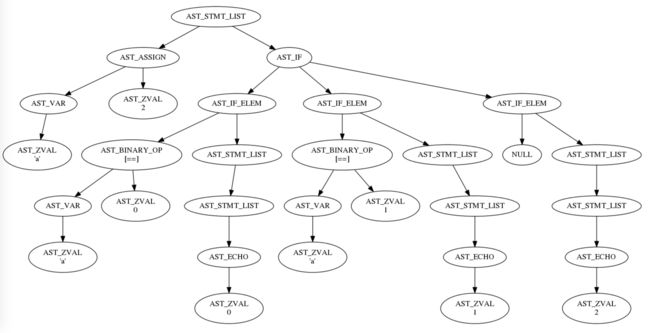
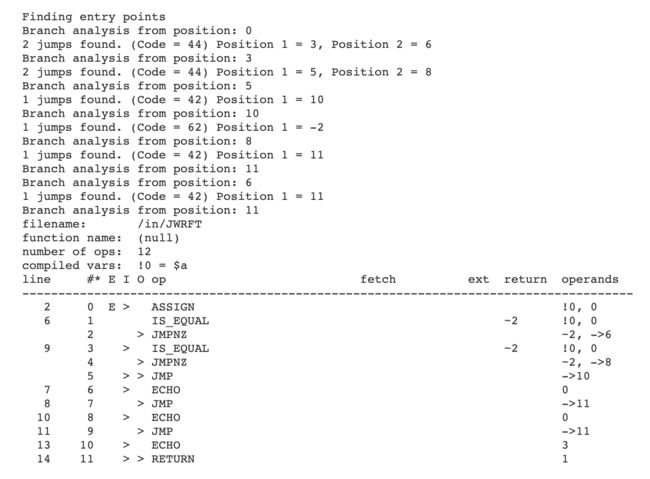
以 if/else 为例,分析普通语句跳转的代码实现:
一、 测试代码:
二、前面过程跳过,直接在编译的地方打断点 zend_compile,单步调试到源码的第 601 行,
// 文件位置:Zend/zend_language_scanner.l:577
599 zend_file_context_begin(&original_file_context);
(gdb)
600 zend_oparray_context_begin(&original_oparray_context);
(gdb)
601 zend_compile_top_stmt(CG(ast));
(gdb)
s 命令 进入 zend_compile_top_stmt(CG(ast)) 方法,这个方法的作用就是递归AST 抽象语法树,生成对应的op_array,最终调用 zend_compile_stmt。
// 文件位置: Zend/zend_compile.c
void zend_compile_top_stmt(zend_ast *ast) /* {{{ */
{
if (!ast) {
return;
}
// 递归处理抽象语法树的节点,根据节点的类型
// 做不同的处理,此处需要处理的是 *ZEND_AST_STMT_LIST* 类型的节点
if (ast->kind == ZEND_AST_STMT_LIST) {
zend_ast_list *list = zend_ast_get_list(ast);
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < list->children; ++i) {
zend_compile_top_stmt(list->child[i]);
}
return;
}
// 根据节点的类型进行相应的编译
zend_compile_stmt(ast);
if (ast->kind != ZEND_AST_NAMESPACE && ast->kind != ZEND_AST_HALT_COMPILER) {
zend_verify_namespace();
}
if (ast->kind == ZEND_AST_FUNC_DECL || ast->kind == ZEND_AST_CLASS) {
CG(zend_lineno) = ((zend_ast_decl *) ast)->end_lineno;
zend_do_early_binding();
}
}
zend_compile_stmt(ast)方法:
//文件位置:Zend/zend_compile.c
void zend_compile_stmt(zend_ast *ast) /* {{{ */
{
...
//根据节点不通的类型进行编译
switch (ast->kind) {
case ZEND_AST_STMT_LIST:
zend_compile_stmt_list(ast);
break;
case ZEND_AST_GLOBAL:
zend_compile_global_var(ast);
break;
...
case ZEND_AST_IF:
zend_compile_if(ast);
break;
...
}
/* }}} */
从代码中可以看出if相关语句,是通过 zend_compile_if(ast) 方法编译的
//文件位置:Zend/zend_compile.c
void zend_compile_if(zend_ast *ast) /* {{{ */
{
zend_ast_list *list = zend_ast_get_list(ast);
uint32_t i;
uint32_t *jmp_opnums = NULL;
if (list->children > 1) {
jmp_opnums = safe_emalloc(sizeof(uint32_t), list->children - 1, 0);//申请一个数组,大小等于 if 分支数,用于存储对应的分支的 opcode 数
}
for (i = 0; i < list->children; ++i) {
zend_ast *elem_ast = list->child[i];
zend_ast *cond_ast = elem_ast->child[0]; //condition:条件
zend_ast *stmt_ast = elem_ast->child[1]; //statement:说明(条件为真时,需要执行的语句)
znode cond_node;
uint32_t opnum_jmpz;
if (cond_ast) {
//编译条件语句
zend_compile_expr(&cond_node, cond_ast);
// 编译生成用于跳转的 opcode,
opnum_jmpz = zend_emit_cond_jump(ZEND_JMPZ, &cond_node, 0);
}
//编译statement语句
zend_compile_stmt(stmt_ast);
if (i != list->children - 1) {
//编译statement执行完后跳出if的opcode:ZEND_JMP(最后一个分支无需这条opcode)
jmp_opnums[i] = zend_emit_jump(0);
}
if (cond_ast) {
//设置ZEND_JMPZ跳过opcode数
zend_update_jump_target_to_next(opnum_jmpz);
}
}
if (list->children > 1) {
for (i = 0; i < list->children - 1; ++i) {
zend_update_jump_target_to_next(jmp_opnums[i]);
}
efree(jmp_opnums);
}
}
/* }}} */
好了,到了这里,就可以看出 if 部分的代码是怎么编译的了,代码中关键的部分也有注释,简单说,就是在条件语句和if 条件成立时需要执行的代码之间,添加了 JMP 和JMPZ 跳转语句来控制代码的执行顺序的。
咱们从头把代码撸一遍:
1.首先,申请一个数组,数组的大小为 if 分支语句的数量(测试代码中一共有 3 个分支)
2.遍历语法树,先编译条件语句,然后生成一个用于跳转的 opcode:JMPZ(表示条件不成立时,跳转到一个地址),并返回需要跳过的 opcode 数。需要注意的是,在没有编译statement 语句时,是不知道要跳过多少条 opcode 的,只有编译完了自己分支下的 statement 后,才能知道。
3.编译 statement 语句,编译完之后,在除了最后一个 statement 之外的其他分支的 statement之后,生成另一个用于跳转的 opcode:JMP(表示直接跳转到某个地址),把需要跳过的 opcode 数,保存到步骤 1 中申请的数组中。
4.更新有条件语句的分支需要跳过的 opcode 数,因为没有条件语句的分支,就是最后一个分支,不需要更新。
5.重新遍历所有分支,把每个 JMP 需要跳过的 opcode 数(跳出 if 判断)更新。
三、opcode 和 ast 语法树查看
- opcode查看:https://3v4l.org
- ast 树查看:https://dooakitestapp.herokuapp.com/phpast/webapp/
digraph ast {
1 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
2 [label = "AST_ASSIGN"]
1 -> 2;
3 [label = "AST_VAR"]
2 -> 3;
4 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n'a'"]
3 -> 4;
5 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n2"]
2 -> 5;
6 [label = "AST_IF"]
1 -> 6;
7 [label = "AST_IF_ELEM"]
6 -> 7;
8 [label = "AST_BINARY_OP\n[==]"]
7 -> 8;
9 [label = "AST_VAR"]
8 -> 9;
10 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n'a'"]
9 -> 10;
11 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
8 -> 11;
12 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
7 -> 12;
13 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
12 -> 13;
14 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
13 -> 14;
15 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
14 -> 15;
16 [label = "AST_IF_ELEM"]
6 -> 16;
17 [label = "AST_BINARY_OP\n[==]"]
16 -> 17;
18 [label = "AST_VAR"]
17 -> 18;
19 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n'a'"]
18 -> 19;
20 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n1"]
17 -> 20;
21 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
16 -> 21;
22 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
21 -> 22;
23 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
22 -> 23;
24 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n1"]
23 -> 24;
25 [label = "AST_IF_ELEM"]
6 -> 25;
uq1 [label = NULL]
25 -> uq1;
26 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
25 -> 26;
27 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
26 -> 27;
28 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
27 -> 28;
29 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n2"]
28 -> 29;
}
四、switch 的编译也是类似的,所以就不具体分析了,我列出源码,opcode 和 ast 大家自己分析一下:
- 源码
//测试代码:
child[0];
zend_ast_list *cases = zend_ast_get_list(ast->child[1]);
uint32_t i;
zend_bool has_default_case = 0;
znode expr_node, case_node;
zend_op *opline;
uint32_t *jmpnz_opnums, opnum_default_jmp;
zend_compile_expr(&expr_node, expr_ast);
zend_begin_loop(ZEND_FREE, &expr_node);
case_node.op_type = IS_TMP_VAR;
case_node.u.op.var = get_temporary_variable(CG(active_op_array));
jmpnz_opnums = safe_emalloc(sizeof(uint32_t), cases->children, 0);
for (i = 0; i < cases->children; ++i) {
zend_ast *case_ast = cases->child[i];
zend_ast *cond_ast = case_ast->child[0];
znode cond_node;
if (!cond_ast) {
if (has_default_case) {
CG(zend_lineno) = case_ast->lineno;
zend_error_noreturn(E_COMPILE_ERROR,
"Switch statements may only contain one default clause");
}
has_default_case = 1;
continue;
}
zend_compile_expr(&cond_node, cond_ast);
if (expr_node.op_type == IS_CONST
&& Z_TYPE(expr_node.u.constant) == IS_FALSE) {
jmpnz_opnums[i] = zend_emit_cond_jump(ZEND_JMPZ, &cond_node, 0);
} else if (expr_node.op_type == IS_CONST
&& Z_TYPE(expr_node.u.constant) == IS_TRUE) {
jmpnz_opnums[i] = zend_emit_cond_jump(ZEND_JMPNZ, &cond_node, 0);
} else {
opline = zend_emit_op(NULL, ZEND_CASE, &expr_node, &cond_node);
SET_NODE(opline->result, &case_node);
if (opline->op1_type == IS_CONST) {
zval_copy_ctor(CT_CONSTANT(opline->op1));
}
jmpnz_opnums[i] = zend_emit_cond_jump(ZEND_JMPNZ, &case_node, 0);
}
}
opnum_default_jmp = zend_emit_jump(0);
for (i = 0; i < cases->children; ++i) {
zend_ast *case_ast = cases->child[i];
zend_ast *cond_ast = case_ast->child[0];
zend_ast *stmt_ast = case_ast->child[1];
if (cond_ast) {
zend_update_jump_target_to_next(jmpnz_opnums[i]);
} else {
zend_update_jump_target_to_next(opnum_default_jmp);
}
zend_compile_stmt(stmt_ast);
}
if (!has_default_case) {
zend_update_jump_target_to_next(opnum_default_jmp);
}
zend_end_loop(get_next_op_number(CG(active_op_array)), &expr_node);
if (expr_node.op_type & (IS_VAR|IS_TMP_VAR)) {
/* don't use emit_op() to prevent automatic live-range construction */
opline = get_next_op(CG(active_op_array));
opline->opcode = ZEND_FREE;
SET_NODE(opline->op1, &expr_node);
SET_UNUSED(opline->op2);
} else if (expr_node.op_type == IS_CONST) {
zval_dtor(&expr_node.u.constant);
}
efree(jmpnz_opnums);
}
/* }}} */
说明:
1.这里多了zend_begin_loop和zend_end_loop这两个方法,这里先不说,循环语句的源码分析中会说;
2.switch的编译,会先编译完所有的 condition ,然后再编译 statement
2.opcode:
3.ast树:
digraph ast {
1 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
2 [label = "AST_ASSIGN"]
1 -> 2;
3 [label = "AST_VAR"]
2 -> 3;
4 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n'a'"]
3 -> 4;
5 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
2 -> 5;
6 [label = "AST_SWITCH"]
1 -> 6;
7 [label = "AST_VAR"]
6 -> 7;
8 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n'a'"]
7 -> 8;
9 [label = "AST_SWITCH_LIST"]
6 -> 9;
10 [label = "AST_SWITCH_CASE"]
9 -> 10;
11 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
10 -> 11;
12 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
10 -> 12;
13 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
12 -> 13;
14 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
13 -> 14;
15 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
14 -> 15;
16 [label = "AST_BREAK"]
12 -> 16;
uq1 [label = NULL]
16 -> uq1;
17 [label = "AST_SWITCH_CASE"]
9 -> 17;
18 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
17 -> 18;
19 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
17 -> 19;
20 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
19 -> 20;
21 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
20 -> 21;
22 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n0"]
21 -> 22;
23 [label = "AST_BREAK"]
19 -> 23;
uq2 [label = NULL]
23 -> uq2;
24 [label = "AST_SWITCH_CASE"]
9 -> 24;
uq3 [label = NULL]
24 -> uq3;
25 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
24 -> 25;
26 [label = "AST_STMT_LIST"]
25 -> 26;
27 [label = "AST_ECHO"]
26 -> 27;
28 [label = "AST_ZVAL\n3"]
27 -> 28;
}