Elasticsearch查询和过滤器DSL
前面采用了query中的match_all进行了数据查询 返回了所有数据,对数据进行分页,以及排序操作
match 查询和term过滤器
- 采用macth查询age为39的用户
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"match": {
"age": {
"query": "39"
}
}
}
}
- 使用term查询
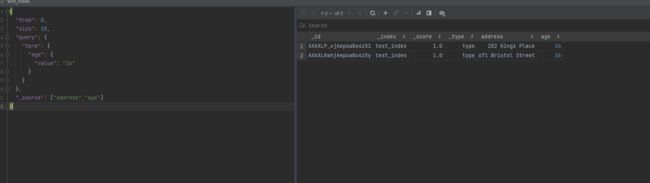
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "36"
}
}
},
"_source": ["address","age"]
}
#terms查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"terms": {
"age":["36","39"]
}
},
"_source": ["address","age"]
}
Elasticsearch查询和过滤器有严格的区分会影响到最终的得分,查询会为有特定的词条计算得分,搜索的过滤器只是为文档是否匹配这个查询返回简单的是或者否。过滤器所需要的处理更少,并且可以被缓存
- match_all查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ["address","age"]
}
match_all 为全部查询 对于es来讲不是很有用,因为使用到es很少使用到全部查询
- query_string查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "address",#设置只针对address字段查询
"query": "451 166"#query的查询条件
}
}
}
query_string查询将会搜索_all字段,通过设置default_field来进行设置针对某个字段查询,query_string是es最强有力的查询之一,但有时候也是最难阅读和扩展的插叙之一,建议替换的方案包括term,terms,match或者muliti_match查询
另一个良好的替换方案可以采用simple_query_string进行替换,simple_query_string查询提供 +-\and\OR 进行查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"simple_query_string": {
"query": "32 -702", #表示查询字段值为32 并且字段值不包含702的数据
"default_operator": "and" #设置默认的一个链接符号查询 等价于 查询参数值 filed=32 and filed!=702
}
}
}
- term查询和term过滤器
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "34"
}
}
}
}
term查询和过滤器是可执行查询中最简单的几个,它们让你可以指定需要搜索的文档字段,和词条。由于被搜索的词条是没有经过分析的,文档中的词条必须要精确匹配才能够被返回。
- match查询和term过滤器
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"match": {
"age": {
"query": "32"
}
}
}
}
- match_phrase查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"age": {
"query": "32",
"slop": 1 //将slop设置为1 告诉Es允许词条之间有间隔
}
}
}
}
match_phrase查询包含的结果,设置slop设置为1或者2表示查询你可能不知道的精确标题,就可以查询到包含该词组的结果
- phrase_prefix查询
和match_phrase_prefix查询类似,phrase_prefix查询可以更近一步搜索词组,不过它是和词组中最后一个词条进行前缀匹配。对于提供搜索框里的自动完成功能而言,这个行为是非常有用的,这样用户输入搜索词条就能获得提示。
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"address": {
"query": "A"
}
}
}
}
使用multi_match来匹配多个字段
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": [
"address",
"age"
],
"query": "171"
}
}
}
组合查询或复合查询
- bool查询
bool查询
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"age": {# 结果文档必须匹配的查询条件
"value": 32
}
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"term": {#文档应该匹配的第一个查询
"gender": {
"value": "M"
}
}
},{
"term": { #文档应该匹配的第二个查询
"balance": {
"value": 19594
}
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 1,#最小的should子句匹配个数
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"account_number": {
"value": "120"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
对应的sql可以写成 age=32 and (gender =M or balance=19594) and account_number!=120
改善bool查询,对于bool查询,可以采用range方式优化查询语句。如下
{
"from": 0,
"size": 100,
"query": {
"range": { #范围性查询
"age": {
"gt": 32, #大于
"lt": 50# 小于
}
}
},
"_source": "age"
}
采用range 属性查询可以替换掉将两个分离的should字句替换掉,现在可以将取值为minmum_should_match和should自居进行替换掉。
超越match和过滤器查询
- range查询和过滤器
range查询用于范围搜索,设置上界和下届。
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 20,
"lt":50
}
}
},
"_source": "age"
}
2.prefix查询和过滤器
根据前缀进行查询,指定字段的包含索引文档
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"prefix": {
"address": {
"value": "7"
}
}
}
}
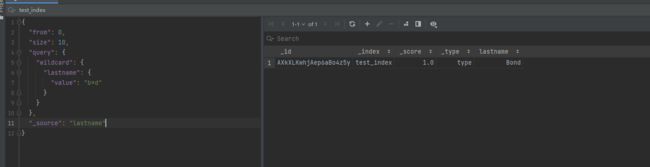
3.wlidcard查询
wildcard查询作为正则表达式进行搜索,但是实际上可能更接进入shell脚本
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"lastname": {
"value": "b*d"
}
}
}
}
使用wildcard查询对于性能消耗过大,谨慎使用
4.exists过滤器
exists过滤器运行你过滤文档,只查找那些特定字段有值的文档。无论其值是多少。
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"exists": {#查询lastname有值的文档
"field": "lastname"
}
},
"_source": "lastname"
}
- 对于搜索狂查询我们可以采用match和query_string查询 进行检索
- match查询对于全文搜索而言是核心类型。但是query_string查询更为灵活,也更为复杂,因为它暴露了Lucence查询语法
- match查询有多个子类型,boolean、phrase、和phrase_prefix主要的区别在于boolean匹配单独的关键词,而phrase会考虑多个单词在词组的顺序。
- 像prefix和wildcard这样的特殊查询Es也是支持的
- exists过滤器恰恰相反,它可以返回拥有指定字段的文档