OpenCV2 颜色识别
在这个例子中,我们开始选定一种颜色,并设置一个阈值
然后把图片中和所选颜色的差别在阈值中的点标定出来
在这个例子中,主要要注意这两点:
1. OpenCV与QT的结合,包括Mat 与 QImage 的转换
2. 我们使用了类来实现此功能,创建了一个单例模式的类
首先我们创建一个简单的图形界面,使用的是QT
创建处理图像用的类
#ifndef COLORDETECTOR_H_
#define COLORDETECTOR_H_
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <string>
class ColorDetector{
private:
int minDist;
cv::Vec3b target;
cv::Mat result;
cv::Mat image;
ColorDetector();
static ColorDetector *singleton;
public:
static ColorDetector * getInstance();
static void destory();
void setColorDistanceThreshold(int);
int getColorDistanceThreshold() const;
void setTargetColor(unsigned char, unsigned char, unsigned char);
void setTargetColor(cv::Vec3b);
cv::Vec3b getTargetColor() const;
void process();
int getDistance(const cv::Vec3b&) const;
cv::Mat getResult() const;
bool setInputImage(std::string);
cv::Mat getInputImage() const;
};
#endif /* COLORDETECTOR_H_ */
将其构造函数声明为private,提供静态的接口来获得ColorDetector对象
void setColorDistanceThreshold(int) 用于设置阈值
void setTargetColor(unsigned char, unsigned char, unsigned char)
void setTargetColor(cv::Vec3b) 用于设置颜色
bool setInputImage(std::string) 用于载入待处理图像
cv::Mat getResult() const 用于返回处理结果,结果用一副图像表示
其具体实现如下
#include "ColorDetector.h"
ColorDetector* ColorDetector::singleton = 0;
ColorDetector::ColorDetector():minDist(100){
target[0] = target[1] = target[2] = 0;
}
ColorDetector* ColorDetector::getInstance(){
if(singleton == 0){
singleton = new ColorDetector;
}
return singleton;
}
void ColorDetector::destory(){
if(singleton!=0){
delete singleton;
}
singleton = 0;
}
void ColorDetector::setColorDistanceThreshold(int distance){
if(distance < 0){
distance = 0;
}
minDist = distance;
}
int ColorDetector::getColorDistanceThreshold() const{
return minDist;
}
void ColorDetector::setTargetColor(unsigned char red,
unsigned char green, unsigned char blue){
target[2] = red;
target[1] = green;
target[0] = blue;
}
void ColorDetector::setTargetColor(cv::Vec3b color){
target = color;
}
cv::Vec3b ColorDetector::getTargetColor() const{
return target;
}
int ColorDetector::getDistance(const cv::Vec3b& color) const{
return abs(color[0]-target[0])+abs(color[1]-target[1])+abs(color[2]-target[2]);
}
void ColorDetector::process(){
result.create(image.rows, image.cols, CV_8U);
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator it = image.begin<cv::Vec3b>();
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator itend = image.end<cv::Vec3b>();
cv::Mat_<uchar>::iterator itout = result.begin<uchar>();
for(; it!=itend; ++it, ++itout){
if(getDistance(*it) < minDist){
*itout = 255;
}else{
*itout = 0;
}
}
}
cv::Mat ColorDetector::getResult() const{
return result;
}
bool ColorDetector::setInputImage(std::string filename){
image = cv::imread(filename);
if(!image.data){
return false;
}
return true;
}
cv::Mat ColorDetector::getInputImage() const{
return image;
}
在前面文章中,讲了遍历像素点的方法,这里用迭代器实现
然后是图像界面中的处理函数
#ifndef WIDGET_H
#define WIDGET_H
#include <QWidget>
#include <QFileDialog>
#include <QImage>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include "colordetector.h"
namespace Ui {
class Widget;
}
class Widget : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Widget(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Widget();
private:
Ui::Widget *ui;
QImage qimage;
cv::Mat image;
private slots:
void openImage();
void dealImage();
void colorSelect();
void changeDis(int);
};
#endif // WIDGET_H
其实现
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QColorDialog>
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent) :
QWidget(parent),
ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
connect(ui->openImage,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(openImage()));
connect(ui->dealImage,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(dealImage()));
connect(ui->colorButton,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(colorSelect()));
connect(ui->verticalSlider,SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)),this,SLOT(changeDis(int)));
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui;
}
void Widget::openImage(){
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this,
tr("Open Image"), ".",
tr("Image Files (*.png *.jpg *.jpeg *.bmp)"));
ColorDetector::getInstance()->setInputImage(fileName.toAscii().data());
cv::namedWindow("image");
cv::imshow("image",ColorDetector::getInstance()->getInputImage());
dealImage();
}
void Widget::dealImage(){
ColorDetector::getInstance()->process();
cv::cvtColor(ColorDetector::getInstance()->getResult(),image,CV_GRAY2RGB);
qimage = QImage((const unsigned char*)(image.data),image.cols,image.rows,QImage::Format_RGB888);
ui->label->setPixmap(QPixmap::fromImage(qimage).scaledToHeight(300));
//ui->label->resize(ui->label->pixmap()->size());
}
void Widget::colorSelect(){
QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::green,this);
if(color.isValid()){
ColorDetector::getInstance()->setTargetColor(
color.red(),color.green(),color.blue());
}
dealImage();
}
void Widget::changeDis(int value){
ColorDetector::getInstance()->setColorDistanceThreshold(value);
dealImage();
}
在QT项目的pro文件中要加入如下几句
INCLUDEPATH += D:\OpenCV\include
LIBS += -LD:\OpenCV\lib \
-lopencv_core230 \
-lopencv_highgui230 \
-lopencv_imgproc230
看看最后效果

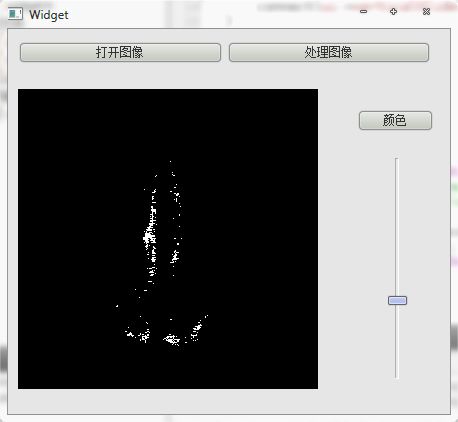
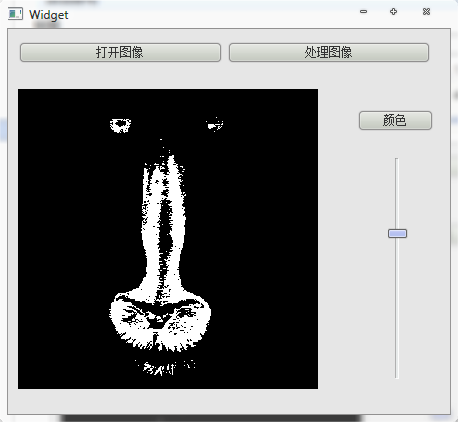

不同颜色,不同阈值的比较效果