,ViewModel、Room等来了解下Compose在现代化的开发上是多么的简单、舒适!
一、需求一览
我们一起来完成一个需求:首先我们需要一个搜索框,在搜索框中输入城市名,点击键盘回车按钮后请求网络接口获取到该城市的天气信息 – 今日天气,9日天气,并展示在页面上。
二、架构、流程
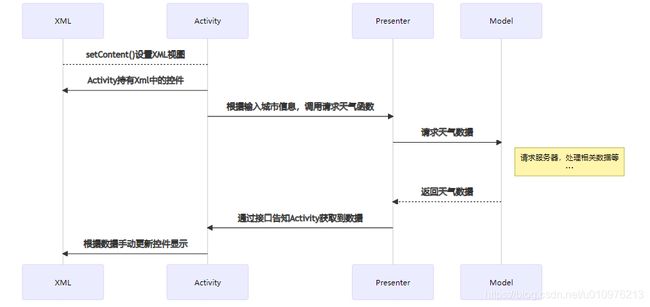
假如使用之前 View + MVP架构 的模式,整体的流程图应该是如下所示:
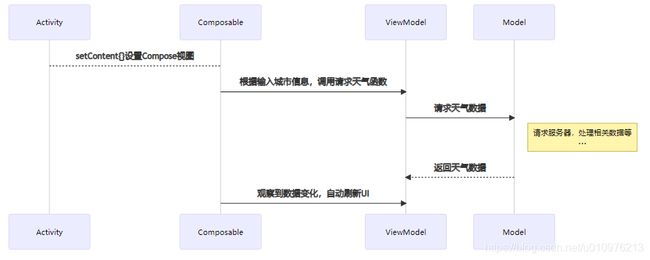
那么在 Compose + MVVM架构 中的话,流程图会有什么变化呢?(其实想使用MVI架构,但是又需要加入一定的解释成本,所以后续文章再专门结合MVI做示例吧)
如上所示,很明显的Activity和Compose在这里只要一个 setContent{} 的关系,后续都是Compose直接和ViewModel之间的交互,Presenter和Model、ViewModel和Model这两层类似,不做赘述。
三、Compose UI开发
接下来我们先使用Compose编写UI,根据需求,我们需要一个搜索框用来输入数据,然后搜索到数据后需要展示今日天气数据、9日天气数据。那么简洁一点,我们就把今日数据用一行文字表示出来,9日温度数据用一个自定义折线图表示出来。
3.1、搜索框
首先是输入框(搜索框),我们使用TextField来完成搜索框功能,通过设置colors相关参数来隐藏其默认自带的下划线指示器,通过shape和modifier参数来控制其圆角边框样式。通过配置keyboardOptions和keyboardActions来获取点击键盘的回车键时触发的事件。 还需要注意一点,这里我们为了在点击回车键后隐藏键盘使用了还在实验阶段的API – LocalSoftwareKeyboardController。整体搜索框代码如下所示:
@ExperimentalComposeUiApi
@Composable
fun SearchView(
onClick: (city: String) -> Unit
) {
val input = remember {
mutableStateOf("")
}
//键盘控制器,可控制键盘的展示和隐藏
val keyboardController = LocalSoftwareKeyboardController.current
//输入框圆角设置
val corner = 20.dp
TextField(
value = input.value,
onValueChange = {
input.value = it
},
colors = TextFieldDefaults.textFieldColors(
//输入框下部的指示线
focusedIndicatorColor = Color.Transparent,
unfocusedIndicatorColor = Color.Transparent,
),
//外观配置
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.border(
width = 2.dp,
color = Color.Black,
shape = RoundedCornerShape(corner)
),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(corner),
//键盘配置,输入完毕后隐藏键盘
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(imeAction = ImeAction.Done),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = {
keyboardController?.hide()
onClick(input.value)
}
)
)
}
3.2、折线图
接下来是自定义温度折线图,首先我们来分析下9天的数据,那么需要9个点,也就是屏幕需要8等分,然后分别绘制线段和端点就可以了。整体关于Canvas绘制的请查看之前的文章,这里我们需要注意一点就是:绘制的端点是有半径的,我们绘制区域的时候,x轴前后需要留出来这个半径能把首尾的端点全部展示出来,否则首尾的端点只能显示半个。代码如下:
@Composable
fun TempLineChart(
modifier: Modifier,
weatherDaily: List<WeatherDaily>
) {
if (weatherDaily.isEmpty()) {
return
}
val days = weatherDaily.size
Canvas(
modifier = modifier
) {
//圆点的集合
val points: ArrayList<Offset> = ArrayList()
//温度的差值(最大温度的差值)
val tempMax = weatherDaily.maxOf {
it.tempMax.toInt()
}
val tempMin = weatherDaily.minOf {
it.tempMax.toInt()
}
val diff = tempMax - tempMin
//绘制的直线的宽度
val lineStrokeWidth = 8f
//绘制的最大圆点的直径,注意是半径,绘制时候需要乘以2
val pointStrokeWidth = 16f
val path = Path()
//起点位置
val startX = pointStrokeWidth
val startY = size.height
//平均每天的步长,需剔除圆点的宽度
val xOffset = (size.width - pointStrokeWidth * 2) / (days - 1)
val endX = size.width - pointStrokeWidth
path.moveTo(startX, startY)
var lastOffset: Offset? = null
for ((index, weatherDailyBean) in weatherDaily.withIndex()) {
val x = startX + xOffset * index
val y =
startY - (size.height / (diff + 2) * ((weatherDailyBean.tempMax.toInt() - tempMin) + 1))
val offset = Offset(x, y)
points.add(offset)
//路径
path.lineTo(x, y)
//绘制直线
if (lastOffset != null) {
drawLine(
color = Color(0xFF357AFF),
start = lastOffset,
end = offset,
strokeWidth = lineStrokeWidth,
)
}
lastOffset = offset
}
path.lineTo(endX, startY)
path.close()
//绘制路径
drawPath(
path = path,
brush = Brush.verticalGradient(
colors = arrayListOf(Color(0x80357AFF), Color(0x00000000))
),
)
//绘制蓝色圆点
drawPoints(
pointMode = PointMode.Points,
color = Color(0xFF357AFF),
strokeWidth = pointStrokeWidth * 2,
points = points,
cap = StrokeCap.Round,
)
//绘制白色圆点
drawPoints(
pointMode = PointMode.Points,
color = Color.White,
strokeWidth = pointStrokeWidth,
points = points,
cap = StrokeCap.Round,
)
}
}
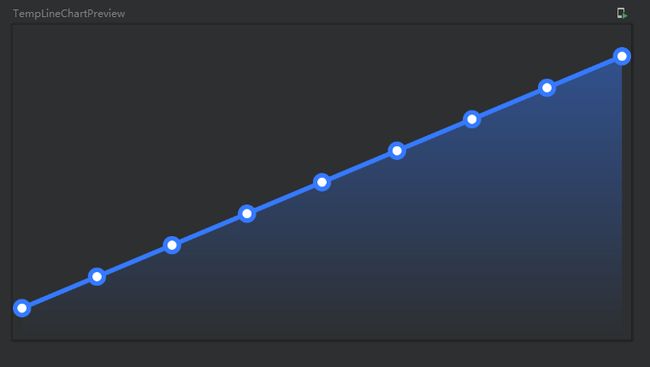
OK,然后造几条伪数据,我们使用@Preview来预览下显示效果:
@Preview
@Composable
fun TempLineChartPreview() {
val weatherDailyList = ArrayList<WeatherDaily>()
for (i in 1..9) {
weatherDailyList.add(WeatherDaily(tempMax = i.toString()))
}
TempLineChart(
modifier = Modifier
.height(200.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
weatherDailyList
)
}
四、ViewModel 业务开发
至此,我们单独的UI已经编写完毕了,接下来是ViewModel的部分,网络请求这块无疑是Retrofit套餐,但是Retrofit和Compose没有任何关系,所以这里我们暂时不花篇幅讲解其使用方式,直接使用伪数据来代替网络请求结果,后续文章我们会结合Hilt来示例Retrofit、Room等相关知识。ViewModel相关代码如下:
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
/**
* 城市名
*/
private val _cityName = MutableLiveData<String>()
/**
* 对外单独暴漏修改城市名方法
*/
fun updateCityName(name: String) {
_cityName.value = name
}
/**
* 当日天气【当_cityName值变更的时候,这里会响应】
*/
val weatherNow: LiveData<String> = Transformations.switchMap(_cityName) {
MutableLiveData(" ${
_cityName.value} 地区,今日天气好的不能再好了!")
}
/**
* n天天气【当_cityName值变更的时候,这里会响应】
*/
val weatherDays: LiveData<List<WeatherDaily>> = Transformations.switchMap(_cityName) {
val weatherDailyList = ArrayList<WeatherDaily>()
for (i in 1..9) {
val temp = (15..20).random()
weatherDailyList.add(WeatherDaily(tempMax = temp.toString()))
}
MutableLiveData(weatherDailyList)
}
}
注意:我们使用了Transformations类,当_cityName的值变化的时候, switchMap( _cityName ) 会响应,我们处理过后返回一个新的LiveData的值,weatherNow和weatherDays这两个变量就会被赋值。
【其实这里的代码设计方式再深入想一下,好像又能感受到一丝 MVI Intent的思想。】
五、Compose和ViewModel建立关系
Compose UI和ViewModel都搞定了,那么他们之间如何像上文流程图中表示的那样可以建立联系呢?其实官方给我们提供了一个库:androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-compose:$latestVersion,该库提供了一个**viewModel()**函数,可以直接在@Composable 函数中访问到相关ViewModel的实例,例如:
@ExperimentalComposeUiApi
@Composable
fun MainScreen(viewModel: MainViewModel = viewModel()) {
val weatherNow = viewModel.weatherNow.observeAsState()
val weatherDays = viewModel.weatherDays.observeAsState(arrayListOf())
}
如上,我们在参数中直接使用viewModel()来获取MainViewModel实例,而在MainScreen()函数中我们还使用到了一个 observeAsState() 函数,使用该函数也需要引用一个扩展库:androidx.compose.runtime:runtime-livedata:$latestVersion,该函数的作用就是将ViewModel提供的LiveData数据转换为Compose需要的State数据。
当LiveData数据更新后,LiveData转换为State,而Compose会根据State数据来自行刷新,所以将之前的UI控件组合起来,再将State数据设置进去,相关代码如下所示:
@ExperimentalComposeUiApi
@Composable
fun MainScreen(viewModel: MainViewModel = viewModel()) {
val weatherNow = viewModel.weatherNow.observeAsState()
val weatherDays = viewModel.weatherDays.observeAsState(arrayListOf())
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
SearchView(
onClick = {
viewModel.updateCityName(it)
})
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
Text(
text = weatherNow.value ?: ""
)
TempLineChart(
modifier = Modifier
.height(200.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
weatherDaily = weatherDays.value
)
}
}
OK,至此整体就大功告成了,运行下代码试试吧,能不能达到如下效果呢?
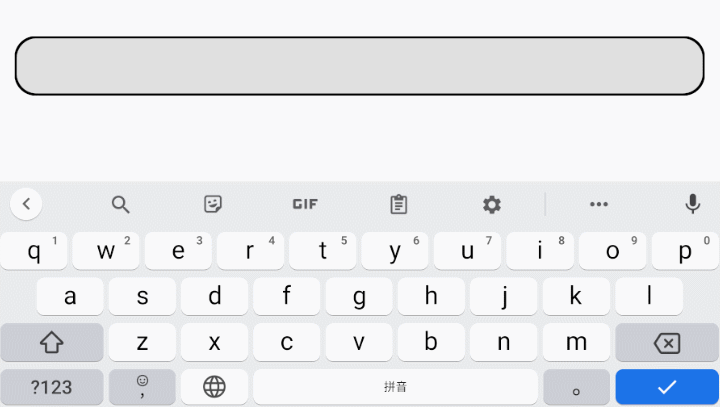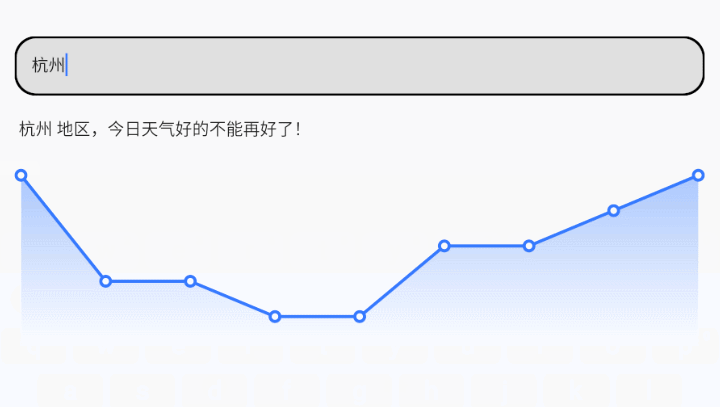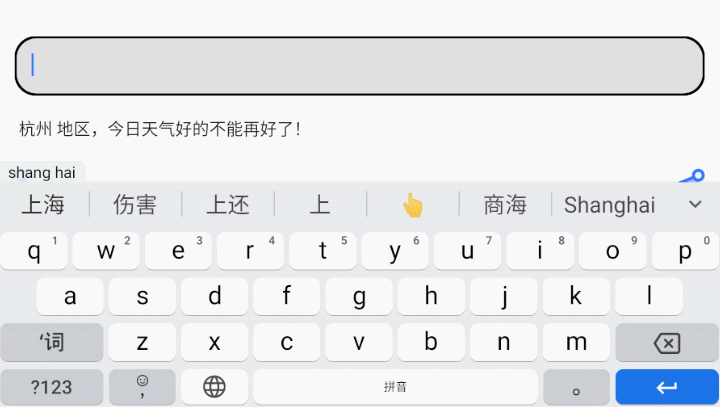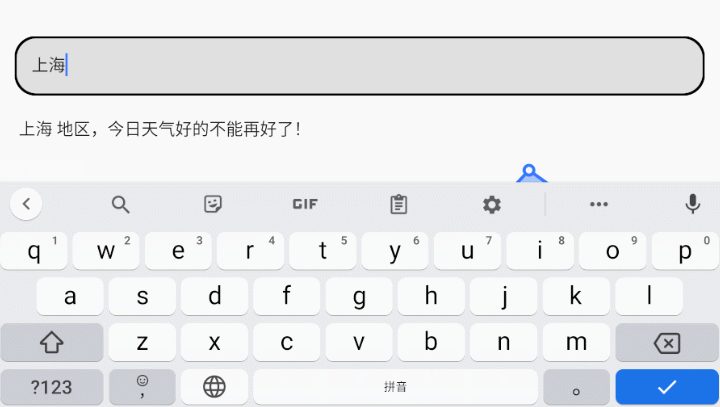
六、总结
整体的话,重点在于Compose和ViewModel的结合、以及LiveData和State的使用。这其中我们还要注意Compose的架构思想:
- 事件向上传递,例如搜索框的回车事件,暴漏出来给上层处理;
- 状态向下传递,例如网络请求结果数据等向UI层传递显示,可以封装成网络请求中、请求成功、请求失败等状态向UI传递;
还有一个也比较重要:
- 单一信任源,上文中没有明显的示例,但是你可以观察到TextField中输入的数据是根据 input 的值来进行变化的。举个View中的例子,比如CheckBox,当你点击的时候,状态会立即进行改变,此时如果网络请求失败了,我们还需要把CheckBox的显示状态重置。但是在Compose中,CheckBox的显示状态改变和TextField一样,只有input的值变化了,它才变化。也就是说CheckBox需要订阅一个变量,你只有请求网络成功后或者失败后更改此变量,CheckBox才会根据此变量更改显示状态。